| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The nares open into the nasal cavity, which is separated into left and right sections by the nasal septum ( [link] ). The nasal septum is formed anteriorly by a portion of the septal cartilage (the flexible portion you can touch with your fingers) and posteriorly by the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone (a cranial bone located just posterior to the nasal bones) and the thin vomer bones (whose name refers to its plough shape). Each lateral wall of the nasal cavity has three bony projections, called the superior, middle, and inferior nasal conchae. The inferior conchae are separate bones, whereas the superior and middle conchae are portions of the ethmoid bone. Conchae serve to increase the surface area of the nasal cavity and to disrupt the flow of air as it enters the nose, causing air to bounce along the epithelium, where it is cleaned and warmed. The conchae and meatuses also conserve water and prevent dehydration of the nasal epithelium by trapping water during exhalation. The floor of the nasal cavity is composed of the palate. The hard palate at the anterior region of the nasal cavity is composed of bone. The soft palate at the posterior portion of the nasal cavity consists of muscle tissue. Air exits the nasal cavities via the internal nares and moves into the pharynx.
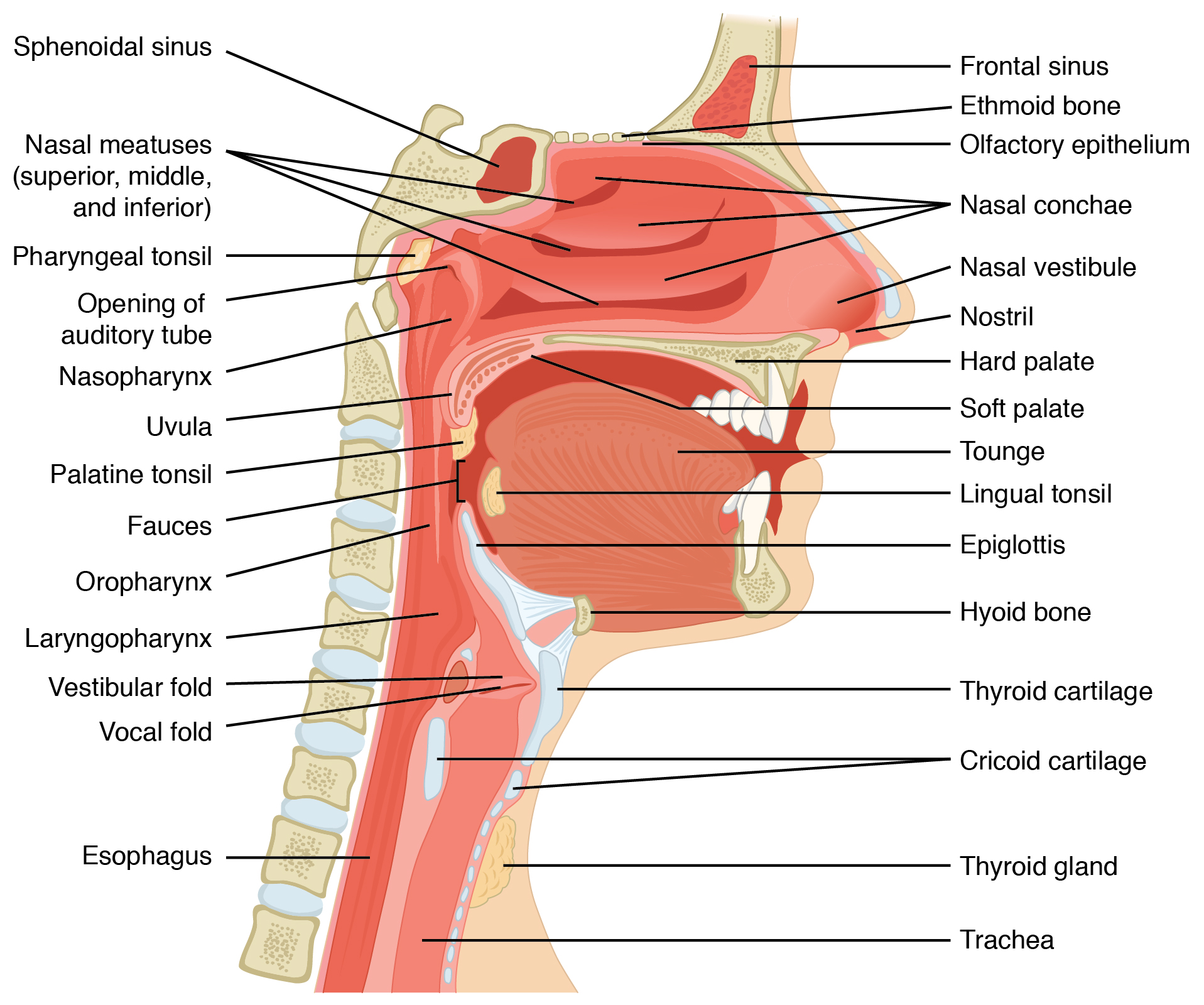
Several bones that help form the walls of the nasal cavity have air-containing spaces called the paranasal sinuses, which serve to warm and humidify incoming air. Sinuses are lined with a mucosa. Each paranasal sinus is named for its associated bone: frontal sinus, maxillary sinus, sphenoidal sinus, and ethmoidal sinus. The sinuses produce mucus and lighten the weight of the skull.
The nares and anterior portion of the nasal cavities are lined with mucous membranes, containing sebaceous glands and hair follicles that serve to prevent the passage of large debris, such as dirt, through the nasal cavity. An olfactory epithelium used to detect odors is found deeper in the nasal cavity.
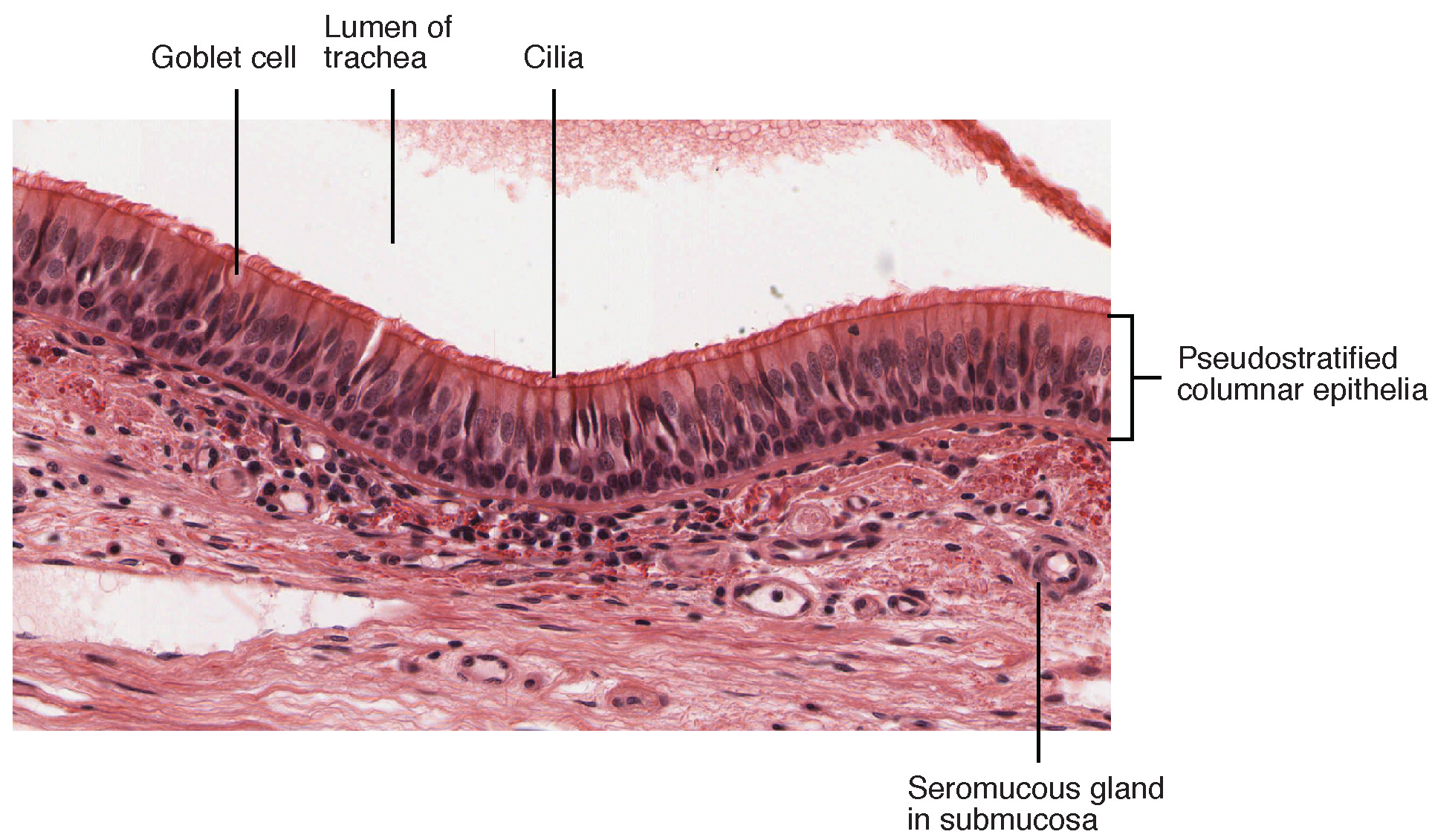
The conchae, meatuses, and paranasal sinuses are lined by respiratory epithelium composed of pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium ( [link] ). The epithelium contains goblet cells, one of the specialized, columnar epithelial cells that produce mucus to trap debris. The cilia of the respiratory epithelium help remove the mucus and debris from the nasal cavity with a constant beating motion, sweeping materials towards the throat to be swallowed. Interestingly, cold air slows the movement of the cilia, resulting in accumulation of mucus that may in turn lead to a runny nose during cold weather. This moist epithelium functions to warm and humidify incoming air. Capillaries located just beneath the nasal epithelium warm the air by convection. Serous and mucus-producing cells also secrete the lysozyme enzyme and proteins called defensins, which have antibacterial properties. Immune cells that patrol the connective tissue deep to the respiratory epithelium provide additional protection.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Anatomy & Physiology: energy, maintenance and environmental exchange' conversation and receive update notifications?