| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The watery material inside of the eyeball is called the vitreous humor . Unlike the conjunctiva, it is protected from contact with the environment and is almost always sterile, with no normal microbiota ( [link] ).
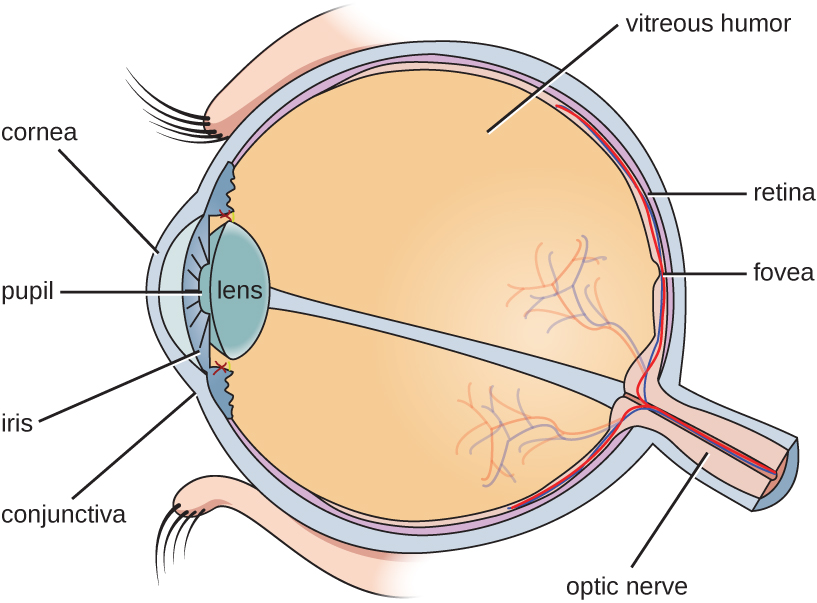
The conjunctiva is a frequent site of infection of the eye; like other mucous membranes, it is also a common portal of entry for pathogens. Inflammation of the conjunctiva is called conjunctivitis , although it is commonly known as pinkeye because of the pink appearance in the eye. Infections of deeper structures, beneath the cornea, are less common ( [link] ). Conjunctivitis occurs in multiple forms. It may be acute or chronic. Acute purulent conjunctivitis is associated with pus formation, while acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis is associated with bleeding in the conjunctiva. The term blepharitis refers to an inflammation of the eyelids, while keratitis refers to an inflammation of the cornea ( [link] ); keratoconjunctivitis is an inflammation of both the cornea and the conjunctiva, and dacryocystitis is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac that can often occur when a nasolacrimal duct is blocked.
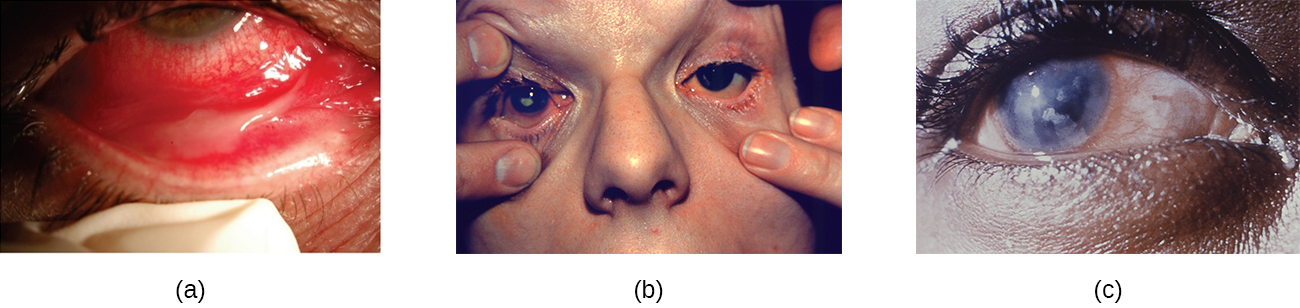
Infections leading to conjunctivitis, blepharitis, keratoconjunctivitis, or dacryocystitis may be caused by bacteria or viruses, but allergens, pollutants, or chemicals can also irritate the eye and cause inflammation of various structures. Viral infection is a more likely cause of conjunctivitis in cases with symptoms such as fever and watery discharge that occurs with upper respiratory infection and itchy eyes. [link] summarizes some common forms of conjunctivitis and blepharitis.
| Types of Conjunctivities and Blepharitis | ||
|---|---|---|
| Condition | Description | Causative Agent(s) |
| Acute purulent conjunctivitis | Conjunctivitis with purulent discharge | Bacterial ( Haemophilus , Staphylococcus ) |
| Acute hemorrhagic conjunctivitis | Involves subconjunctival hemorrhages | Viral ( Picornaviradae ) |
| Acute ulcerative blepharitis | Infection involving eyelids; pustules and ulcers may develop | Bacterial ( Staphylococcal ) or viral (herpes simplex, varicella-zoster, etc.) |
| Follicular conjunctivitis | Inflammation of the conjunctiva with nodules (dome-shaped structures that are red at the base and pale on top) | Viral ( adenovirus and others); environmental irritants |
| Dacryocystitis | Inflammation of the lacrimal sac often associated with a plugged nasolacrimal duct | Bacterial ( Haemophilus, Staphylococcus , Streptococcus ) |
| Keratitis | Inflammation of cornea | Bacterial, viral, or protozoal; environmental irritants |
| Keratoconjunctivitis | Inflammation of cornea and conjunctiva | Bacterial, viral (adenoviruses), or other causes (including dryness of the eye) |
| Nonulcerative blepharitis | Inflammation, irritation, redness of the eyelids without ulceration | Environmental irritants; allergens |
| Papillary conjunctivitis | Inflammation of the conjunctiva; nodules and papillae with red tops develop | Environmental irritants; allergens |
The ________ is the outermost layer of the epidermis.
stratum corneum
The mucous membrane that covers the surface of the eyeball and inner eyelid is called the ________.
conjunctiva
What is the role of keratin in the skin?
What are two ways in which tears help to prevent microbial colonization?
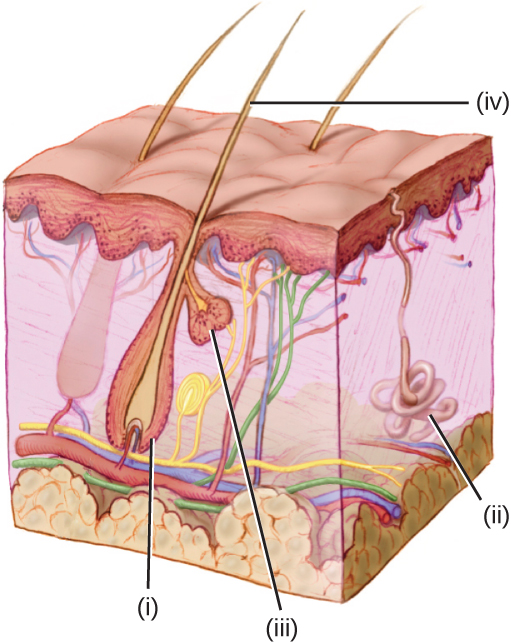
Which label indicates a sweat gland?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?