| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
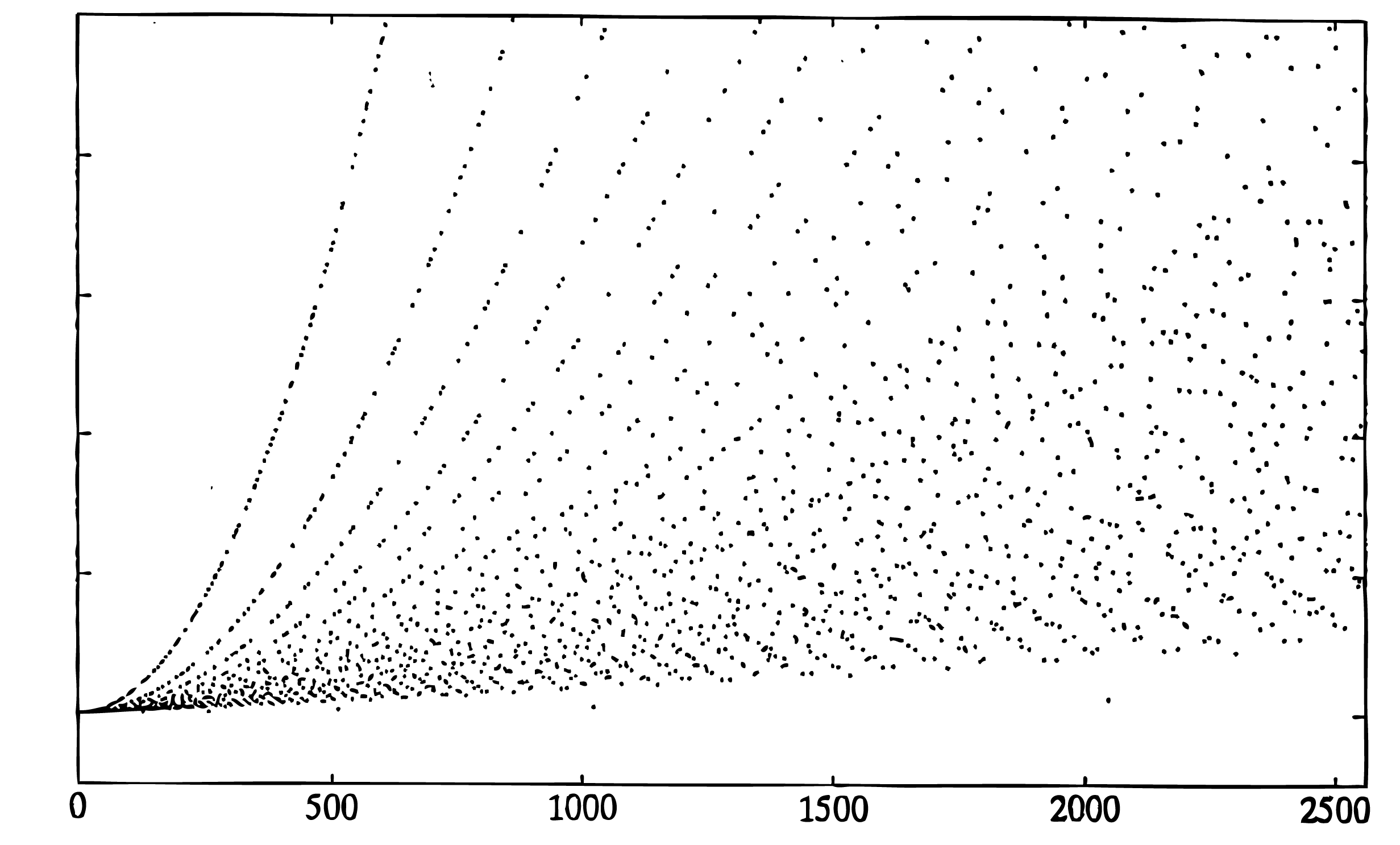
The Glassman-Ferguson FFT is a compact implementation of a mixed-radix Cooley-Tukey FFT with the short DFTs for each factor being calculated by a Goertzel-like algorithm. This means there are twiddle factor multiplications even when the factors are relatively prime, however, the indexing is simple and compact. It will calculate the DFT of a sequence of any length but is efficient only if the length is highly composite. The figures contain plots of the number of floating point multiplications plus additions vs. the length of the FFT. The numbers on the vertical axis have relative meaning but no absolute meaning.
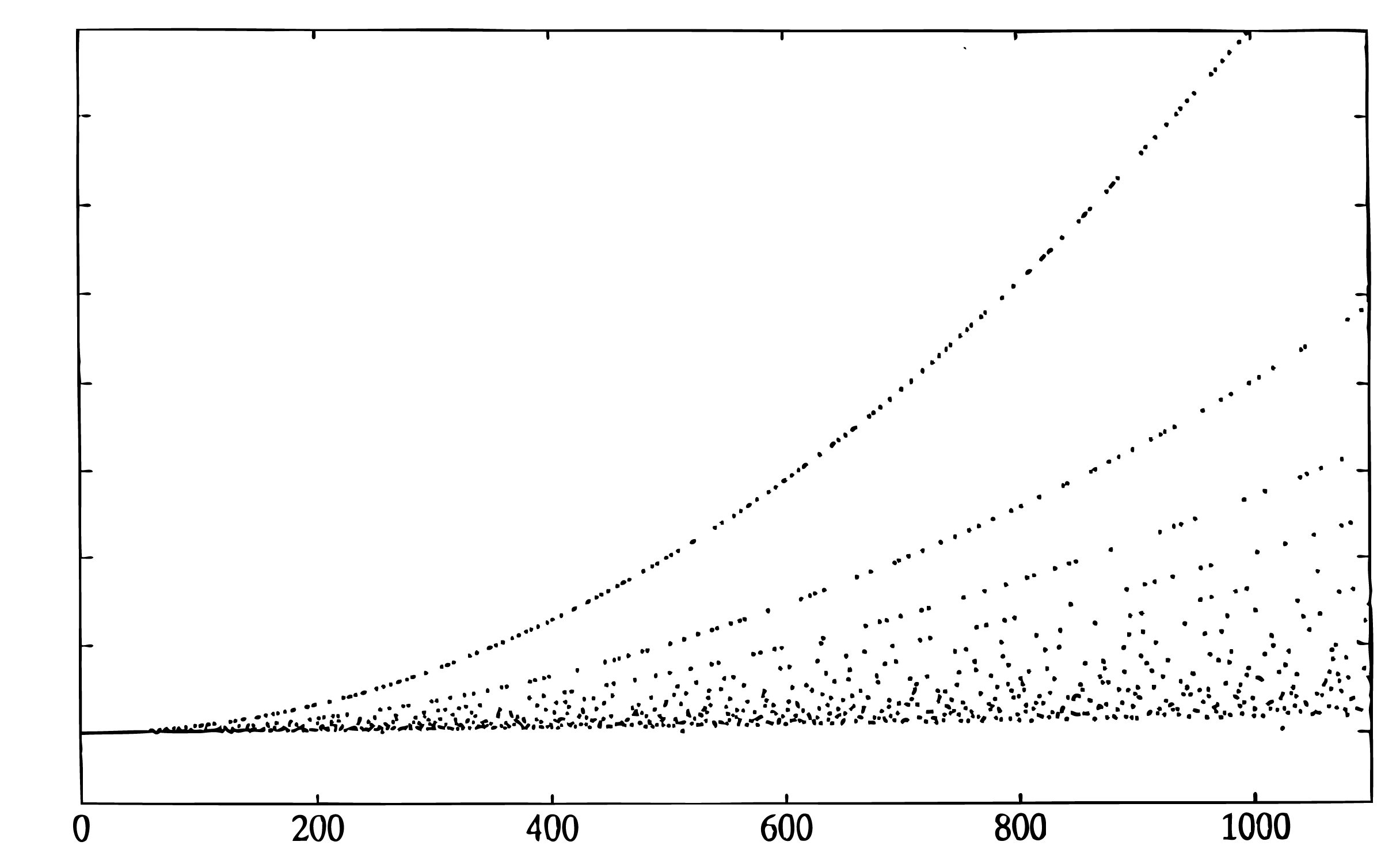
Note the parabolic shape of the curve for certain values. The upper curve is for prime lengths, the next one is for lengths that are two times a prime, and the next one is for lengths that are for three times a prime, etc. The shape of the lower boundary is roughly N log N. The program that generated these two figures used a Cooley-Tukey FFT if the length is two to a power which accounts for the points that are below the major lower boundary.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Fast fourier transforms' conversation and receive update notifications?