| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Find the antiderivative of
Apply the formula with Then,
Evaluate the definite integral
Use the formula for the inverse tangent. We have
In the following exercises, evaluate each integral in terms of an inverse trigonometric function.
In the following exercises, find each indefinite integral, using appropriate substitutions.
Explain the relationship Is it true, in general, that
So, They differ by a constant.
Explain the relationship Is it true, in general, that
Explain what is wrong with the following integral:
is not defined as a real number when
Explain what is wrong with the following integral:
In the following exercises, solve for the antiderivative of f with then use a calculator to graph f and the antiderivative over the given interval Identify a value of C such that adding C to the antiderivative recovers the definite integral
[T] over
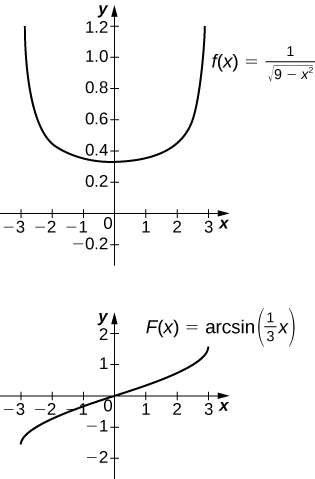
The antiderivative is
Taking
recovers the definite integral.
[T] over
![Two graphs. The first shows the function f(x) = cos(x) / (4 + sin(x)^2). It is an oscillating function over [-6, 6] with turning points at roughly (-3, -2.5), (0, .25), and (3, -2.5), where (0,.25) is a local max and the others are local mins. The second shows the function F(x) = .5 * arctan(.5*sin(x)), which also oscillates over [-6,6]. It has turning points at roughly (-4.5, .25), (-1.5, -.25), (1.5, .25), and (4.5, -.25).](/ocw/mirror/col11965_1.2_complete/m53636/CNX_Calc_Figure_05_07_203.jpg)
The antiderivative is
Taking
recovers the definite integral.
In the following exercises, compute the antiderivative using appropriate substitutions.
In the following exercises, use a calculator to graph the antiderivative with over the given interval Approximate a value of C , if possible, such that adding C to the antiderivative gives the same value as the definite integral
[T] over
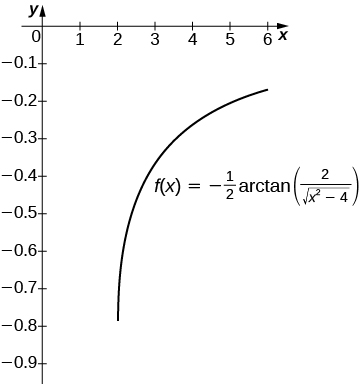
The antiderivative is
Taking
recovers the definite integral over
[T] over
![The graph of f(x) = arctan(x sin(x)) over [-6,6]. It has five turning points at roughly (-5, -1.5), (-2,1), (0,0), (2,1), and (5,-1.5).](/ocw/mirror/col11965_1.2_complete/m53636/CNX_Calc_Figure_05_07_207.jpg)
The general antiderivative is
Taking
recovers the definite integral.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 2' conversation and receive update notifications?