| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
The foreign exchange market involves firms, households, and investors who demand and supply currencies coming together through their banks and the key foreign exchange dealers. [link] (a) offers an example for the exchange rate between the U.S. dollar and the Mexican peso. The vertical axis shows the exchange rate for U.S. dollars, which in this case is measured in pesos. The horizontal axis shows the quantity of U.S. dollars being traded in the foreign exchange market each day. The demand curve (D) for U.S. dollars intersects with the supply curve (S) of U.S. dollars at the equilibrium point (E), which is an exchange rate of 10 pesos per dollar and a total volume of $8.5 billion.
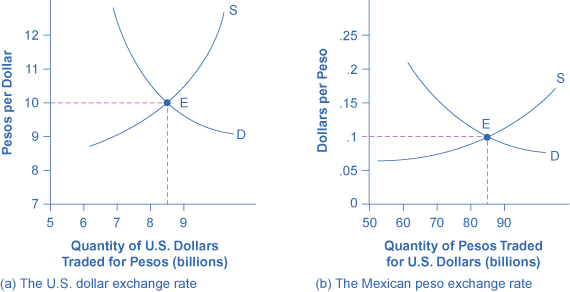
[link] (b) presents the same demand and supply information from the perspective of the Mexican peso. The vertical axis shows the exchange rate for Mexican pesos, which is measured in U.S. dollars. The horizontal axis shows the quantity of Mexican pesos traded in the foreign exchange market. The demand curve (D) for Mexican pesos intersects with the supply curve (S) of Mexican pesos at the equilibrium point (E), which is an exchange rate of 10 cents in U.S. currency for each Mexican peso and a total volume of 85 billion pesos. Note that the two exchange rates are inverses: 10 pesos per dollar is the same as 10 cents per peso (or $0.10 per peso). In the actual foreign exchange market, almost all of the trading for Mexican pesos is done for U.S. dollars. What factors would cause the demand or supply to shift, thus leading to a change in the equilibrium exchange rate ? The answer to this question is discussed in the following section.
One reason to demand a currency on the foreign exchange market is the belief that the value of the currency is about to increase. One reason to supply a currency—that is, sell it on the foreign exchange market—is the expectation that the value of the currency is about to decline. For example, imagine that a leading business newspaper, like the Wall Street Journal or the Financial Times , runs an article predicting that the Mexican peso will appreciate in value. The likely effects of such an article are illustrated in [link] . Demand for the Mexican peso shifts to the right, from D 0 to D 1 , as investors become eager to purchase pesos. Conversely, the supply of pesos shifts to the left, from S 0 to S 1 , because investors will be less willing to give them up. The result is that the equilibrium exchange rate rises from 10 cents/peso to 12 cents/peso and the equilibrium exchange rate rises from 85 billion to 90 billion pesos as the equilibrium moves from E 0 to E 1 .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Principles of macroeconomics for ap® courses' conversation and receive update notifications?