| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Kerry, a 40-year-old airline pilot, has made an appointment with her primary care physician to discuss a rash that develops whenever she spends time in the sun. As she explains to her physician, it does not seem like sunburn. She is careful not to spend too much time in the sun and she uses sunscreen. Despite these precautions, the rash still appears, manifesting as red, raised patches that get slightly scaly. The rash persists for 7 to 10 days each time, and it seems to largely go away on its own. Lately, the rashes have also begun to appear on her cheeks and above her eyes on either side of her forehead.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box.
In Adaptive Specific Host Defenses , we discussed the mechanisms by which adaptive immune defenses, both humoral and cellular, protect us from infectious diseases. However, these same protective immune defenses can also be responsible for undesirable reactions called hypersensitivity reactions. Hypersensitivity reactions are classified by their immune mechanism.
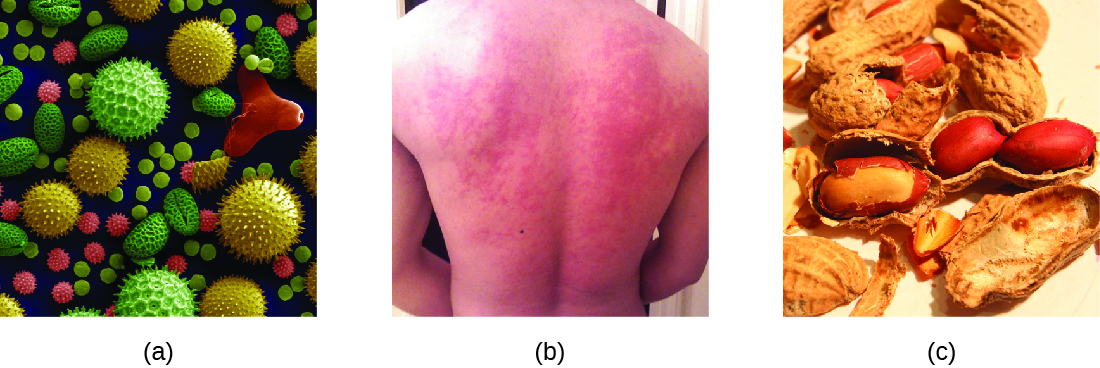
When a presensitized individual is exposed to an allergen , it can lead to a rapid immune response that occurs almost immediately. Such a response is called an allergy and is classified as a type I hypersensitivity . Allergens may be seemingly harmless substances such as animal dander, molds, or pollen. Allergens may also be substances considered innately more hazardous, such as insect venom or therapeutic drugs. Food intolerances can also yield allergic reactions as individuals become sensitized to foods such as peanuts or shellfish ( [link] ). Regardless of the allergen, the first exposure activates a primary IgE antibody response that sensitizes an individual to type I hypersensitivity reaction upon subsequent exposure.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?