| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
While this “warm classroom” example is based on observational results, other hypotheses and experiments might have clearer controls. For instance, a student might attend class on Monday and realize she had difficulty concentrating on the lecture. One observation to explain this occurrence might be, “When I eat breakfast before class, I am better able to pay attention.” The student could then design an experiment with a control to test this hypothesis.
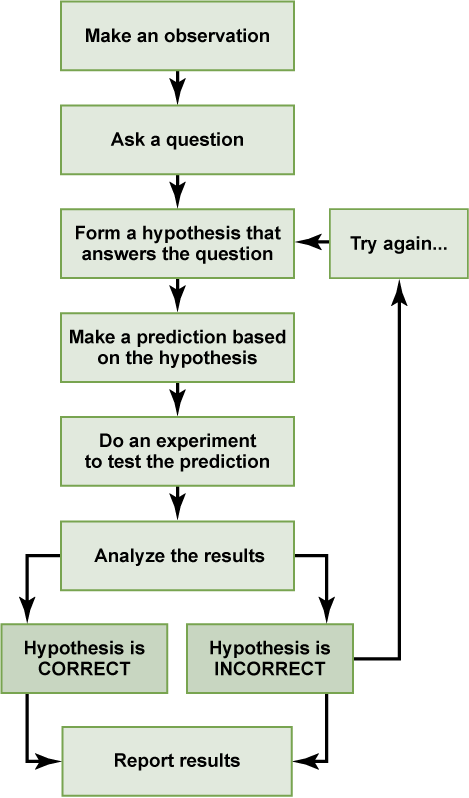
In the example below, the scientific method is used to solve an everyday problem. Order the scientific method steps (numbered items) with the process of solving the everyday problem (lettered items). Then, based on the results of the experiment, is the hypothesis correct? If it is incorrect, propose some alternative hypotheses.
In hypothesis-based science, specific results are predicted from a general premise. This type of reasoning is called deductive reasoning: deduction proceeds from the general to the particular. But the reverse of the process is also possible: sometimes, scientists reach a general conclusion from a number of specific observations. This type of reasoning is called inductive reasoning, and it proceeds from the particular to the general. Inductive and deductive reasoning are often used in tandem to advance scientific knowledge ( [link] ).
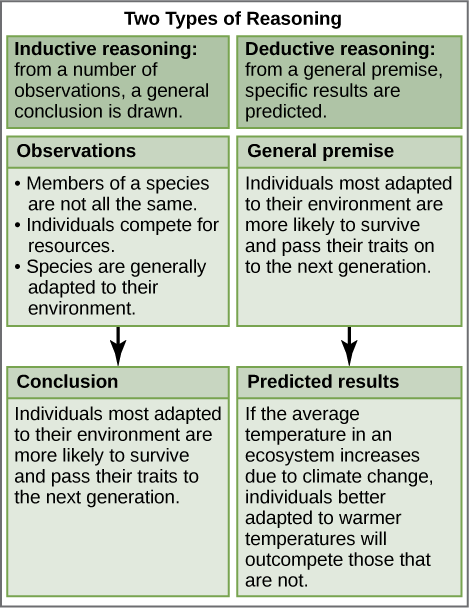
Decide if each of the following is an example of inductive or deductive reasoning.
The scientific method may seem too rigid and structured. It is important to keep in mind that, although scientists often follow this sequence, there is flexibility. Sometimes an experiment leads to conclusions that favor a change in approach; often, an experiment brings entirely new scientific questions to the puzzle. Many times, science does not operate in a linear fashion; instead, scientists continually draw inferences and make generalizations, finding patterns as their research proceeds. Scientific reasoning is more complex than the scientific method alone suggests. Notice, too, that the scientific method can be applied to solving problems that aren’t necessarily scientific in nature.
BIS 2A the first course in the Biological Sciences lower division core sequence. This sequence provides a foundation in modern biology for a broad range of majors. In BIS2A we introduce you to the fundamental chemical, molecular, genetic, and cellular building blocks of living organisms and universal core concepts in biology. There is a heavy focus on the fundamental unit of living systems, the cell. In BIS 2B you will examine ecological and evolutionary processes that shape biological diversity. Finally in BIS 2C you will examine biological diversity in detail. BIS2A is intended to provide you with foundational knowledge that you will build on in 2B and 2C and carry with you throughout your subsequent courses. We will stress important concepts but will also expect you to learn some of the vocabulary of Biology. This should be fun!
BIS 2A focuses on developing your understanding of several core concepts in biology that can be applied in contexts beyond the boundaries of this course. We expect that once you have successfully completed this course that you will be able to:
[link] Decide if each of the following is an example of inductive or deductive reasoning.
[link] 1: inductive; 2: deductive; 3: deductive; 4: inductive.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Introduction to bis2a: modules 0.0 to 1.2' conversation and receive update notifications?