| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In the previous sections of this course. we have concentrated on singleprocessor architectures and techniques to improve upon their performance, such as:
– Efficient algebraic hardware implementations
– Enhanced processor operation through pipelined instruction execution and multiplicity of functional units
– Memory hierarchy
– Control unit design
– I/O operations
Through these techniques and implementation improvements, the processing power of a computer system has increased by an order of magnitude every 5 years. We are (still) approaching performance bounds due to physical limitations of the hardware.
– Improve the basic performance of a single processor machine
Architecture / organization improvements
Implementation improvements
SSI -->VLSI -->ULSI
Clock speed
Packaging
– Multiple processor system architectures
Tightly coupled system
Loosely coupled system
Distributed computing system
- Parallel computer: SIMD computer, MIMD computer
System with multiprocessor CPUs can be divided into multiprocessor and multicomputers. In this section we will first study multiprocessors and then multicomputers
A parallel computer in which all the CPUs share a common memory is called a tightly coupled systems

Figure 16.1. Tightly coupled systems, Shased-memory multiprocessor
– Multiple processors
– Shared, common memory system
– Processors under the integrated control of a common operating system
– Data is exchanged between processors by accessing common shared variable locations in memory
– Common shared memory ultimates presents an overall system bottleneck that effectively limits the sizes of these systems to a fairly small number of processors (dozens)
A parallel computer in which all the CPUs has a local independent memory is called a loosely coupled systems
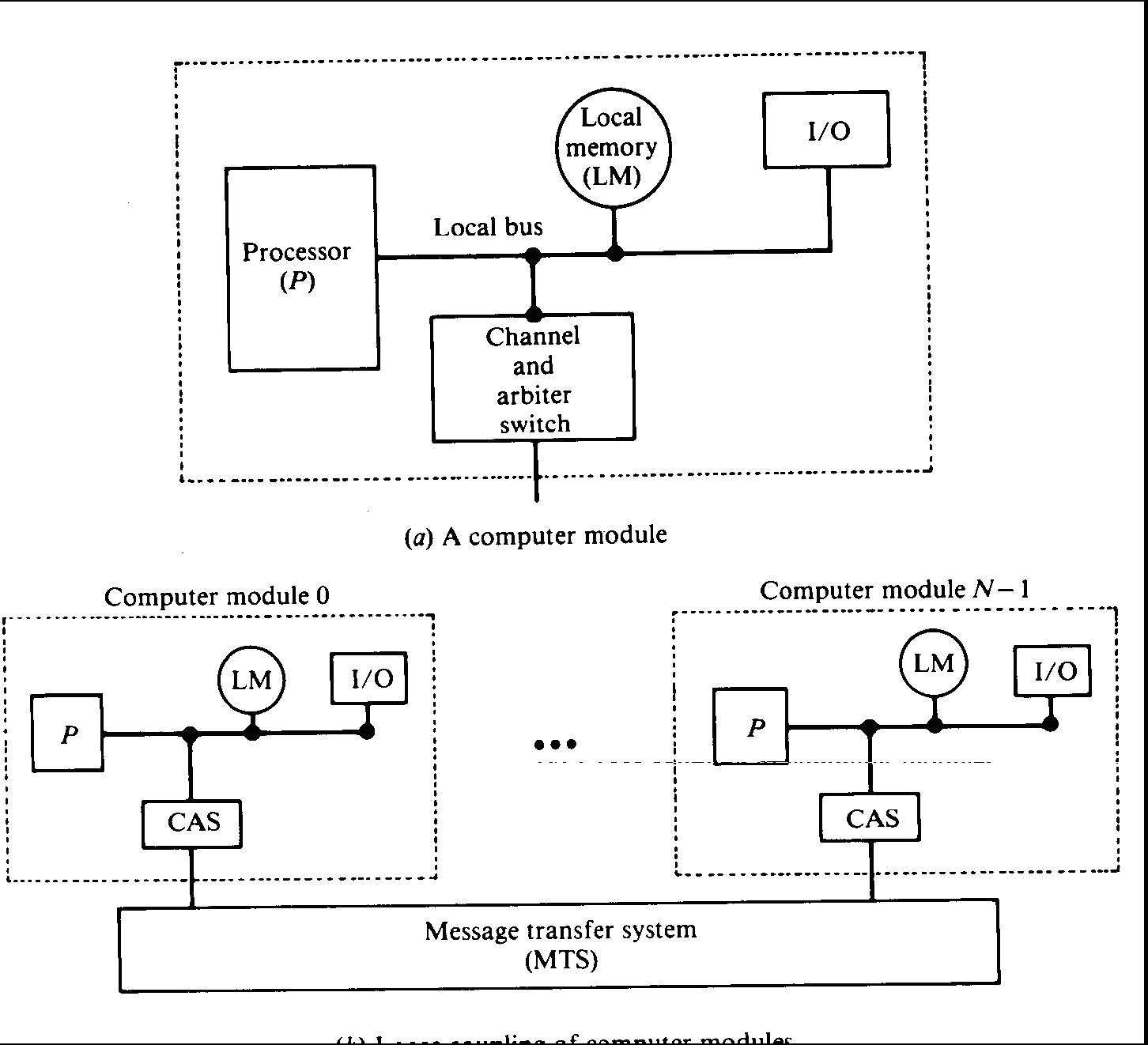
Figure 16.2. Loosely coupled systems, Message-passing multiprocessor
– Multiple processors
– Each processor has its own independent memory system
– Processors under the integrated control of a common operating system
– Data exchanged between processors via interprocessor messages
– This definition does not agree with the one given in the text
Now we can see the message-passing computer that multicomputer are held togerther by network.
– Collections of relatively autonomous computers, each capable of independent operation
– Example systems are local area networks of computer workstations
+ Each machine is running its own “copy” of the operating system
+ Some tasks are done on different machines (e.g., mail handler is on one machine)
+ Supports multiple independent users
+ Load balancing between machines can cause a user’s job on one machine to be shifted to another

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Computer architecture' conversation and receive update notifications?