| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
A non-electrolyte is a material that does not increase the conductivity of water when dissolved in it. The substance goes into solution and becomes surrounded by water molecules, so that the molecules of the chemical become separated from each other. However, although the substance does dissolve, it is not changed in any way and no chemical bonds are broken. The change is a physical change . In the oxygen example below, the reaction is shown to be reversible because oxygen is only partially soluble in water and comes out of solution very easily.
The conductivity of water is therefore affected by the following factors:
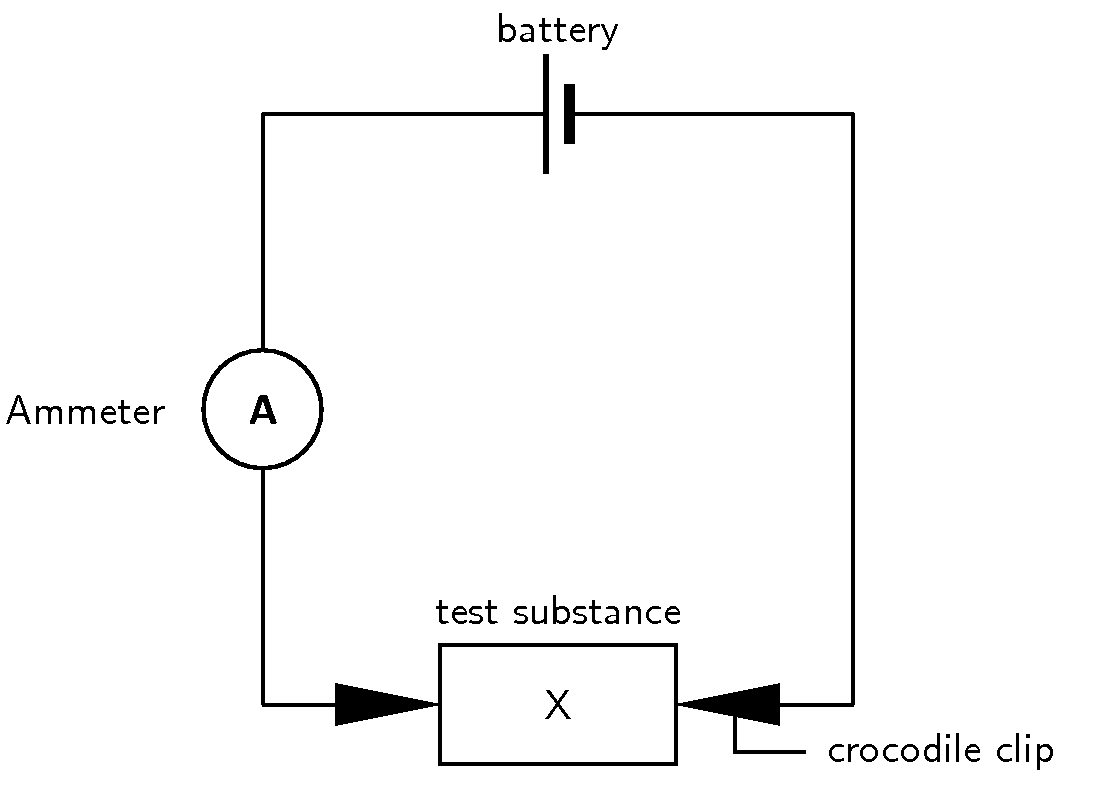
| Test substance | Ammeter reading |
What do you notice? Can you explain these observations?
Remember that for electricity to flow, there needs to be a movement of charged particles e.g. ions. With the solid crystals, there was no flow of electricity recorded on the ammeter. Although the solid is made up of ions, they are held together very tightly within the crystal lattice and therefore no current will flow. Distilled water, benzene and alcohol also don't conduct a current because they are covalent compounds and therefore do not contain ions.
The ammeter should have recorded a current when the salt solutions and the acid and base solutions were connected in the circuit. In solution, salts dissociate into their ions, so that these are free to move in the solution. Acids and bases behave in a similar way and dissociate to form hydronium and oxonium ions. Look at the following examples:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chemistry grade 10 [caps]' conversation and receive update notifications?