| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Despite the discovery of DNA in the late 1800s, scientists did not make the association with heredity for many more decades. To make this connection, scientists, including a number of microbiologists, performed many experiments on plants, animals, and bacteria.
While Miescher was isolating and discovering DNA in the 1860s, Austrian monk and botanist Johann Gregor Mendel (1822–1884) was experimenting with garden peas, demonstrating and documenting basic patterns of inheritance, now known as Mendel’s laws.
In 1856, Mendel began his decade-long research into inheritance patterns. He used the diploid garden pea, Pisum sativum , as his primary model system because it naturally self-fertilizes and is highly inbred, producing “true-breeding” pea plant lines—plants that always produce offspring that look like the parent. By experimenting with true-breeding pea plants, Mendel avoided the appearance of unexpected traits in offspring that might occur if he used plants that were not true-breeding. Mendel performed hybridizations, which involve mating two true-breeding individuals (P generation) that have different traits, and examined the characteristics of their offspring (first filial generation, F 1 ) as well as the offspring of self-fertilization of the F 1 generation (second filial generation, F 2 ) ( [link] ).
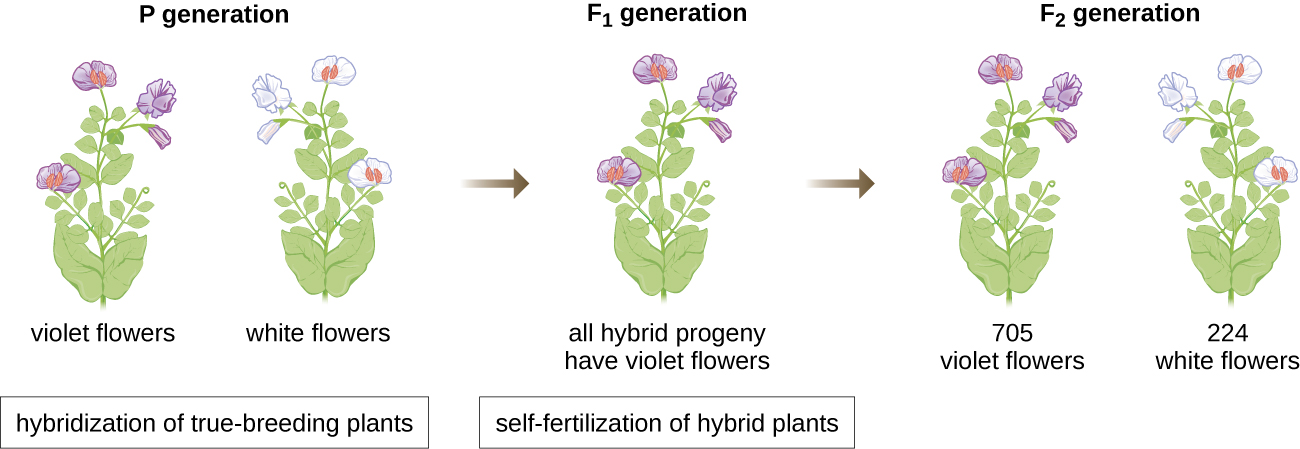
In 1865, Mendel presented the results of his experiments with nearly 30,000 pea plants to the local natural history society. He demonstrated that traits are transmitted faithfully from parents to offspring independently of other traits. In 1866, he published his work, “Experiments in Plant Hybridization,” J.G. Mendel. “Versuche über Pflanzenhybriden.” Verhandlungen des naturforschenden Vereines in Brünn, Bd. Abhandlungen 4 (1865):3–7. (For English translation, see http://www.mendelweb.org/Mendel.plain.html) in the Proceedings of the Natural History Society of Brünn . Mendel’s work went virtually unnoticed by the scientific community, which believed, incorrectly, in the theory of blending of traits in continuous variation.
He was not recognized for his extraordinary scientific contributions during his lifetime. In fact, it was not until 1900 that his work was rediscovered, reproduced, and revitalized by scientists on the brink of discovering the chromosomal basis of heredity.
Mendel carried out his experiments long before chromosomes were visualized under a microscope. However, with the improvement of microscopic techniques during the late 1800s, cell biologists could stain and visualize subcellular structures with dyes and observe their actions during meiosis . They were able to observe chromosomes replicating, condensing from an amorphous nuclear mass into distinct X-shaped bodies and migrating to separate cellular poles. The speculation that chromosomes might be the key to understanding heredity led several scientists to examine Mendel’s publications and re-evaluate his model in terms of the behavior of chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?