| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
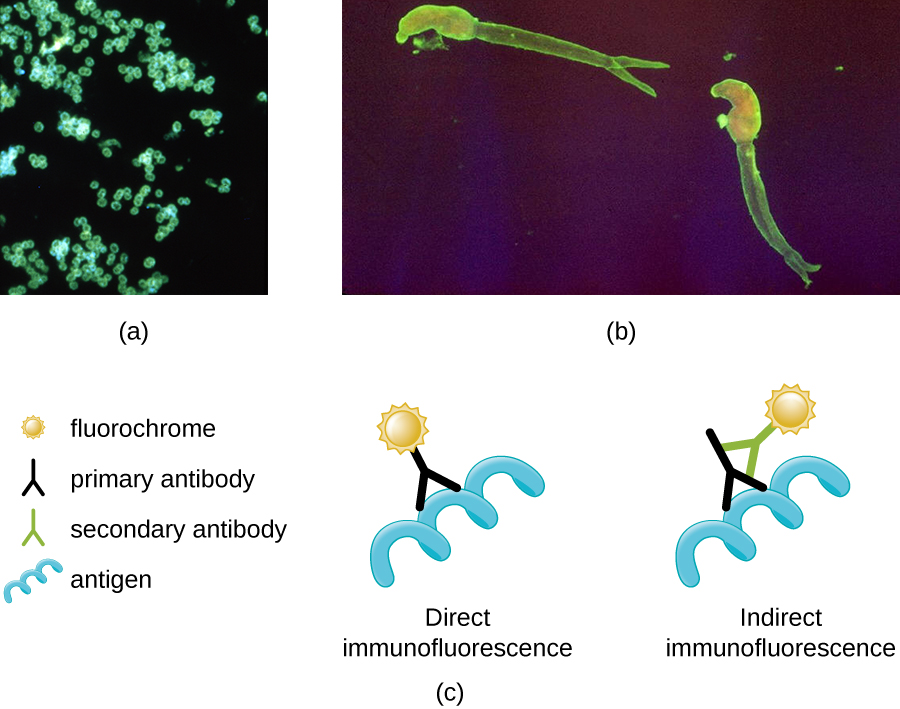
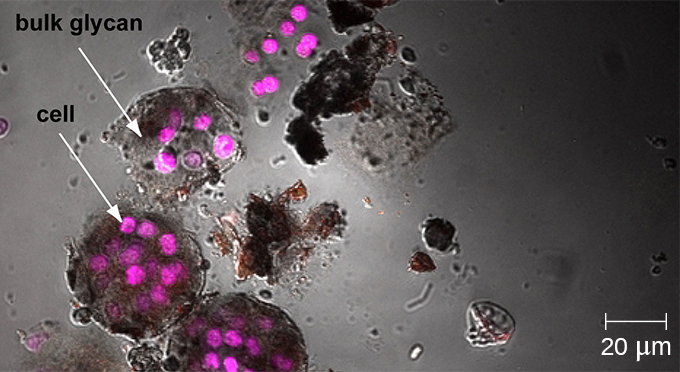
Whereas other forms of light microscopy create an image that is maximally focused at a single distance from the observer (the depth, or z-plane), a confocal microscope uses a laser to scan multiple z-planes successively. This produces numerous two-dimensional, high-resolution images at various depths, which can be constructed into a three-dimensional image by a computer. As with fluorescence microscopes, fluorescent stains are generally used to increase contrast and resolution. Image clarity is further enhanced by a narrow aperture that eliminates any light that is not from the z-plane. Confocal microscopes are thus very useful for examining thick specimens such as biofilms, which can be examined alive and unfixed ( [link] ).

Explore a rotating three-dimensional view of a biofilm as observed under a confocal microscope. After navigating to the webpage, click the “play” button to launch the video.
While the original fluorescent and confocal microscopes allowed better visualization of unique features in specimens, there were still problems that prevented optimum visualization. The effective sensitivity of fluorescence microscopy when viewing thick specimens was generally limited by out-of-focus flare, which resulted in poor resolution. This limitation was greatly reduced in the confocal microscope through the use of a confocal pinhole to reject out-of-focus background fluorescence with thin (<1 μm), unblurred optical sections. However, even the confocal microscopes lacked the resolution needed for viewing thick tissue samples. These problems were resolved with the development of the two-photon microscope , which uses a scanning technique, fluorochromes, and long-wavelength light (such as infrared) to visualize specimens. The low energy associated with the long-wavelength light means that two photons must strike a location at the same time to excite the fluorochrome. The low energy of the excitation light is less damaging to cells, and the long wavelength of the excitation light more easily penetrates deep into thick specimens. This makes the two-photon microscope useful for examining living cells within intact tissues—brain slices, embryos, whole organs, and even entire animals.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?