| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this section, we consider centers of mass (also called centroids , under certain conditions) and moments. The basic idea of the center of mass is the notion of a balancing point. Many of us have seen performers who spin plates on the ends of sticks. The performers try to keep several of them spinning without allowing any of them to drop. If we look at a single plate (without spinning it), there is a sweet spot on the plate where it balances perfectly on the stick. If we put the stick anywhere other than that sweet spot, the plate does not balance and it falls to the ground. (That is why performers spin the plates; the spin helps keep the plates from falling even if the stick is not exactly in the right place.) Mathematically, that sweet spot is called the center of mass of the plate .
In this section, we first examine these concepts in a one-dimensional context, then expand our development to consider centers of mass of two-dimensional regions and symmetry. Last, we use centroids to find the volume of certain solids by applying the theorem of Pappus.
Let’s begin by looking at the center of mass in a one-dimensional context. Consider a long, thin wire or rod of negligible mass resting on a fulcrum, as shown in [link] (a). Now suppose we place objects having masses and at distances and from the fulcrum, respectively, as shown in [link] (b).
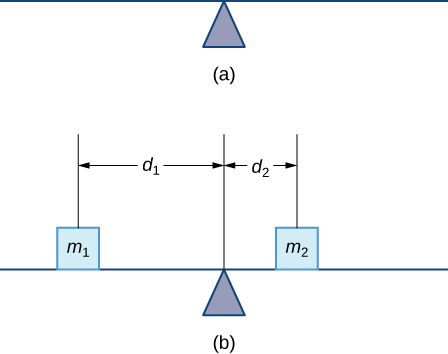
The most common real-life example of a system like this is a playground seesaw, or teeter-totter, with children of different weights sitting at different distances from the center. On a seesaw, if one child sits at each end, the heavier child sinks down and the lighter child is lifted into the air. If the heavier child slides in toward the center, though, the seesaw balances. Applying this concept to the masses on the rod, we note that the masses balance each other if and only if
In the seesaw example, we balanced the system by moving the masses (children) with respect to the fulcrum. However, we are really interested in systems in which the masses are not allowed to move, and instead we balance the system by moving the fulcrum. Suppose we have two point masses, and located on a number line at points and respectively ( [link] ). The center of mass, is the point where the fulcrum should be placed to make the system balance.
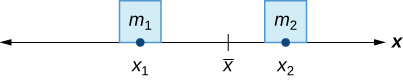
Thus, we have
The expression in the numerator, is called the first moment of the system with respect to the origin. If the context is clear, we often drop the word first and just refer to this expression as the moment of the system. The expression in the denominator, is the total mass of the system. Thus, the center of mass of the system is the point at which the total mass of the system could be concentrated without changing the moment.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?