| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
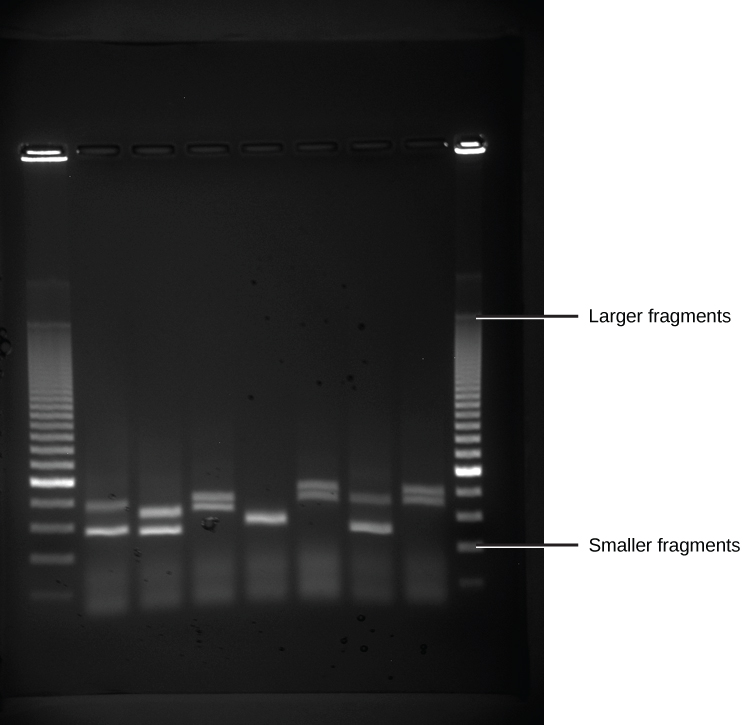
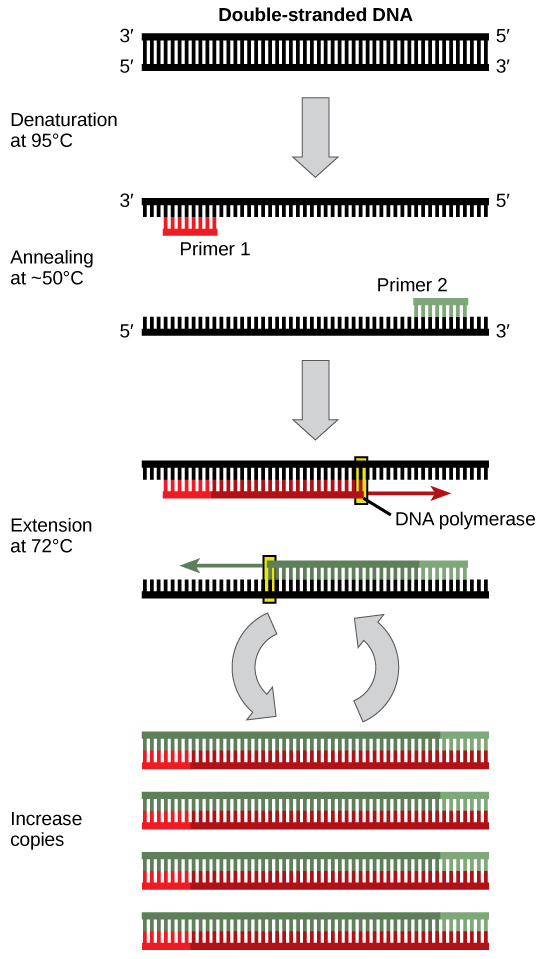
DNA analysis often requires focusing on one or more specific regions of the genome. It also frequently involves situations in which only one or a few copies of a DNA molecule are available for further analysis. These amounts are insufficient for most procedures, such as gel electrophoresis. Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a technique used to rapidly increase the number of copies of specific regions of DNA for further analyses ( [link] ). PCR uses a special form of DNA polymerase, the enzyme that replicates DNA, and other short nucleotide sequences called primers that base pair to a specific portion of the DNA being replicated. PCR is used for many purposes in laboratories. These include: 1) the identification of the owner of a DNA sample left at a crime scene; 2) paternity analysis; 3) the comparison of small amounts of ancient DNA with modern organisms; and 4) determining the sequence of nucleotides in a specific region.
In general, cloning means the creation of a perfect replica. Typically, the word is used to describe the creation of a genetically identical copy. In biology, the re-creation of a whole organism is referred to as “reproductive cloning.” Long before attempts were made to clone an entire organism, researchers learned how to copy short stretches of DNA—a process that is referred to as molecular cloning.
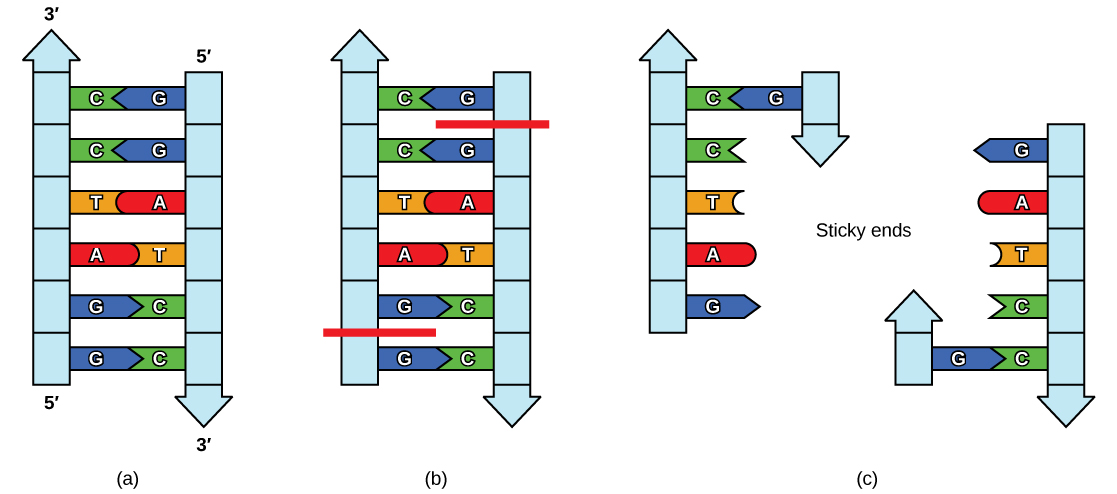
Cloning allows for the creation of multiple copies of genes, expression of genes, and study of specific genes. To get the DNA fragment into a bacterial cell in a form that will be copied or expressed, the fragment is first inserted into a plasmid. A plasmid (also called a vector in this context) is a small circular DNA molecule that replicates independently of the chromosomal DNA in bacteria. In cloning, the plasmid molecules can be used to provide a "vehicle" in which to insert a desired DNA fragment. Modified plasmids are usually reintroduced into a bacterial host for replication. As the bacteria divide, they copy their own DNA (including the plasmids). The inserted DNA fragment is copied along with the rest of the bacterial DNA.
Plasmids occur naturally in bacterial populations (such as Escherichia coli ) and have genes that can contribute favorable traits to the organism, such as antibiotic resistance (the ability to be unaffected by antibiotics). Plasmids have been highly engineered as vectors for molecular cloning and for the subsequent large-scale production of important molecules, such as insulin. A valuable characteristic of plasmid vectors is the ease with which a foreign DNA fragment can be introduced.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Environmental biology' conversation and receive update notifications?