| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Nội dung:
Ly hợp có nhiệm vụ như là một khớp nối, đóng nhả thường xuyên khi thay đổi số truyền. Do cần phải đóng từ từ, êm dịu, vì vậy dẫn đến hiện tượng mòn gây trượt li hợp. Không được phép bôi trơn bề mặt ma sát. Ly hợp gồm các phần chính sau:
Cơ cấu dẫn động ly hợp, bộ phận trợ lực.
Đĩa ép.
Đĩa ma sát
Các lò xo
Sơ đồ dẫn động ly hợp:
a. Ly hợp bị trượt: biểu hiện khi tăng ga, tốc độ xe không tăng theo tương ứng.
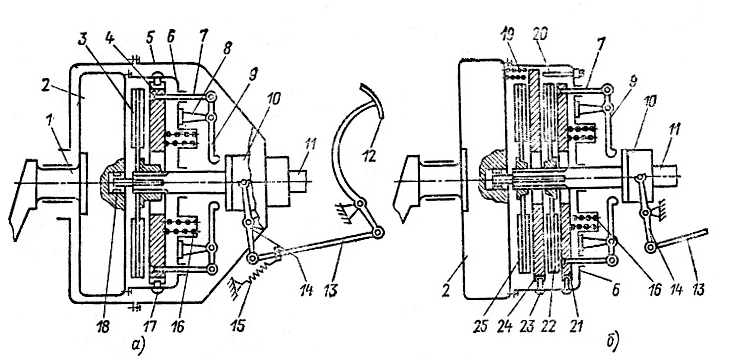
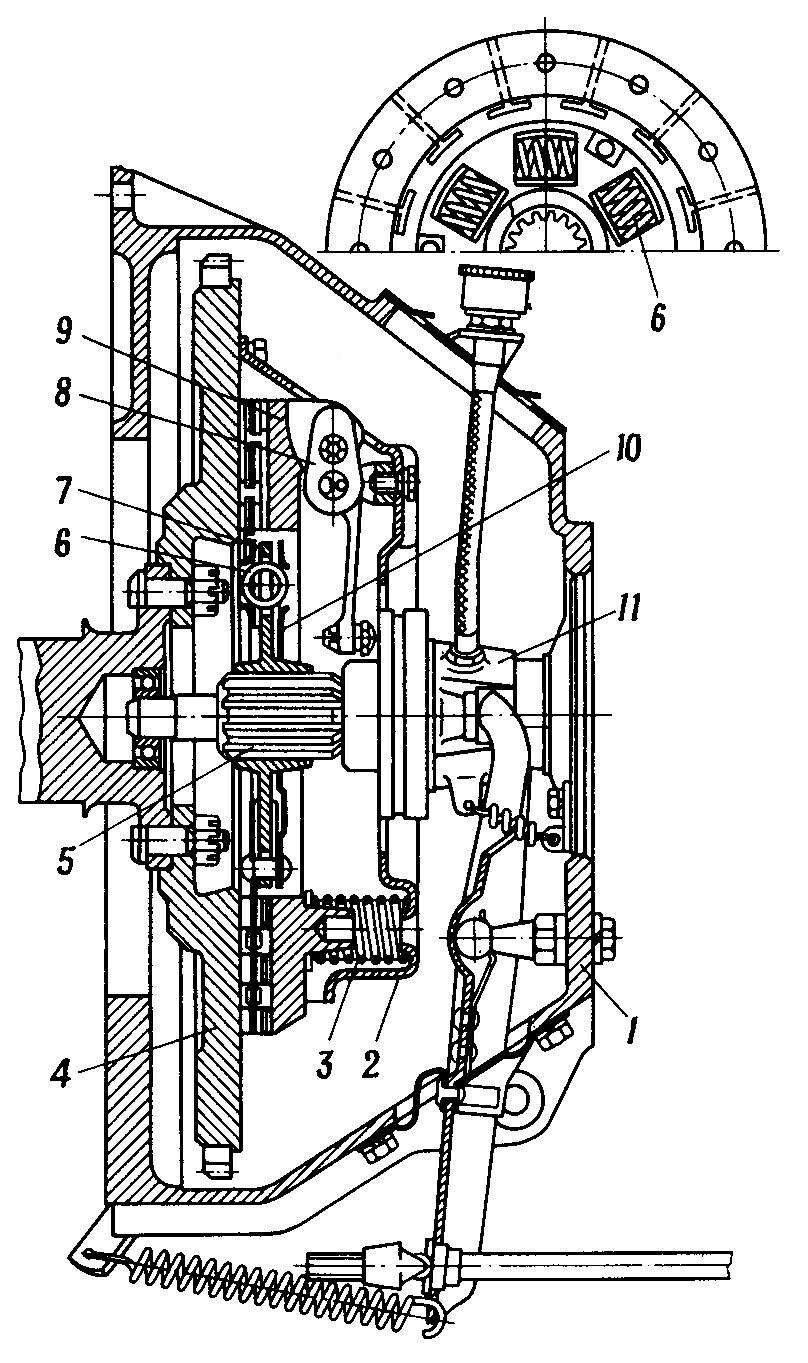
| Đĩa ma sát và đĩa ép bị mòn nhiều, lò xo ép bị gãy hoặc yếu.Đĩa ma sát bị dính dầu hoặc bị chai cứng.Bàn đạp ly hợp không có hành trình tự do, thể hiện xe kéo tải kém, ly hợp bị nóng.Hình10.2. Ly hợp một đĩa GAZ-53A1-vỏ bao bánh đà, 2-vỏ bộ ly hợp, 3-lò xo bên ngoài, 4-bánh đà, 5-trục dẫn động hợp số, 6-lò xo chống rung, 7-đĩa bị dẫn, 8-cần ngắt ly hợp, 9-đĩa ép, 10-đĩa chống rung có bộ phận hắt dầu, 11-khớp ngắt ly hợp |
 |
|
|
|
| Hình 10.3 Sơ đồ li hợp dẫn động cơ khí | Hình 10.4. Sơ đồ li hợp dẫn động thuỷ lực |
Các phương pháp xác định trạng thái trượt:
a.1. Gài số cao, đóng ly hợp
Chọn một đoạn đường bằng, cho xe đứng yên tại chỗ, nổ máy, gài số tiến ở số cao nhất (số 4 hay số 5), đạp và giữ phanh chân, cho động cơ hoạt động ở chế độ tải lớn bằng tay ga, từ từ nhả bàn đạp ly hợp. Nếu động cơ bị chết máy chứng tỏ ly hợp làm việc tốt, nếu động cơ không tắt máy chứng tỏ ly hợp đã trượt lớn.
a.2. Giữ trên dốc
Chọn đoạn đường phẳng và tốt có độ dốc (8-10) độ. Xe đứng bằng phanh trên mặt dốc, đầu xe theo chiều xuống dốc, tắt động cơ, tay số để ở số thấp nhất, từ từ nhả bàn đạp phanh, bánh xe không bị lăn xuống dốc chứng tỏ ly hợp tốt, còn nếu bánh xe lăn chứng tỏ ly hợp trượt.
a.3. Đẩy xe
Chọn một đoạn đường bằng, cho xe đứng yên tại chỗ, không nổ máy, gài số tiến ở số thấp nhất (số 1), đẩy xe. Xe không chuyển động chứng tỏ ly hợp tốt, nếu xe chuyển động chứng tỏ ly hợp bị trượt. Phương pháp này chỉ dùng cho ô tô con, với lực đẩy của 3 đến 4 người.
a.4. Xác định ly hợp bị trượt qua mùi khét
Xác định ly hợp bị trượt qua mùi khét đặc trưng khi ô tô thường xuyên làm việc ở chế độ đầy tải. Cảm nhận mùi khét chỉ khi ly hợp bị trượt nhiều, tức là ly hợp đã cần tiến hành thay đĩa bị động hay các thông số điều chỉnh đã bị thay đổi.
b. Ly hợp ngắt không hoàn toàn: biểu hiện sang số khó, gây va đập ở hộp số.
Hành trình tự do bàn đạp ly hợp quá lớn.
Các đầu đòn mở không nằm trong cùng mặt phẳng do đĩa ma sát và đĩa ép bị vênh. Do khe hở đầu đòn mở lớn quá không mở được đĩa ép làm cho đĩa ép bị vênh.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Giáo trình chẩn đoán kỹ thuật ô tô' conversation and receive update notifications?