| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Write each number in standard form:
fifty-three million, eight hundred nine thousand, fifty-one.
53,809,051
Write each number in standard form:
two billion, twenty-two million, seven hundred fourteen thousand, four hundred sixty-six.
2,022,714,466
A state budget was about billion. Write the budget in standard form.
Identify the periods. In this case, only two digits are given and they are in the billions period. To write the entire number, write zeros for all of the other periods.
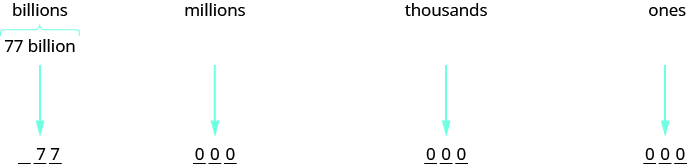
So the budget was about
Write each number in standard form:
The closest distance from Earth to Mars is about million miles.
34,000,000 miles
Write each number in standard form:
The total weight of an aircraft carrier is million pounds.
204,000,000 pounds
In the U.S. Census Bureau reported the population of the state of New York as people. It might be enough to say that the population is approximately million. The word approximately means that million is not the exact population, but is close to the exact value.
The process of approximating a number is called rounding . Numbers are rounded to a specific place value depending on how much accuracy is needed. Saying that the population of New York is approximately million means we rounded to the millions place. The place value to which we round to depends on how we need to use the number.
Using the number line can help you visualize and understand the rounding process. Look at the number line in [link] . Suppose we want to round the number to the nearest ten. Is closer to or on the number line?

Now consider the number Find in [link] .

How do we round to the nearest ten. Find in [link] .

So that everyone rounds the same way in cases like this, mathematicians have agreed to round to the higher number, So, rounded to the nearest ten is
Now that we have looked at this process on the number line, we can introduce a more general procedure. To round a number to a specific place, look at the number to the right of that place. If the number is less than round down. If it is greater than or equal to round up.
So, for example, to round to the nearest ten, we look at the digit in the ones place.
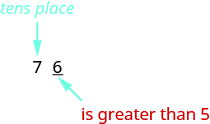
The digit in the ones place is a Because is greater than or equal to we increase the digit in the tens place by one. So the in the tens place becomes an Now, replace any digits to the right of the with zeros. So, rounds to
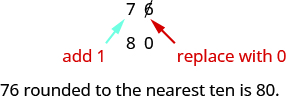
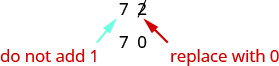
Let’s look again at rounding to the nearest Again, we look to the ones place.
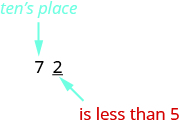
The digit in the ones place is Because is less than we keep the digit in the tens place the same and replace the digits to the right of it with zero. So rounded to the nearest ten is

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Prealgebra' conversation and receive update notifications?