| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
(a) Petrol – motor-car
Gas – stove
Coal – steam locomotive
Wood – fire to provide heat
Crude oil – aeroplane fuel is derived from it
(b) Wind-propelled devices – wind farm
Engines that move by means of used cooking-oil
Solar heating for warmth
(c) Advantages and disadvantages of nuclear fuels and fossil fuels.
(i) Fossil fuels
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| Quite readily available. | Causes air pollution – emits smoke and harmful gases. |
| Can easily be converted to energy. | Presents a fire hazard. |
| Relatively inexpensive. | Mining defaces the environment. |
(ii) Nuclear fuels
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
| A great deal is available. | Health risks caused by radioactive eradiation. |
| Minimal pollution of the environment. | Energy must be transported over long distances, seeing that power stations have to be built near the coast because of the water cooling systems that are used. |
| A small amount produces a great deal of energy. | Radioactive waste must be stored safely for years until the radioactivity disappears. |
Leaner Section
(a) Name five common fuels and one use of each:
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
(b) It is very important for people to find other sources of energy. Try to suggest ways in which people can use energy differently or make use of other sources, e.g. electric cars.
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
(c) Name three advantages and three disadvantages of:
(i) Fossil fuels
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
| 1.___________________________________________________________ | 1.___________________________________________________________ |
| 2.___________________________________________________________ | 2.___________________________________________________________ |
| 3.___________________________________________________________ | 3.___________________________________________________________ |
(ii) Nuclear fuels
| ADVANTAGES | DISADVANTAGES |
| 1.___________________________________________________________ | 1.___________________________________________________________ |
| 2.___________________________________________________________ | 2.___________________________________________________________ |
| 3.___________________________________________________________ | 3.___________________________________________________________ |
(d) Consider the sources of energy that we have been discussing and then draw up a list to show how you could conserve energy, e.g. by switching off the lights in the classroom when the sun is shining.
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________
The human body does not use fuel (food) in the form in which we take it. The food is broken down into simple substances that are conserved in the muscles, in the particular form that can be used by the muscles. There therefore is energy in the substances that are stored in the muscles. Energy that is stored in chemical substances like food and fuel is known as chemical energy. All fuels therefore contain chemical energy.

Chemical energy is released when some reaction occurs. If coal is burnt, for instance, it releases heat that can then be used to generate steam for a steam locomotive.
Heat energy is used every day. We need it to cook our food and to keep warm.
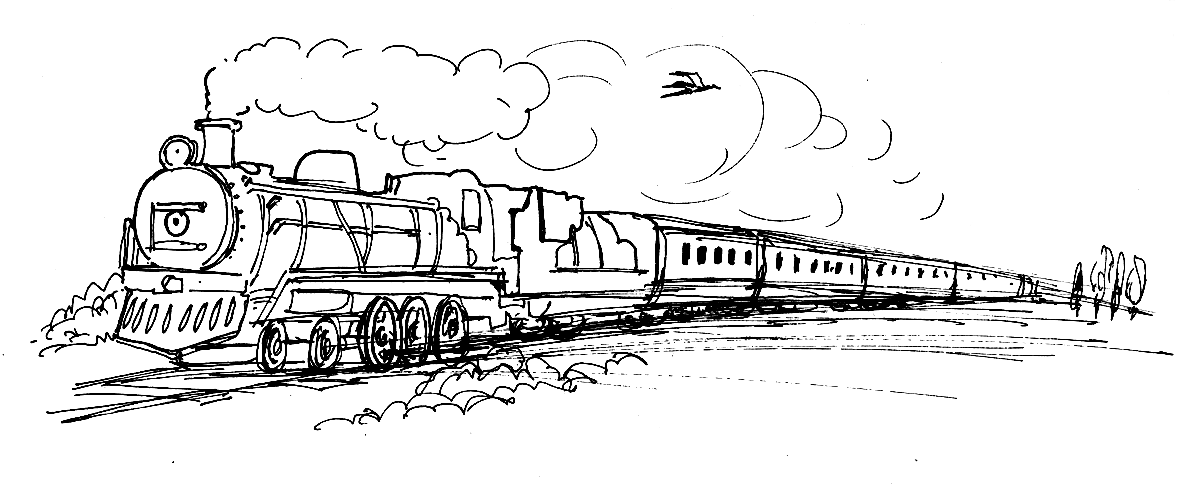
Heat energy boils the water in the locomotive’s kettle and this forms steam.The steam drives the locomotive.
The sun provides us with light, as do fuels and electricity. When electricity flows through the filament in a light bulb, the wire is heated and glows. It releases light energy , as well as a small amount of heat energy. Some worms, fireflies and fish also radiate light energy.

Kinetic energy results from movement. Moving water can turn a water wheel, while wind can drive a wind pump.

Energy that is stored in things and waiting to be released by some means or other is called potential energy. The spring of an air gun that is loaded has the ability to fire. We therefore say that the loaded spring has potential energy.


Learning Outcome 1: The learner will be able to act confidently on curiosity about natural phenomena, and to investigate relationships and solve problems in scientific, technological and environmental contexts.
Assessment Standard 1.3: We know this when the learner evaluates data and communicates findings: generalises in terms of relevant aspects and describes how the data support the generalisation.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Natural sciences grade 7' conversation and receive update notifications?