| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
To learn more about the nitrogen cycle, visit the PBS website.
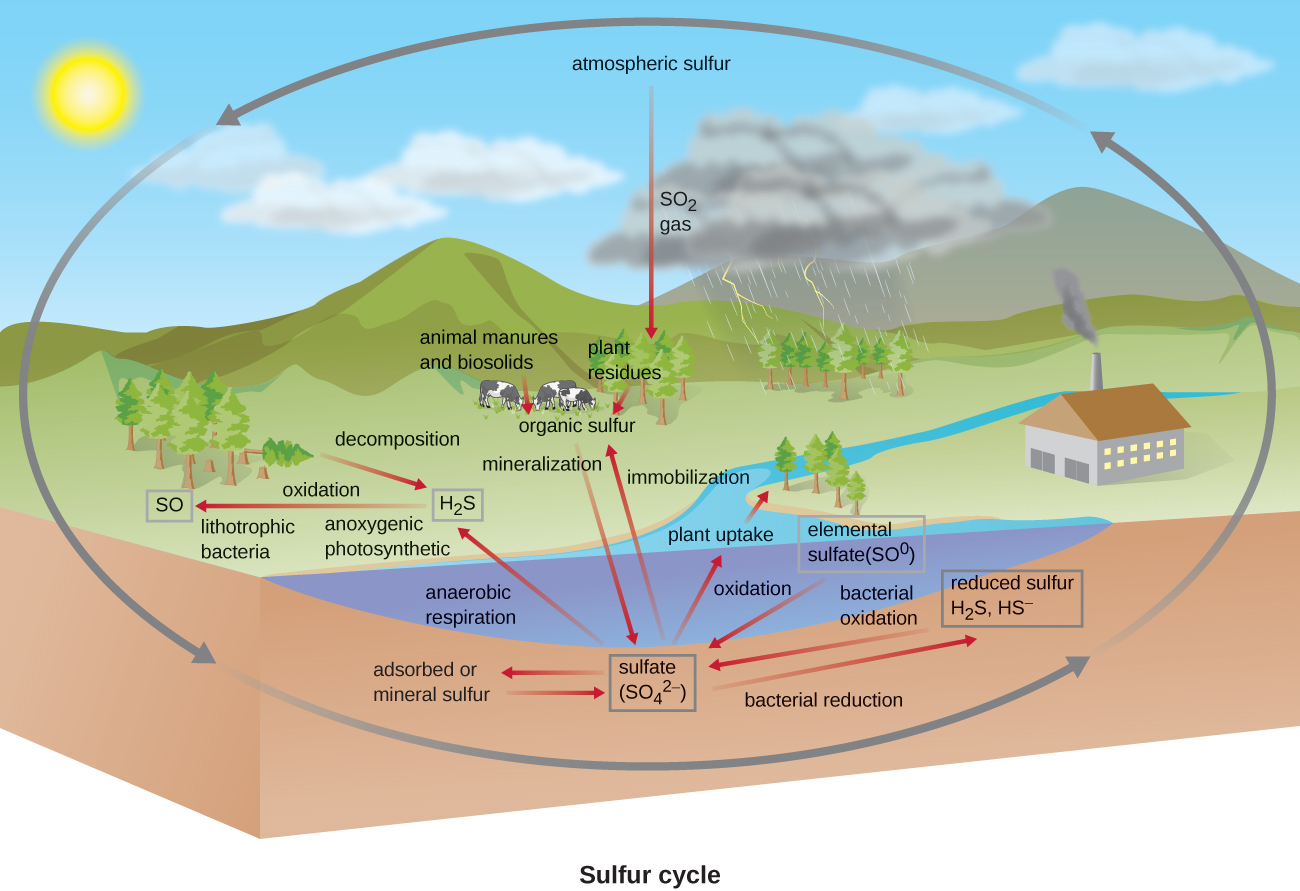
Sulfur is an essential element for the macromolecules of living organisms. As part of the amino acids cysteine and methionine, it is involved in the formation of proteins. It is also found in several vitamins necessary for the synthesis of important biological molecules like coenzyme A . Several groups of microbes are responsible for carrying out processes involved in the sulfur cycle ( [link] ). Anoxygenic photosynthetic bacteria as well as chemoautotrophic archaea and bacteria use hydrogen sulfide as an electron donor , oxidizing it first to elemental sulfur (S 0 ), then to sulfate This leads to stratification of hydrogen sulfide in soil, with levels increasing at deeper, more anaerobic depths.
Many bacteria and plants can use sulfate as a sulfur source. Decomposition dead organisms by fungi and bacteria remove sulfur groups from amino acids, producing hydrogen sulfide, returning inorganic sulfur to the environment.
Beyond their involvement in the carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycles, prokaryotes are involved in other biogeochemical cycles as well. Like the carbon, nitrogen, and sulfur cycles, several of these additional biogeochemical cycles, such as the iron (Fe), manganese (Mn), and chromium (Cr) cycles, also involve redox chemistry, with prokaryotes playing roles in both oxidation and reduction. Several other elements undergo chemical cycles that do not involve redox chemistry. Examples of these are phosphorus (P), calcium (Ca), and silica (Si) cycles. The cycling of these elements is particularly important in oceans because large quantities of these elements are incorporated into the exoskeletons of marine organisms. These biogeochemical cycle s do not involve redox chemistry but instead involve fluctuations in the solubility of compounds containing calcium, phosphorous, and silica. The overgrowth of naturally occurring microbial communities is typically limited by the availability of nitrogen (as previously mentioned), phosphorus, and iron. Human activities introducing excessive amounts of iron, nitrogen, or phosphorus (typically from detergents) may lead to eutrophication .
Microbial bioremediation leverages microbial metabolism to remove xenobiotic s or other pollutants. Xenobiotics are compounds synthesized by humans and introduced into the environment in much higher concentrations than would naturally occur. Such environmental contamination may involve adhesives, dyes, flame retardants, lubricants, oil and petroleum products, organic solvents, pesticides, and products of the combustion of gasoline and oil. Many xenobiotics resist breakdown, and some accumulate in the food chain after being consumed or absorbed by fish and wildlife, which, in turn, may be eaten by humans. Of particular concern are contaminants like polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) , a carcinogenic xenobiotic found in crude oil, and trichloroethylene (TCE) , a common groundwater contaminant.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?