| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A mirror is a highly reflective surface. The most common mirrors are flat and are known as plane mirrors . Household mirrors are plane mirrors. They are made of a flat piece of glass with a thin layer of silver nitrate or aluminium on the back. However, other mirrors are curved and are either convex mirrors or are concave mirrors . The reflecting properties of all three types of mirrors will be discussed in this section.
An image is a representation of an object formed by a mirror or lens. Light from the image is seen.
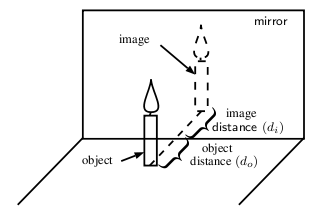
If you place a candle in front of a mirror, you now see two candles. The actual, physical candle is called the object and the picture you see in the mirror is called the image. The object is the source of the incident rays. The image is the picture that is formed by the reflected rays.
The object could be an actual source that emits light, such as a light bulb or a candle. More commonly, the object reflects light from another source. When you look at your face in the mirror, your face does not emit light. Instead, light from a light bulb or from the sun reflects off your face and then hits the mirror. However, in working with light rays, it is easiest to pretend the light is coming from the object.
An image formed by reflection may be real or virtual. A real image occurs when light rays actually intersect at the image. A real image is inverted, or upside down. A virtual image occurs when light rays do not actually meet at the image. Instead, you "see" the image because your eye projects light rays backward. You are fooled into seeing an image! A virtual image is erect, or right side up (upright).
You can tell the two types apart by putting a screen at the location of the image. A real image can be formed on the screen because the light rays actually meet there. A virtual image cannot be seen on a screen, since it is not really there.
To describe objects and images, we need to know their locations and their sizes. The distance from the mirror to the object is the object distance , .
The distance from the mirror to the image is the image distance , .

When you look into a mirror, you see an image of yourself.
The image created in the mirror has the following properties:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Siyavula textbooks: grade 10 physical science' conversation and receive update notifications?