| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
[link] summarizes the various types of antibody-antigen assays discussed in this section.
| Mechanisms of Select Antibody-Antigen Assays | ||
|---|---|---|
| Type of Assay | Mechanism | Examples |
| Precipitation | Antibody binds to soluble antigen, forming a visible precipitin | Precipitin ring test to visualize lattice formation in solution |
| Immunoelectrophoresis to examine distribution of antigens following electrophoresis | ||
| Ouchterlony assay to compare diverse antigens | ||
| Radial immunodiffusion assay to quantify antigens | ||
| Flocculation | Antibody binds to insoluble molecules in suspension, forming visible aggregates | VDRL test for syphilis |
| Neutralization | Antibody binds to virus, blocking viral entry into target cells and preventing formation of plaques | Plaque reduction assay for detecting presence of neutralizing antibodies in patient sera |
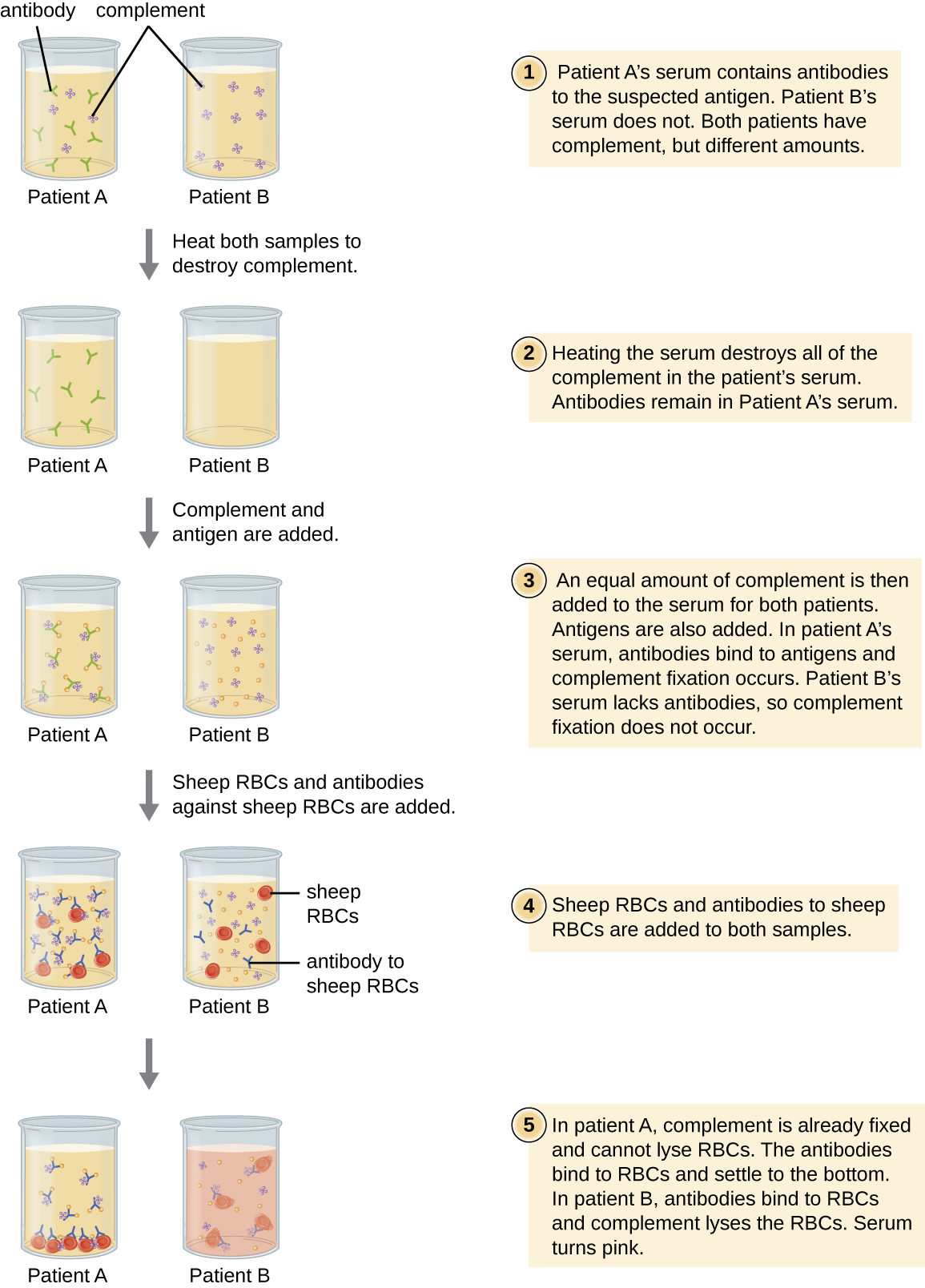
| Complement activation | Antibody binds to antigen, inducing complement activation and leaving no complement to lyse red blood cells | Complement fixation test for patient antibodies against hard-to-culture bacteria such as Chlamydia |
When slowly adding antigen to an antiserum, the amount of precipitin would gradually increase until reaching the ________; addition of more antigen after this point would actually decrease the amount of precipitin.
equivalence zone or zone of equivalence
The radial immunodiffusion test quantifies antigen by mixing ________ into a gel and then allowing antigen to diffuse out from a well cut in the gel.
antiserum
Explain why hemolysis in the complement fixation test is a negative test for infection.
What is meant by the term “neutralizing antibodies,” and how can we quantify this effect using the viral neutralization assay?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?