| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Notice that and that showing that is a unitary operator on . Also these operators change only in since for and . The interval is the action region of the folding/unfolding operator. is called a folding operator acting at zero because for smooth , has a discontinuity at zero. By translation and dilation of one can define and that folds and unfolds respectively about with action region and action radius .
Notice [link] and [link] do not define the value and because of the discontinuity that is potentially introduced. An elementary exercise in calculusdivulges the nature of this discontinuity. If , then . At , left and right derivatives exist with all even-order left-derivativesand all odd order right-derivatives (upto and including ) being zero. Conversely, given any function which has a discontinuity of the above type, has a unique extension across (i.e., a choice of value for ( ) that is in . One can switch the signs in [link] and [link] to obtain another set of folding and unfolding operators. In this case,for , will have its even-order right derivatives and odd-order left derivatives equal to zero.We will use , and , , respectively to distinguish between the two types of folding/unfolding operators and call them positive and negativepolarity folding/unfolding operators respectively.
So far we have seen that the folding operator is associated with a rising cutoff function, acts at a certain point, has a certainaction region and radius and has a certain polarity. To get a qualitative idea of what these operators do, let us look at someexamples.
First, consider a case where is even- or-odd symmetric about the folding point on theaction interval. Then, corresponds to simply windowing by an appropriate window function. Indeed,if on ,
and if on
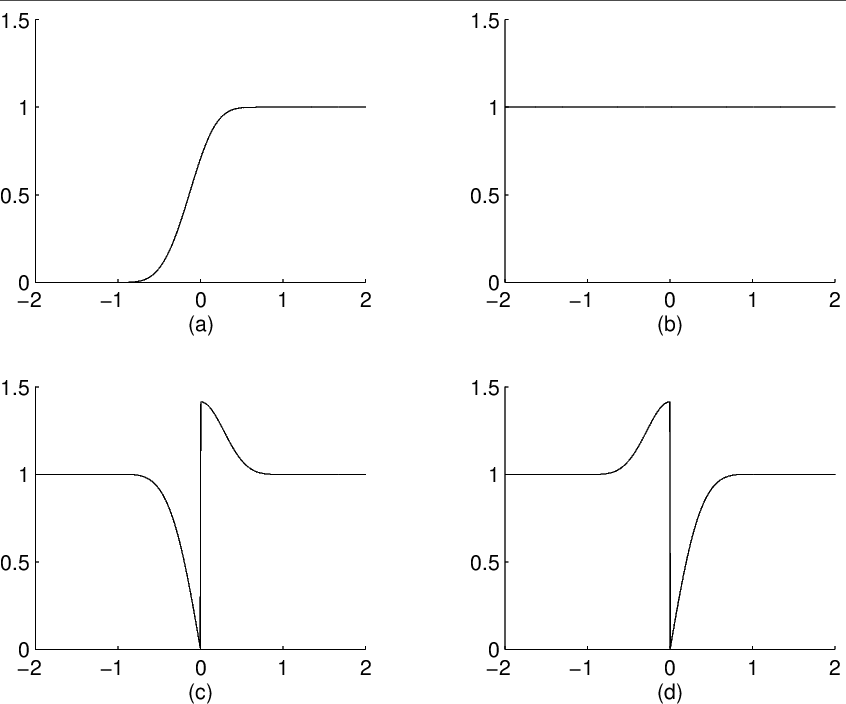
[link] shows a rising cutoff function and the action of the folding operators of both polarities on the constant function. Observethe nature of the discontinuity at and the effect of polarityreversal.
We saw that for signals with symmetry in the action region folding, corresponds to windowing. Next we look at signals that aresupported to the right (or left) of the folding point and see what unfolding does to them. In this case, is obtained by windowing the even (or odd) extension of about the folding point. Indeed if
and if ,
[link] shows the effect of the positive unfolding operator acting on cosine and sine functions supported on theright and left half-lines respectively. Observe that unfolding removes the discontinuities at . If the polarity is reversed, the effects on signals on the half-lineare switched; the right half-line is associated with windowed odd extensions and left half-line with windowed even extensions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Wavelets and wavelet transforms' conversation and receive update notifications?