| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
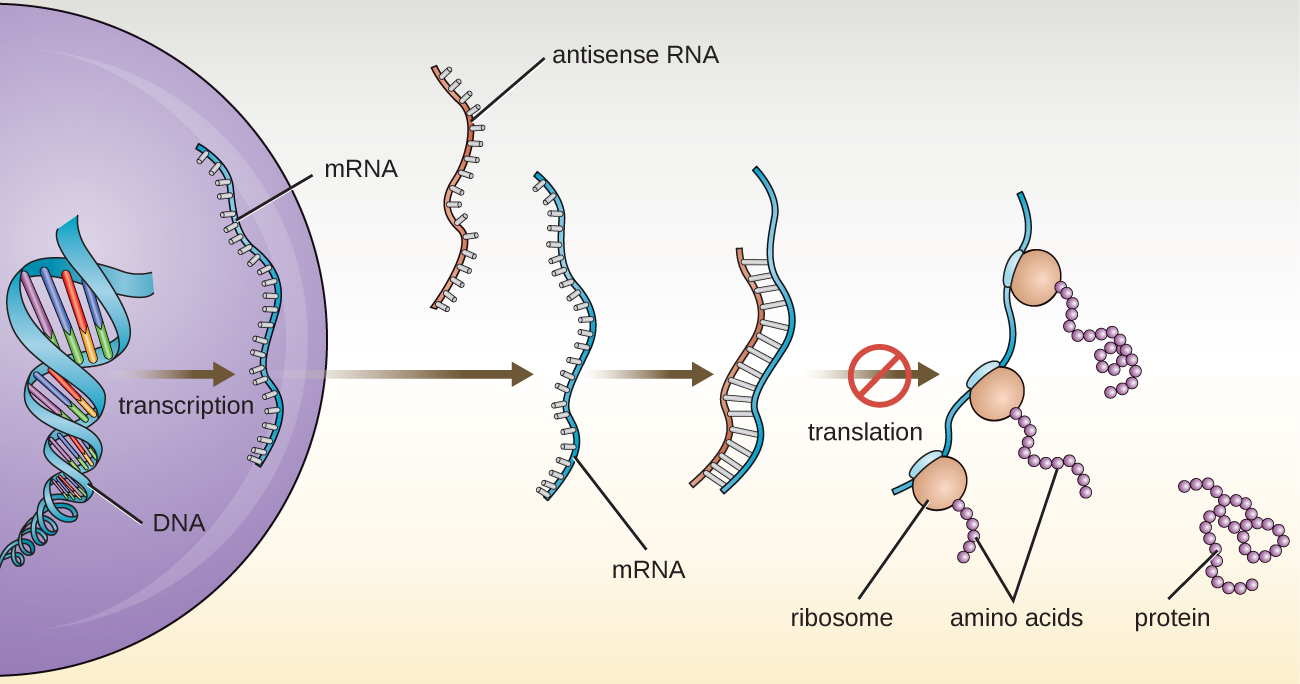
In Structure and Function of RNA , we described the function of mRNA, rRNA, and tRNA. In addition to these types of RNA, cells also produce several types of small noncoding RNA molecules that are involved in the regulation of gene expression. These include antisense RNA molecules, which are complementary to regions of specific mRNA molecules found in both prokaryotes and eukaryotic cells. Non-coding RNA molecules play a major role in RNA interference (RNAi) , a natural regulatory mechanism by which mRNA molecules are prevented from guiding the synthesis of proteins. RNA interference of specific genes results from the base pairing of short, single-stranded antisense RNA molecules to regions within complementary mRNA molecules, preventing protein synthesis. Cells use RNA interference to protect themselves from viral invasion, which may introduce double-stranded RNA molecules as part of the viral replication process ( [link] ).
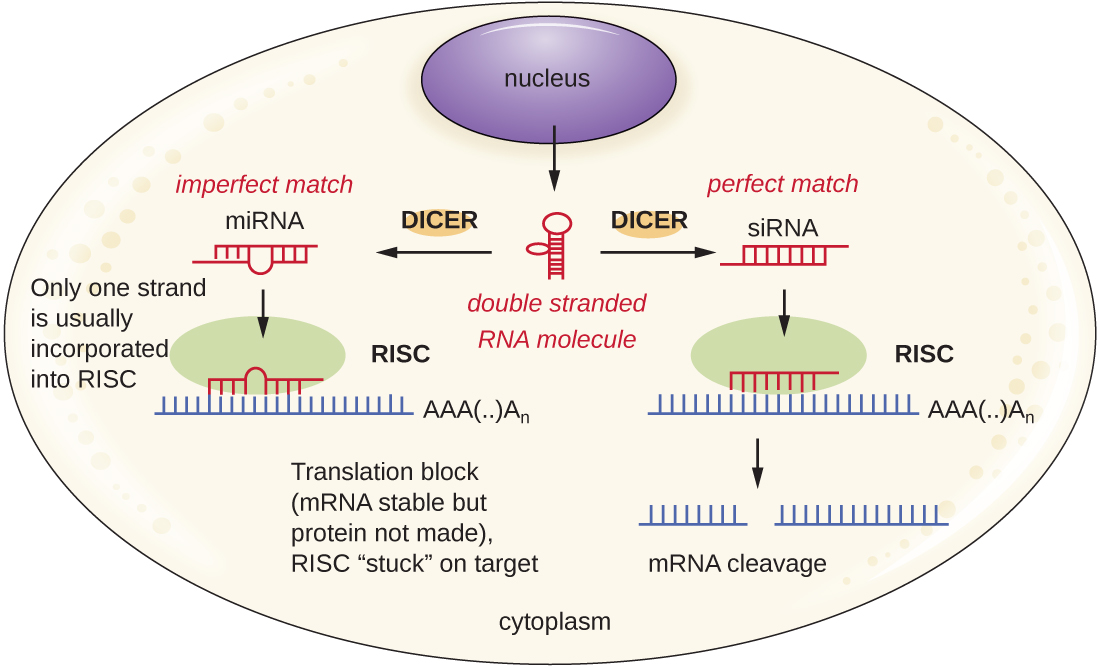
Researchers are currently developing techniques to mimic the natural process of RNA interference as a way to treat viral infections in eukaryotic cells. RNA interference technology involves using small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) or microRNAs (miRNAs) ( [link] ). siRNAs are completely complementary to the mRNA transcript of a specific gene of interest while miRNAs are mostly complementary. These double-stranded RNAs are bound to DICER, an endonuclease that cleaves the RNA into short molecules (approximately 20 nucleotides long). The RNAs are then bound to RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC), a ribonucleoprotein. The siRNA-RISC complex binds to mRNA and cleaves it. For miRNA, only one of the two strands binds to RISC. The miRNA-RISC complex then binds to mRNA, inhibiting translation. If the miRNA is completely complementary to the target gene, then the mRNA can be cleaved. Taken together, these mechanisms are known as gene silencing .
The application of genomics to evaluate the effectiveness and safety of drugs on the basis of information from an individual’s genomic sequence is called ____________.
pharmacogenomics or toxicogenomics
A gene whose expression can be easily visualized and monitored is called a ________.
reporter gene
RNA interference does not influence the sequence of genomic DNA.
true
If all cellular proteins are encoded by the cell’s genes, what information does proteomics provide that genomics cannot?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?