| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
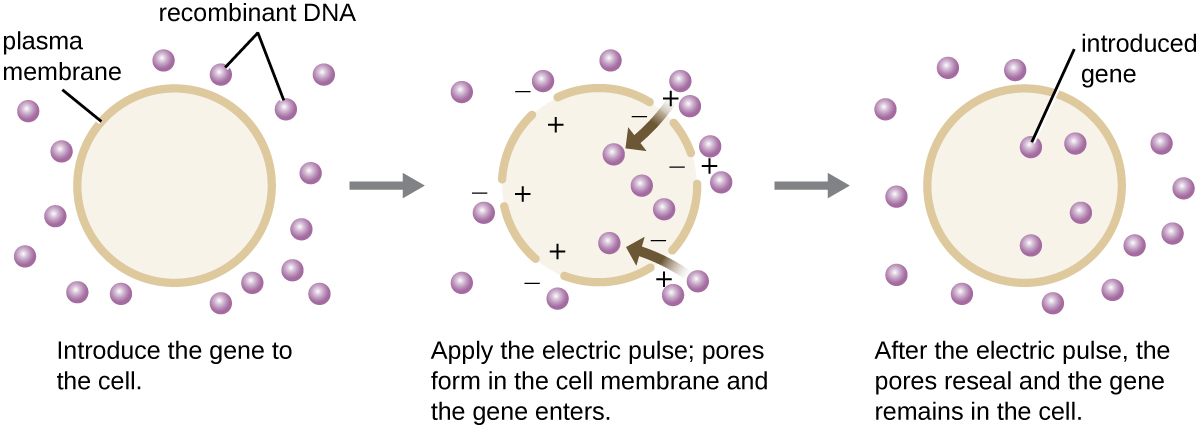
Compared to bacterial cells, eukaryotic cells tend to be less amenable as hosts for recombinant DNA molecules. Because eukaryotes are typically neither competent to take up foreign DNA nor able to maintain plasmids, transfection of eukaryotic hosts is far more challenging and requires more intrusive techniques for success. One method used for transfecting cells in cell culture is called electroporation . A brief electric pulse induces the formation of transient pores in the phospholipid bilayers of cells through which the gene can be introduced. At the same time, the electric pulse generates a short-lived positive charge on one side of the cell’s interior and a negative charge on the opposite side; the charge difference draws negatively charged DNA molecules into the cell ( [link] ).
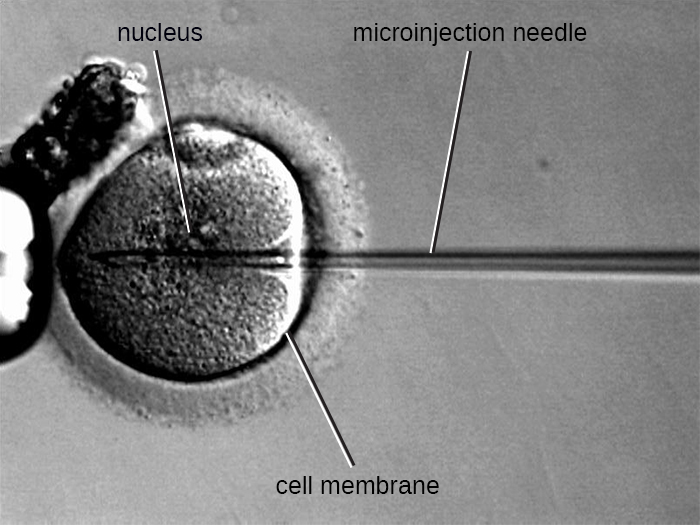
An alternative method of transfection is called microinjection . Because eukaryotic cells are typically larger than those of prokaryotes, DNA fragments can sometimes be directly injected into the cytoplasm using a glass micropipette, as shown in [link] .
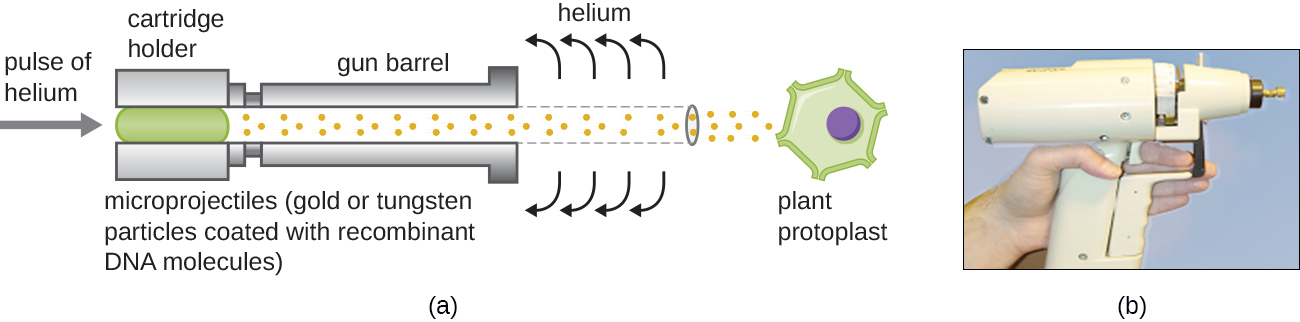
Transfecting plant cells can be even more difficult than animal cells because of their thick cell walls. One approach involves treating plant cells with enzymes to remove their cell walls, producing protoplasts. Then, a gene gun is used to shoot gold or tungsten particles coated with recombinant DNA molecules into the plant protoplasts at high speeds. Recipient protoplast cells can then recover and be used to generate new transgenic plants ( [link] ).
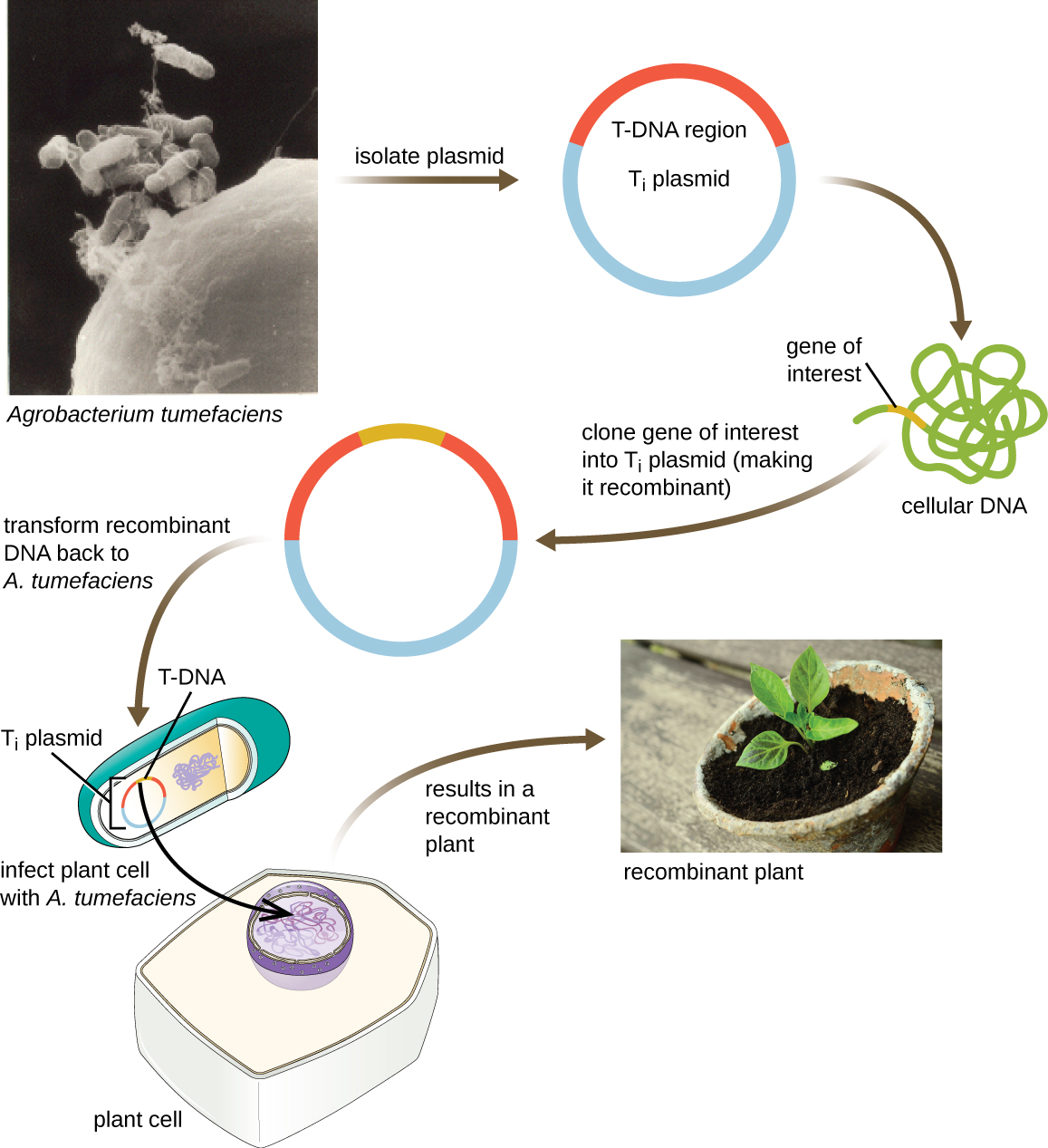
Another method of transfecting plants involves shuttle vectors , plasmids that can move between bacterial and eukaryotic cells. The tumor-inducing (T i ) plasmids originating from the bacterium Agrobacterium tumefaciens are commonly used as shuttle vectors for incorporating genes into plants ( [link] ). In nature, the T i plasmids of A. tumefaciens cause plants to develop tumors when they are transferred from bacterial cells to plant cells. Researchers have been able to manipulate these naturally occurring plasmids to remove their tumor-causing genes and insert desirable DNA fragments. The resulting recombinant T i plasmids can be transferred into the plant genome through the natural transfer of T i plasmids from the bacterium to the plant host. Once inside the plant host cell, the gene of interest recombines into the plant cell’s genome.
Viral vectors can also be used to transfect eukaryotic cells. In fact, this method is often used in gene therapy (see Gene Therapy ) to introduce healthy genes into human patients suffering from diseases that result from genetic mutations. Viral genes can be deleted and replaced with the gene to be delivered to the patient; William S.M. Wold and Karoly Toth. “Adenovirus Vectors for Gene Therapy, Vaccination and Cancer Gene Therapy.” Current Gene Therapy 13 no. 6 (2013): 421. the virus then infects the host cell and delivers the foreign DNA into the genome of the targeted cell. Adenoviruses are often used for this purpose because they can be grown to high titer and can infect both nondividing and dividing host cells. However, use of viral vectors for gene therapy can pose some risks for patients, as discussed in Gene Therapy .
Recombination is a process not usually observed in nature.
false
It is generally easier to introduce recombinant DNA into prokaryotic cells than into eukaryotic cells.
true
The process of introducing DNA molecules into eukaryotic cells is called ________.
transfection
Name three elements incorporated into a plasmid vector for efficient cloning.
When would a scientist want to generate a cDNA library instead of a genomic library?
What is one advantage of generating a genomic library using phages instead of plasmids?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?