| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
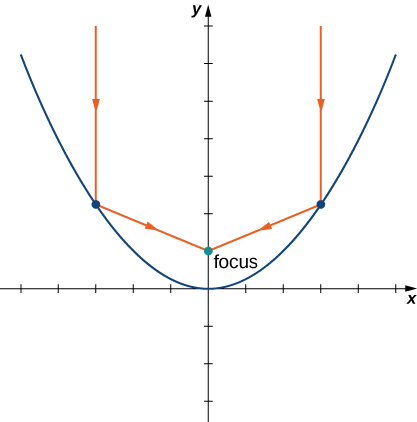
Consider a parabolic dish designed to collect signals from a satellite in space. The dish is aimed directly at the satellite, and a receiver is located at the focus of the parabola. Radio waves coming in from the satellite are reflected off the surface of the parabola to the receiver, which collects and decodes the digital signals. This allows a small receiver to gather signals from a wide angle of sky. Flashlights and headlights in a car work on the same principle, but in reverse: the source of the light (that is, the light bulb) is located at the focus and the reflecting surface on the parabolic mirror focuses the beam straight ahead. This allows a small light bulb to illuminate a wide angle of space in front of the flashlight or car.
An ellipse can also be defined in terms of distances. In the case of an ellipse, there are two foci (plural of focus), and two directrices (plural of directrix). We look at the directrices in more detail later in this section.
An ellipse is the set of all points for which the sum of their distances from two fixed points (the foci) is constant.

A graph of a typical ellipse is shown in [link] . In this figure the foci are labeled as and Both are the same fixed distance from the origin, and this distance is represented by the variable c . Therefore the coordinates of are and the coordinates of are The points and are located at the ends of the major axis of the ellipse, and have coordinates and respectively. The major axis is always the longest distance across the ellipse, and can be horizontal or vertical. Thus, the length of the major axis in this ellipse is 2 a. Furthermore, and are called the vertices of the ellipse. The points and are located at the ends of the minor axis of the ellipse, and have coordinates and respectively. The minor axis is the shortest distance across the ellipse. The minor axis is perpendicular to the major axis.
According to the definition of the ellipse, we can choose any point on the ellipse and the sum of the distances from this point to the two foci is constant. Suppose we choose the point P. Since the coordinates of point P are the sum of the distances is
Therefore the sum of the distances from an arbitrary point A with coordinates is also equal to 2 a. Using the distance formula, we get
Subtract the second radical from both sides and square both sides:
Now isolate the radical on the right-hand side and square again:
Isolate the variables on the left-hand side of the equation and the constants on the right-hand side:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Calculus volume 3' conversation and receive update notifications?