| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
We next define the moments of as
and the discrete moments of as
Theorem 36 (Equivalent Characterizations of K-Regular M-Band Filters) A unitary scaling filter is K-regular if and only if the following equivalentstatements are true:
This powerful result [link] , [link] is similar to the case presented in Chapter: Regularity, Moments, and Wavelet System Design . It not only ties the number of zero moments to the regularity but also to the degree of polynomials that canbe exactly represented by a sum of weighted and shifted scaling functions. Note the location of the zeros of are equally spaced around the unit circle, resulting in a narrower frequency response than for thehalf-band filters if . This is consistent with the requirements given in [link] and illustrated in [link] .
Sketches of some of the derivations in this section are given in the Appendix or are simple extensions of the case. More details are given in [link] , [link] , [link] .
Calculating values of can be done by the same methods given in Section: Calculating the Basic Scaling Function and Wavelet . However, the design of the scaling coefficients parallels that for the two-band case but is somewhat more difficult [link] .
One special set of cases turns out to be a simple extension of the two-band system. If the multiplier , then the scaling function is simply a scaled version of the case and a particular set of corresponding wavelets are those obtained by iterating the waveletbranches of the Mallat algorithm tree as is done for wavelet packets described in [link] . For other values of , especially odd values, the situation is more complex.
For the wavelet coefficients are not uniquely determined by the scaling coefficients, as was the case for . This is both a blessing and a curse. It gives us more flexibility in designing specific systems,but it complicates the design considerably. For small and , the designs can be done directly, but for longer lengths and/or for large , direct design becomes impossible and something like the cosine modulateddesign of the wavelets from the scaling function as described in Chapter: Filter Banks and Transmultiplexers , is probably the bestapproach [link] , [link] , [link] , [link] , [link] [link] , [link] , [link] , [link] , [link] , [link] , [link] , [link] , [link] .
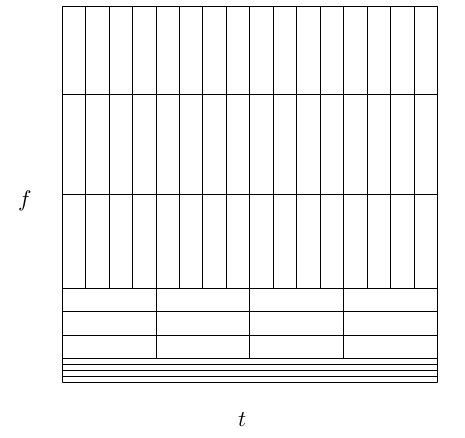
The classical wavelet system results in a logarithmic frequency resolution. The low frequencies have narrow bandwidths and the highfrequencies have wide bandwidths, as illustrated in Figure: Frequency Bands for the Analysis Tree . This is called “constant-Q" filtering and is appropriate for someapplications but not all. The wavelet packet system was proposed by Ronald Coifman [link] , [link] to allow a finer and adjustable resolution of frequencies at high frequencies. It also gives a rich structure thatallows adaptation to particular signals or signal classes. The cost of this richer structureis a computational complexity of , similar to the FFT, in contrast to the classical wavelet transform which is .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Wavelets and wavelet transforms' conversation and receive update notifications?