| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Cache memory is the fast and small memory. The basis idea of using a cache is simple. When CPU need a word, it first looks in the cache. Only if the word is not there does it go to main memory. If a substantial fraction of the words are in the cache, the average access time can be greatly reduced. So the success or faillure thus depends on what fraction of the words are in cache. The idea solution is that when a word is referenced, it and some of its neighbors are brought from the large slow memory into the cache, so that the next time it can be accessed quickly.
The memory mean access time, TM, is considered as follow:
TM = c + (1- h).m
Where:
c : the cache access time
m: the main memory access time
h: the hit ratio, which is the fraction of all references that can be satisfied out of cache (the success of cache), also the miss ratio is 1-h.

Figure 10.1. The cache is logically between the CPU and main memory in the the memory hierarchy. Physically, there are several possible places it could be located.
– Compared to the size of main memory, cache is relatively small
– Operates at or near the speed of the processor
– Cache is very expensive compared to main memory
– Cache contains copies of sections of main memory
– Assume an access to main memory causes a block of K words to be transferred to the cache
– The block transferred from main memory is stored in the cache as a single unit called a slot, line, or page
– Once copied to the cache, individual words within a line can be accessed by the CPU
– Because of the high speeds involved with the cache, management of the data transfer and storage in the cache is done in hardware
- If there are 2n words in the main memory, then there will be M=2n /K blocks in the memory
– M will be much greater than the number of lines, C, in the cache
– Every line of data in the cache must be tagged in some way to identify what main memory block it is. The line of data and its tag are stored in the cache.
- Mapping function between main memory and the cache
- Line replacement algorithm
- Write policy
- Block size
- Number and type of caches
Mapping function organization: Mapping functions since M>>C, how are blocks mapped to specific lines in cache
a/ Organization:
The simplest cache is known as a direct-mapped cache or direct mapping, it is shown in Figure 10.2.
– Direct mapping cache treats a main memory address as 3 distinct fields
+ Tag identifier
+ Line number identifier
+ Word identifier (offset)
– Word identifier specifies the specific word (or addressable unit) in a cache line that is to be read
– Line identifier specifies the physical line in cache that will hold the referenced address
– The tag is stored in the cache along with the data words of the line
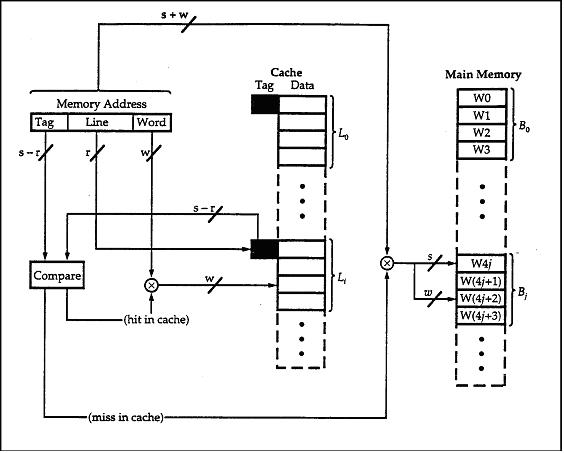
Figure 10.2. Direct mapping cache Organization

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Computer architecture' conversation and receive update notifications?