| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Many different types of erythrocyte antigen s have been discovered since the description of the ABO red cell antigens. The second most frequently described RBC antigens are Rh factor s, named after the rhesus macaque ( Macaca mulatta ) factors identified by Karl Landsteiner and Alexander Weiner in 1940. The Rh system of RBC antigens is the most complex and immunogenic blood group system, with more than 50 specificities identified to date. Of all the Rh antigens, the one designated Rho (Weiner) or D (Fisher-Race) is the most immunogenic. Cells are classified as Rh positive (Rh+) if the Rho/D antigen is present or as Rh negative (Rh−) if the Rho/D antigen is absent. In contrast to the carbohydrate molecules that distinguish the ABO blood groups and are the targets of IgM isohemagglutinins in HTRs, the Rh factor antigens are proteins. As discussed in B Lymphocytes and Humoral Immunity , protein antigens activate B cells and antibody production through a T-cell–dependent mechanism, and the T H 2 cells stimulate class switching from IgM to other antibody classes. In the case of Rh factor antigens, T H 2 cells stimulate class switching to IgG, and this has important implications for the mechanism of HDN.
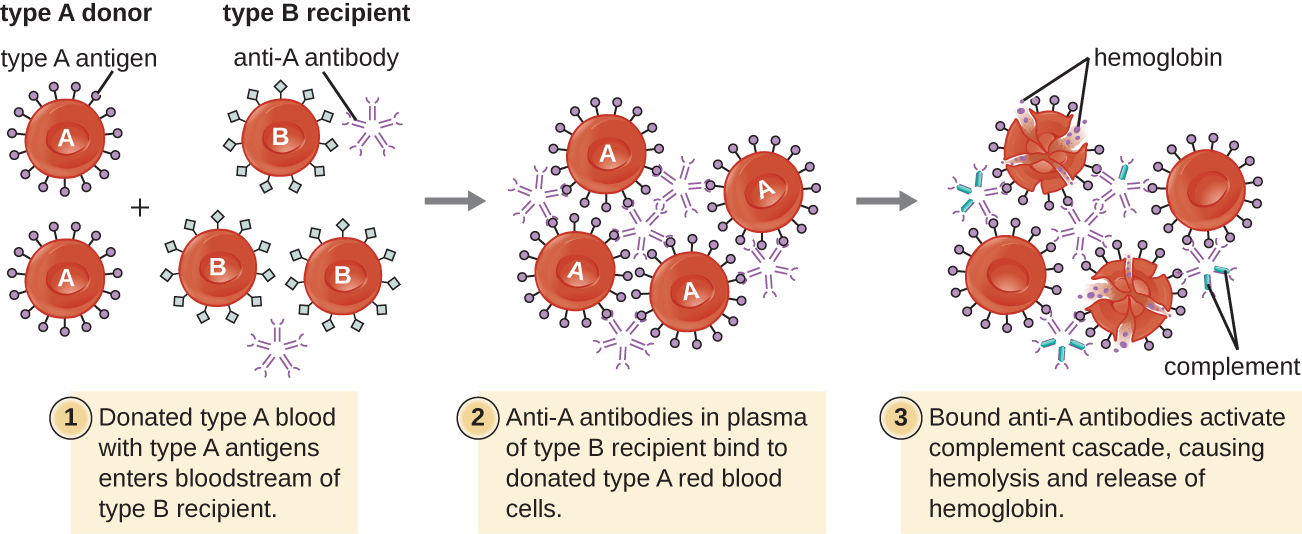
Like ABO incompatibilities, blood transfusion s from a donor with the wrong Rh factor antigens can cause a type II hypersensitivity HTR. However, in contrast to the IgM isohemagglutinins produced early in life through exposure to environmental antigens, production of anti-Rh factor antibodies requires the exposure of an individual with Rh− blood to Rh+ positive RBCs and activation of a primary antibody response. Although this primary antibody response can cause an HTR in the transfusion patient, the hemolytic reaction would be delayed up to 2 weeks during the extended lag period of a primary antibody response ( B Lymphocytes and Humoral Immunity ). However, if the patient receives a subsequent transfusion with Rh+ RBCs, a more rapid HTR would occur with anti-Rh factor antibody already present in the blood. Furthermore, the rapid secondary antibody response would provide even more anti-Rh factor antibodies for the HTR.
Rh factor incompatibility between mother and fetus can also cause a type II hypersensitivity hemolytic reaction, referred to as hemolytic disease of the newborn (HDN) ( [link] ). If an Rh− woman carries an Rh+ baby to term, the mother’s immune system can be exposed to Rh+ fetal red blood cells . This exposure will usually occur during the last trimester of pregnancy and during the delivery process. If this exposure occurs, the Rh+ fetal RBCs will activate a primary adaptive immune response in the mother, and anti-Rh factor IgG antibodies will be produced. IgG antibodies are the only class of antibody that can cross the placenta from mother to fetus; however, in most cases, the first Rh+ baby is unaffected by these antibodies because the first exposure typically occurs late enough in the pregnancy that the mother does not have time to mount a sufficient primary antibody response before the baby is born.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?