| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In 1983 the United Nations General Assembly passed resolution 38/161 entitled “ Process of Preparation of the Environmental Perspective to the Year 2000 and Beyond ,” establishing a special commission whose charge was:
The commission later adopted the formal name “World Commission on Environment and Development” (WCED) but became widely known by the name of its chair Gro Harlem Brundtland , a medical doctor and public health advocate who had served as Norway’s Minister for Environmental Affairs and subsequently held the post of Prime Minister during three periods. The commission had twenty-one members drawn from across the globe, half representing developing nations. In addition to its fact-finding activities on the state of the global environment, the commission held fifteen meetings in various cities around the world seeking firsthand experiences on the how humans interact with the environment. The Brundtland Commission issued its final report “ Our Common Future ” in 1987.
Although the Brundtland Report did not technically invent the term “sustainability,” it was the first credible and widely-disseminated study that probed its meaning in the context of the global impacts of humans on the environment. Its main and often quoted definition refers to sustainable development as “…development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.” The report uses the terms “sustainable development,” “sustainable,” and “sustainability” interchangeably, emphasizing the connections among social equity, economic productivity, and environmental quality. The pathways for integration of these may differ nation by nation; still these pathways must share certain common traits: “the essential needs of the world's poor, to which overriding priority should be given, and the idea of limitations imposed by the state of technology and social organization on the environment's ability to meet present and future needs.”
Thus there are three dimensions that sustainability seeks to integrate: economic, environmental, and social (including sociopolitical). Economic interests define the framework for making decisions, the flow of financial capital, and the facilitation of commerce, including the knowledge, skills, competences and other attributes embodied in individuals that are relevant to economic activity. Environmental aspects recognize the diversity and interdependence within living systems, the goods and services produced by the world’s ecosystems, and the impacts of human wastes. Socio-political refers to interactions between institutions/firms and people, functions expressive of human values, aspirations and well-being, ethical issues, and decision-making that depends upon collective action. The report sees these three elements as part of a highly integrated and cohesively interacting, if perhaps poorly understood, system.
The Brundtland Report makes it clear that while sustainable development is enabled by technological advances and economic viability, it is first and foremost a social construct that seeks to improve the quality of life for the world’s peoples: physically, through the equitable supply of human and ecological goods and services; aspirationally, through making available the widespread means for advancement through access to education, systems of justice, and healthcare; and strategically, through safeguarding the interests of generations to come. In this sense sustainability sits among a series of human social movements that have occurred throughout history: human rights, racial equality, gender equity, labor relations, and conservation, to name a few.
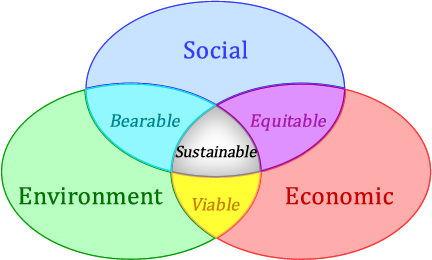
The intersection of social and economic elements can form the basis of social equity. In the sense of enlightened management, "viability" is formed through consideration of economic and environmental interests. Between environment and social elements lies “bearability,” the recognition that the functioning of societies is dependent on environmental resources and services. At the intersection of all three of these lies sustainability.
The US Environmental Protection Agency (US EPA) takes the extra step of drawing a distinction between sustainability and sustainable development, the former encompassing ideas, aspirations and values that inspire public and private organizations to become better stewards of the environment and that promote positive economic growth and social objectives, the latter implying that environmental protection does not preclude economic development and that economic development must be ecologically viable now and in the long run.
The Chapter The Evolution of Environmental Policy in the United States presents information on how the three components that comprise sustainability have influenced the evolution of environmental public policy. The Chapter Sustainability: Ethics, Culture, and History explores in greater detail the ethical basis for sustainability and its cultural and historical significance.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Sustainability: a comprehensive foundation' conversation and receive update notifications?