| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In this exercise we will determine the Mach Number for the different aircraft in the previous table. To help you get started we have calculated the Mach Number for the Concord with a speed of sound .
For the Condorde we know the speed and we know that:
For the Concorde this means that
| Aircraft | speed at altitude ( ) | speed at altitude ( ) | Mach Number |
| Concorde | 2 330 | 647 | 1.9 |
| Gripen | 2 410 | 669 | |
| Mirage F1 | 2 573 | 715 | |
| Mig 27 | 1 885 | 524 | |
| F 15 | 2 660 | 739 | |
| F 16 | 2 414 | 671 |
Now calculate the Mach Numbers for the other aircraft in the table.
The shape of the Mach Cone depends on the speed of the aircraft. When the Mach Number is 1 there is no cone but as the aircraft goes faster and faster the angle of the cone gets smaller and smaller.
If we go back to the supersonic picture we can work out what the angle of the cone must be.

We build a triangle between how far the plane has moved and how far a wavefront at right angles to the direction the plane is flying has moved:
An aircraft emits a sound wavefront. The wavefront moves at the speed of sound 340 and the aircraft moves at Mach 1.5, which is . The aircraft travels faster than the wavefront. If we let the wavefront travel for a time then the following diagram will apply:
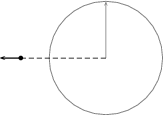
We know how fast the wavefront and the aircraft are moving so we know the distances that they have traveled:

The angle between the cone that forms and the direction of the plane can be found from the right-angle triangle we have drawn into the figure. We know that which in this figure means:
In this case we have used sound and aircraft but a more general way of saying this is:
We often just write the equation as:
From this equation, we can see that the faster the source (aircraft) moves, the smaller the angle of the Mach cone.
In this exercise we will determine the Mach Cone Angle for the different aircraft in the table mentioned above. To help you get started we have calculated the Mach Cone Angle for the Concorde with a speed of sound .
For the Condorde we know the speed and we know that:
For the Concorde this means that
| Aircraft | speed at altitude ( ) | speed at altitude ( ) | Mach Cone Angle (degrees) |
| Concorde | 2 330 | 647 | 31.7 |
| Gripen | 2 410 | 669 | |
| Mirage F1 | 2 573 | 715 | |
| Mig 27 | 1 885 | 524 | |
| F 15 | 2 660 | 739 | |
| F 16 | 2 414 | 671 |
Now calculate the Mach Cone Angles for the other aircraft in the table.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Maths test' conversation and receive update notifications?