| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |

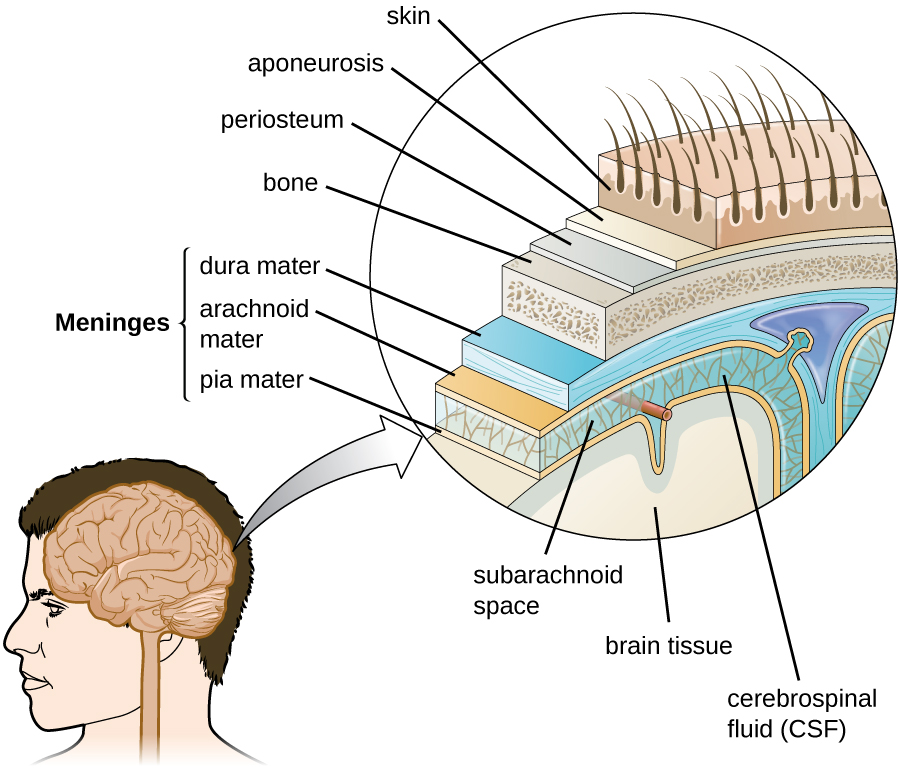
The tissues of the CNS have extra protection in that they are not exposed to blood or the immune system in the same way as other tissues. The blood vessels that supply the brain with nutrients and other chemical substances lie on top of the pia mater. The capillaries associated with these blood vessels in the brain are less permeable than those in other locations in the body. The capillary endothelial cells form tight junctions that control the transfer of blood components to the brain. In addition, cranial capillaries have far fewer fenestra (pore-like structures that are sealed by a membrane) and pinocytotic vesicles than other capillaries. As a result, materials in the circulatory system have a very limited ability to interact with the CNS directly. This phenomenon is referred to as the blood-brain barrier .
The blood-brain barrier protects the cerebrospinal fluid from contamination, and can be quite effective at excluding potential microbial pathogens. As a consequence of these defenses, there is no normal microbiota in the cerebrospinal fluid. The blood-brain barrier also inhibits the movement of many drugs into the brain, particularly compounds that are not lipid soluble. This has profound ramifications for treatments involving infections of the CNS, because it is difficult for drugs to cross the blood-brain barrier to interact with pathogens that cause infections.
The spinal cord also has protective structures similar to those surrounding the brain. Within the bones of the vertebrae are meninges of dura mater (sometimes called the dural sheath ), arachnoid mater, pia mater, and a blood-spinal cord barrier that controls the transfer of blood components from blood vessels associated with the spinal cord.
To cause an infection in the CNS, pathogens must successfully breach the blood-brain barrier or blood-spinal cord barrier. Various pathogens employ different virulence factors and mechanisms to achieve this, but they can generally be grouped into four categories: intercellular (also called paracellular), transcellular, leukocyte facilitated, and nonhematogenous. Intercellular entry involves the use of microbial virulence factors, toxins, or inflammation-mediated processes to pass between the cells of the blood-brain barrier. In transcellular entry, the pathogen passes through the cells of the blood-brain barrier using virulence factors that allow it to adhere to and trigger uptake by vacuole- or receptor-mediated mechanisms. Leukocyte-facilitated entry is a Trojan-horse mechanism that occurs when a pathogen infects peripheral blood leukocytes to directly enter the CNS. Nonhematogenous entry allows pathogens to enter the brain without encountering the blood-brain barrier; it occurs when pathogens travel along either the olfactory or trigeminal cranial nerves that lead directly into the CNS.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?