| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Method
1. Cut a very thin slice (cross section) from the middle of the celery stem or the carrot root.
2. Place this section on a glass slide.
3. Cover the specimen with iodine solution in order to stain it. This makes it more visible under the microscope. The specimen can also be placed on a drop ofwater if iodine is not available.
4. Cover the specimen by carefully lowering the cover slip onto it with a dissecting needle or tweezers. Take care not to trap any air bubbles.
This link gives information about making a wet mount microscope slide and shows an instructional video.
http://www.microbehunter.com/2010/08/13/making-a-wet-mount-microscope-slide/
5. Call your teacher.
6. Switch on the microscope making sure the lowest objective is in position (the 4x objective).
7. Place your slide on the stage.
8. Focus the image under the 4x objective (lowest objective) and view the structure of the celery stem. Switch to the 10x objective to look a little moreclosely. To see amazing details of the structure of plant tissue, use the 40x objective and the slide, carefully observing all of the parts and differentcells.
9. Once you are able to see cells,
10. Call your teacher.
11. Make a biological drawing of your specimen as viewed under the microscope. Take note of the magnification and draw a scale bar. Label your diagramaccording to the tissues you have learnt about.
Variation: Be creative and try using your favourite vegetables! Which vegetables are roots, stems and leaves?
To prepare a slide:
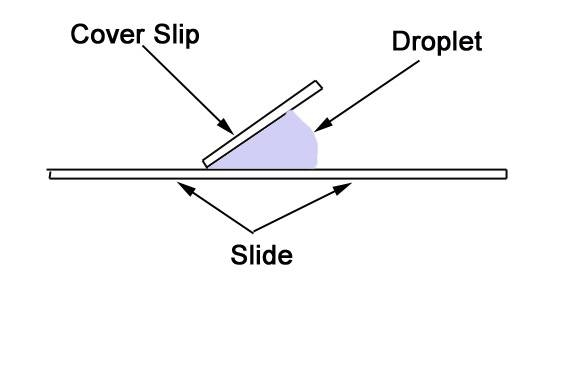
Place the sample in the centre of the slide. Add a drop of iodine or water on top of the sample. Place the cover slip next to the droplet as shown in thediagram.
Lower the coverslip into place with tweezers. As you lower the coverslip downwards, the drop will spread outward and suspend the sample between theslide and the coverslip.
(Diagrams from http://www.ehow.com/how_5164819_prepare-wet-mount-slide.html )
Aim: To examine the uptake of water by the stem
Apparatus:
Method:
Before starting this experiment, try to guess how the dye might move up the stem into the flower.
1. Fill one jar with plain water, and one with water containing several drops of food colouring dye.
2. Take the flower and carefully cut the stem lengthwise, either part way up the stem or right up to the base of the flower (try both – the results willbe different!)
3. Put one half of the stem into the jar containing plain water and one half of the stem into the jar containing food colouring dye. To make it easier to insert the stalks without breaking them, it helps to wedge paper underneath thejars so that you can tilt them towards each other. Tape the jars or cylinders down onto a tray so that they do not fall over.
4. Observe the flowers after a few hours and the next day, and note where the dye ends up in the flowerhead. You can leave the flowers up to a week but besure to make sure that they have enough water.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula: life sciences grade 10' conversation and receive update notifications?