| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
We need to emphasize that fiscal policy is the use of government spending and tax policy to alter the economy. Fiscal policy does not include all spending (such as the increase in spending that accompanies a war).
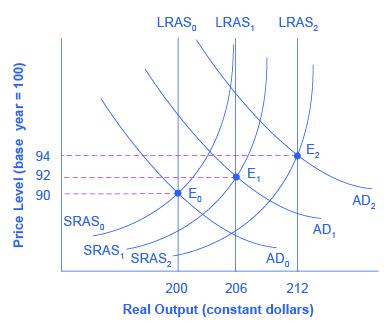
Graphically, we see that fiscal policy, whether through change in spending or taxes, shifts the aggregate demand outward in the case of expansionary fiscal policy and inward in the case of contractionary fiscal policy . [link] illustrates the process by using an aggregate demand/aggregate supply diagram in a growing economy. The original equilibrium occurs at E 0 , the intersection of aggregate demand curve AD 0 and aggregate supply curve SRAS 0 , at an output level of 200 and a price level of 90.
One year later, aggregate supply has shifted to the right to SRAS 1 in the process of long-term economic growth, and aggregate demand has also shifted to the right to AD 1 , keeping the economy operating at the new level of potential GDP. The new equilibrium (E 1 ) is an output level of 206 and a price level of 92. One more year later, aggregate supply has again shifted to the right, now to SRAS 2 , and aggregate demand shifts right as well to AD 2 . Now the equilibrium is E 2 , with an output level of 212 and a price level of 94. In short, the figure shows an economy that is growing steadily year to year, producing at its potential GDP each year, with only small inflationary increases in the price level.
Aggregate demand and aggregate supply do not always move neatly together. Aggregate demand may fail to increase along with aggregate supply, or aggregate demand may even shift left, for a number of possible reasons: households become hesitant about consuming; firms decide against investing as much; or perhaps the demand from other countries for exports diminishes. For example, investment by private firms in physical capital in the U.S. economy boomed during the late 1990s, rising from 14.1% of GDP in 1993 to 17.2% in 2000, before falling back to 15.2% by 2002. Conversely, if shifts in aggregate demand run ahead of increases in aggregate supply, inflationary increases in the price level will result. Business cycles of recession and recovery are the consequence of shifts in aggregate supply and aggregate demand.
Monetary Policy and Bank Regulation shows us that a central bank can use its powers over the banking system to engage in countercyclical—or “against the business cycle”—actions. If recession threatens, the central bank uses an expansionary monetary policy to increase the supply of money, increase the quantity of loans, reduce interest rates, and shift aggregate demand to the right. If inflation threatens, the central bank uses contractionary monetary policy to reduce the supply of money, reduce the quantity of loans, raise interest rates, and shift aggregate demand to the left. Fiscal policy is another macroeconomic policy tool for adjusting aggregate demand by using either government spending or taxation policy.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of macroeconomics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?