| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Activity 1
The basics of sketching
Focus task 1
Although we quite readily use the excuse that we “cannot draw”, it is useful to remember that sketches were used in prehistoric times, even before people learnt how to write. It may be true that some people have greater artistic ability than others when it comes to drawing, but even the greatest artists did not just begin to make art. You are also able to develop your drawing skill and it is important to do this by practising methods that will help you to make good sketches. Bear in mind that sketches are free-hand drawings.
Some guidelines:
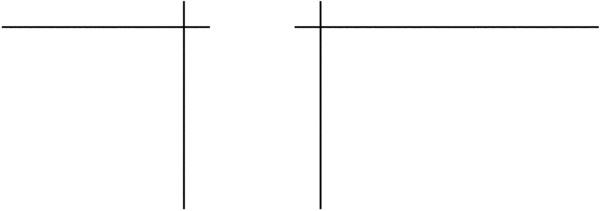
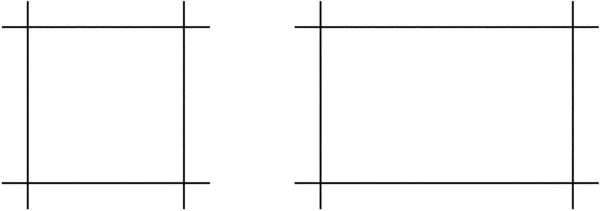
Try the following steps:





| LO 2.1 | ||||
| LO 2 |
| TECHNOLOGICAL KNOWLEDGE AND UNDERSTANDING The learner will be able to understand and apply relevant technological knowledge ethically and responsibly. |
| This is demonstrated when the learner: |
| structures:2.1 demonstrate knowledge and understanding of frame structures: |
|
| processing:2.2 demonstrates a knowledge and understanding of how materials can be processed to change or improve their properties by adapting them to suit particular purposes: |
|
ACTIVITY 1
2. and 3. Suggest that learners practise drawing straight freehand lines on loose sheets of paper.
4. and 5. Bear in mind that these are freehand sketches. Adequate opportunity for practising freehand drawing on loose paper is therefore important. Also encourage learners to practise in context, e.g. by drawing the wheels of a vehicle, etc.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Technology grade 8' conversation and receive update notifications?