| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Each operon includes DNA sequences that influence its own transcription; these are located in a region called the regulatory region. The regulatory region includes the promoter and the region surrounding the promoter, to which transcription factors , proteins encoded by regulatory genes, can bind. Transcription factors influence the binding of RNA polymerase to the promoter and allow its progression to transcribe structural genes. A repressor is a transcription factor that suppresses transcription of a gene in response to an external stimulus by binding to a DNA sequence within the regulatory region called the operator , which is located between the RNA polymerase binding site of the promoter and the transcriptional start site of the first structural gene. Repressor binding physically blocks RNA polymerase from transcribing structural genes. Conversely, an activator is a transcription factor that increases the transcription of a gene in response to an external stimulus by facilitating RNA polymerase binding to the promoter. An inducer , a third type of regulatory molecule, is a small molecule that either activates or represses transcription by interacting with a repressor or an activator.
In prokaryotes, there are examples of operons whose gene products are required rather consistently and whose expression, therefore, is unregulated. Such operons are constitutively expressed , meaning they are transcribed and translated continuously to provide the cell with constant intermediate levels of the protein products. Such genes encode enzymes involved in housekeeping functions required for cellular maintenance, including DNA replication, repair, and expression, as well as enzymes involved in core metabolism. In contrast, there are other prokaryotic operons that are expressed only when needed and are regulated by repressors, activators, and inducers.
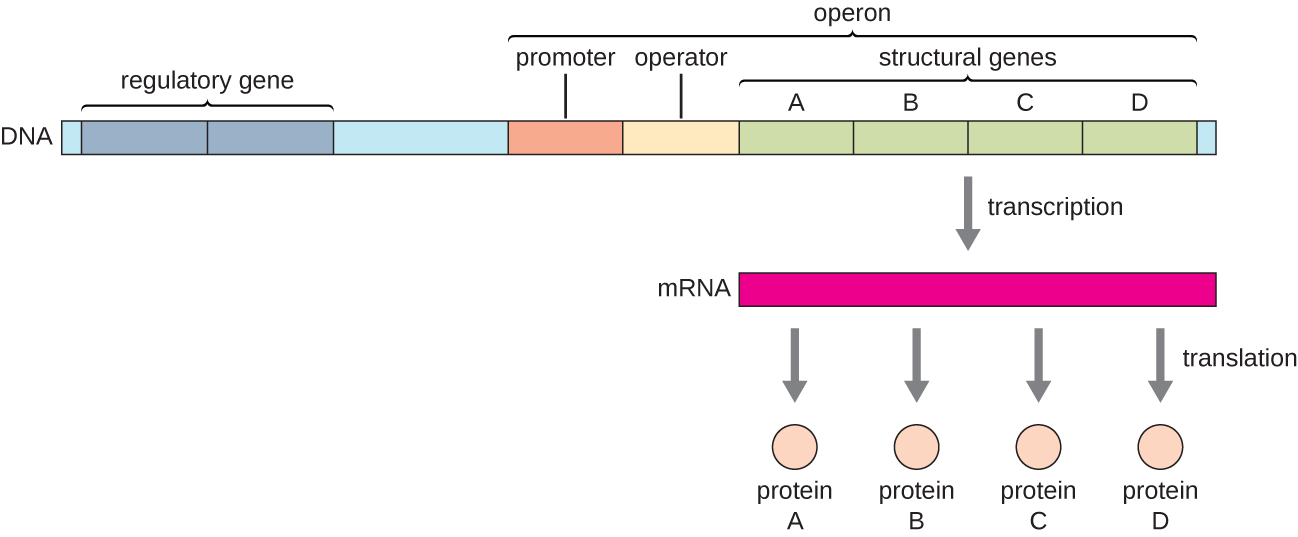
Prokaryotic operons are commonly controlled by the binding of repressors to operator regions, thereby preventing the transcription of the structural genes. Such operons are classified as either repressible operon s or inducible operons. Repressible operons, like the tryptophan ( trp ) operon, typically contain genes encoding enzymes required for a biosynthetic pathway. As long as the product of the pathway, like tryptophan, continues to be required by the cell, a repressible operon will continue to be expressed. However, when the product of the biosynthetic pathway begins to accumulate in the cell, removing the need for the cell to continue to make more, the expression of the operon is repressed. Conversely, inducible operon s , like the lac operon of E. coli , often contain genes encoding enzymes in a pathway involved in the metabolism of a specific substrate like lactose. These enzymes are only required when that substrate is available, thus expression of the operons is typically induced only in the presence of the substrate.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?