| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
From the designer's point of view, the machine instruction set provides the functional requirements for the CPU: Implementing the CPU is a task that in large part involves implementing the machine instruction set.
From the user's side, the user who chooses to program in machine language (actually, in assembly language) becomes aware of the register and memory structure, the types of data directly supported by the machine, and the functioning of the ALU.
Each instruction must have elements that contain the information required by the CPU for execution. These elements are as follows
The next instruction to be fetched is located in main memory or, in the case of a virtual memory system, in either main memory or secondary memory (disk). In most cases, the next instruction to be fetched immediately follows the current instruction. In those cases, there is no explicit reference to the next instruction. Source and result operands can be in one of three areas:
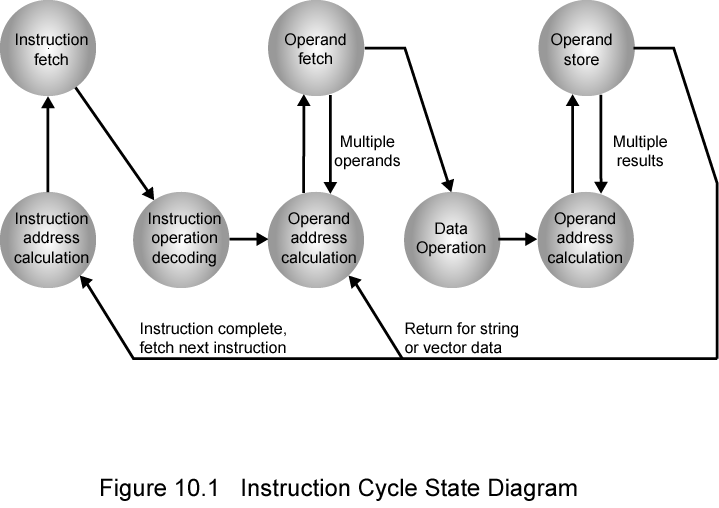
Within the computer, each instruction is represented by a sequence of bits. The instruction is divided into fields, corresponding to the constituent elements of the instruction. During instruction execution, an instruction is read into an instruction register (IR) in the CPU. The CPU must be able to extract the data from the various instruction fields to perform the required operation.
It is difficult for both the programmer and the reader of textbooks to deal with binary representations of machine instructions. Thus, it has become common practice to use a symbolic representation of machine instructions. Opcodes are represented by abbreviations, called mnemonics, that indicate the operation. Common examples include
| ADD | Add |
| SUB | Subtract |
| MPY | Multiply |
| DIV | Divide |
| LOAD | Load data from memory |
| STOR | Store data to memory |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Computer architecture' conversation and receive update notifications?