| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Amnesia is the loss of long-term memory that occurs as the result of disease, physical trauma, or psychological trauma.
There are two common types of amnesia: anterograde amnesia and retrograde amnesia ( [link] ). Anterograde amnesia is commonly caused by brain trauma, such as a blow to the head. With anterograde amnesia , you cannot remember new information, although you can remember information and events that happened prior to your injury. The hippocampus is usually affected (McLeod, 2011). This suggests that damage to the brain has resulted in the inability to transfer information from short-term to long-term memory; that is, the inability to consolidate memories.
Many people with this form of amnesia are unable to form new episodic or semantic memories, but are still able to form new procedural memories (Bayley&Squire, 2002). This was true of H. M., which was discussed earlier. The brain damage caused by his surgery resulted in anterograde amnesia. H. M. would read the same magazine over and over, having no memory of ever reading it—it was always new to him. He also could not remember people he had met after his surgery. If you were introduced to H. M. and then you left the room for a few minutes, he would not know you upon your return and would introduce himself to you again. However, when presented the same puzzle several days in a row, although he did not remember having seen the puzzle before, his speed at solving it became faster each day (because of relearning) (Corkin, 1965, 1968).
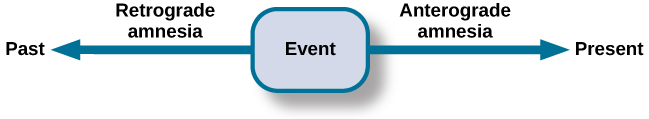
Retrograde amnesia is loss of memory for events that occurred prior to the trauma. People with retrograde amnesia cannot remember some or even all of their past. They have difficulty remembering episodic memories. What if you woke up in the hospital one day and there were people surrounding your bed claiming to be your spouse, your children, and your parents? The trouble is you don’t recognize any of them. You were in a car accident, suffered a head injury, and now have retrograde amnesia. You don’t remember anything about your life prior to waking up in the hospital. This may sound like the stuff of Hollywood movies, and Hollywood has been fascinated with the amnesia plot for nearly a century, going all the way back to the film Garden of Lies from 1915 to more recent movies such as the Jason Bourne trilogy starring Matt Damon and 50 First Dates with Drew Barrymore. However, for real-life sufferers of retrograde amnesia, like former NFL football player Scott Bolzan, the story is not a Hollywood movie. Bolzan fell, hit his head, and deleted 46 years of his life in an instant. He is now living with one of the most extreme cases of retrograde amnesia on record.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Chapter 8: memory sw' conversation and receive update notifications?