| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
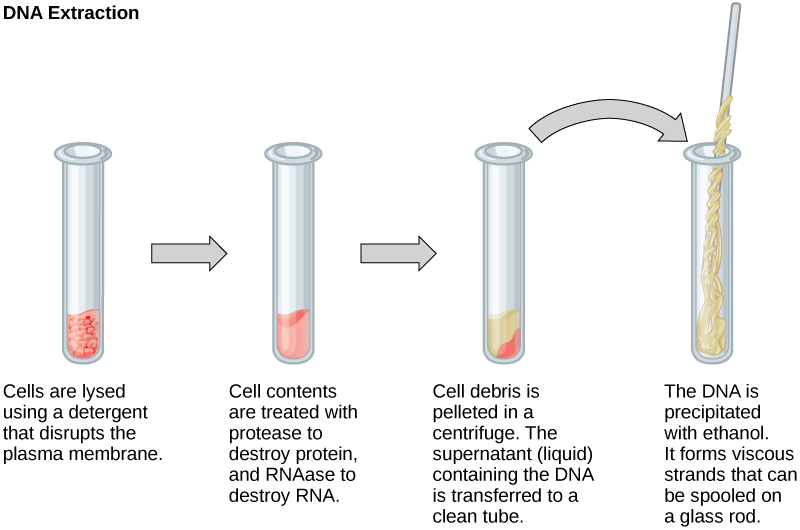
RNA analysis is performed to study gene expression patterns in cells. RNA is naturally very unstable because RNAses are commonly present in nature and very difficult to inactivate. Similar to DNA, RNA extraction involves the use of various buffers and enzymes to inactivate macromolecules and preserve the RNA.
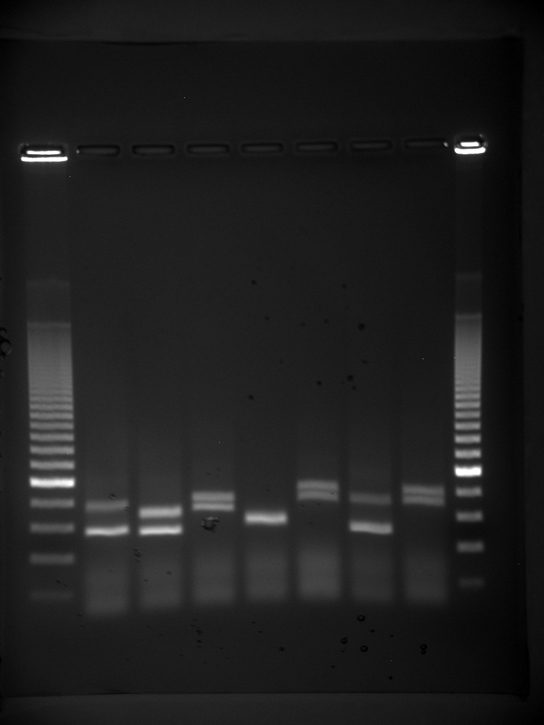
Because nucleic acids are negatively charged ions at neutral or basic pH in an aqueous environment, they can be mobilized by an electric field. Gel electrophoresis is a technique used to separate molecules on the basis of size, using this charge. The nucleic acids can be separated as whole chromosomes or fragments. The nucleic acids are loaded into a slot near the negative electrode of a semisolid, porous gel matrix and pulled toward the positive electrode at the opposite end of the gel. Smaller molecules move through the pores in the gel faster than larger molecules; this difference in the rate of migration separates the fragments on the basis of size. There are molecular weight standard samples that can be run alongside the molecules to provide a size comparison. Nucleic acids in a gel matrix can be observed using various fluorescent or colored dyes. Distinct nucleic acid fragments appear as bands at specific distances from the top of the gel (the negative electrode end) on the basis of their size ( [link] ). A mixture of genomic DNA fragments of varying sizes appear as a long smear, whereas uncut genomic DNA is usually too large to run through the gel and forms a single large band at the top of the gel.
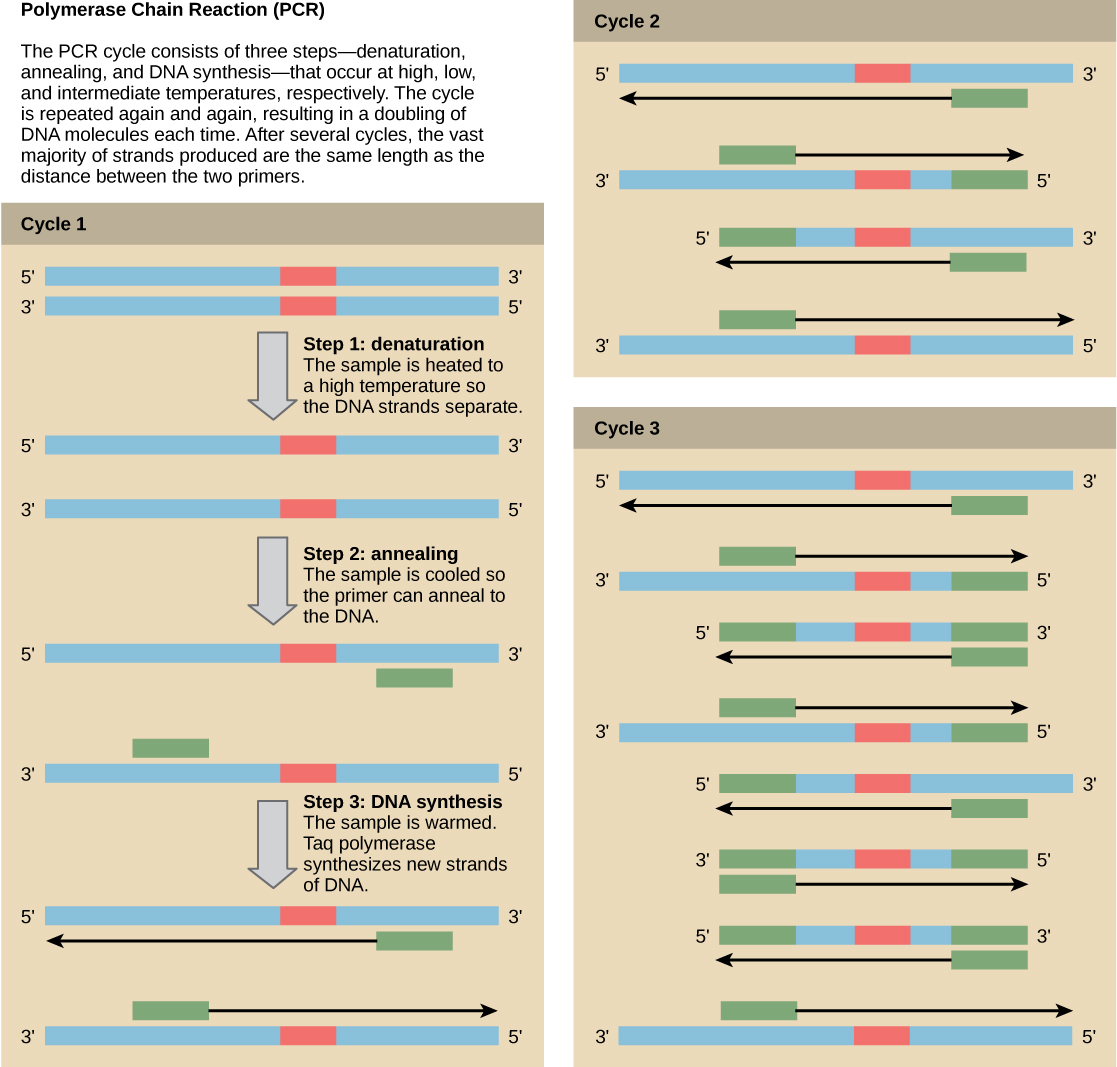
Although genomic DNA is visible to the naked eye when it is extracted in bulk, DNA analysis often requires focusing on one or more specific regions of the genome. Polymerase chain reaction ( PCR ) is a technique used to amplify specific regions of DNA for further analysis ( [link] ). PCR is used for many purposes in laboratories, such as the cloning of gene fragments to analyze genetic diseases, identification of contaminant foreign DNA in a sample, and the amplification of DNA for sequencing. More practical applications include the determination of paternity and detection of genetic diseases.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Genetics and evolution' conversation and receive update notifications?