| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Activity 1:
To do an architectural drawing of the new classroom
An architectural drawing is called a plan. The house you live in was first planned by an architect and the plans were given to the builder who built the house according to the plan. A plan is more complex than an orthographic drawing. It often includes the building materials, kitchen and bathroom layout, furniture, electrical points and water layout. All plans must comply with building regulations and must be approved by a local building department. Plans are used to determine the cost of a building. The building cost of a house these days varies from R2 000 to R5 000 per square meter (R2 000 - R5 000 / m2 ).

SECTION DD
1:100
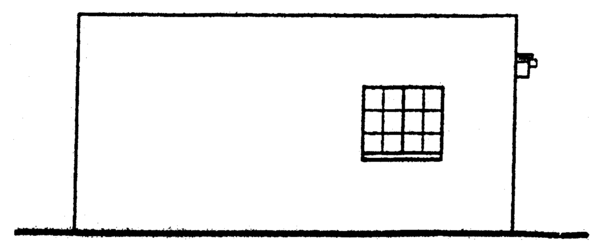
WEST ELEVATION: 1: 100

east elevation: 1:100

NORTH ELEVATION: 1: 100

SOUTH ELEVATION: 1: 100
Focus task a
Use grid paper and produce a location drawing (plan view) of your classroom. You must indicate where the doors and windows are to be placed. Also add dimensions to your drawing. The grid will help you with the scale. Use one block for 1 meter. Calculate what the cost of the classroom will be if the building cost is R3 000 per square meter (R3 000 / m 2 ).
The following is an example of a plan view of a building.

| LO 1.9 | ||||
Activity 2:
To develop a scale model of the new classroom
Most architects produce scale models to show their clients what the final product will look like. Materials such as paper, cardboard or styrofoam can be used to convert all the 2-D drawings into a 3-D model. Cardboard can easily be cut and then glued on to grid paper to establish the right scale. Add some colour and you have developed a demonstration model.
Focus task b
1. Produce a scale model of your classroom. You might leave one section of the roof off to show the layout on the inside.
| LO 1.10 | ||||
2. Formulate at least five criteria for the evaluation of your plan (refer to the design brief), and evaluate the model. Write down the outcome.
| LO 1.13 | ||||
3. Present your idea to the rest of the class.
| LO 1.15 | ||||
| Learning outcomes(LOs) |
| LO 1 |
| TECHNOLOGICAL PROCESSES AND SKILLS The learner will be able to apply technological processes and skills ethically and responsibly using appropriate information and communication technology. |
| Assessment standards(ASs) |
| We know this when the learner: |
| investigates:1.1 identifies and explains a problem, need or opportunity from a real-life context, and investigates the context, the nature of the need, the environmental situation, and the people concerned; |
1.4 uses a variety of available technologies and methods to:
|
| designs:1.5 writes or communicates a short and clear statement or a design brief for the development of a product or system related to a context, problem, need or opportunity that has been identified by self; |
1.6 lists product specifications and design specifications and constraints for a solution to an identified problem, need or opportunity based on all of the design key words listed below:
|
| 1.7 generates a range of possible solutions that are significantly different from each other, and that show clear links to the design brief and specifications and constraints; |
makes:1.9 develops plans for making that include all of the following:
|
| 1.10 chooses and uses appropriate tools and materials to make designed products with precision and control by measuring, marking, cutting or separating, shaping or forming, joining or combining, and finishing a range of materials accurately and efficiently; |
| evaluates:1.13 evaluates the product or system based on self-generated objective criteria linked directly to the design brief, specifications and constraints using self-designed procedures (e.g. surveys, questionnaires, testing procedures) for self-testing, and suggests sensible improvements or modifications that would clearly result in a more effective or higher-quality end product; |
communicates:1.15 presents ideas (in a project portfolio) using formal techniques, in two-dimensional or three-dimensional sketches, circuit diagrams or systems diagrams that include all of the following features:
|

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 9' conversation and receive update notifications?