| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
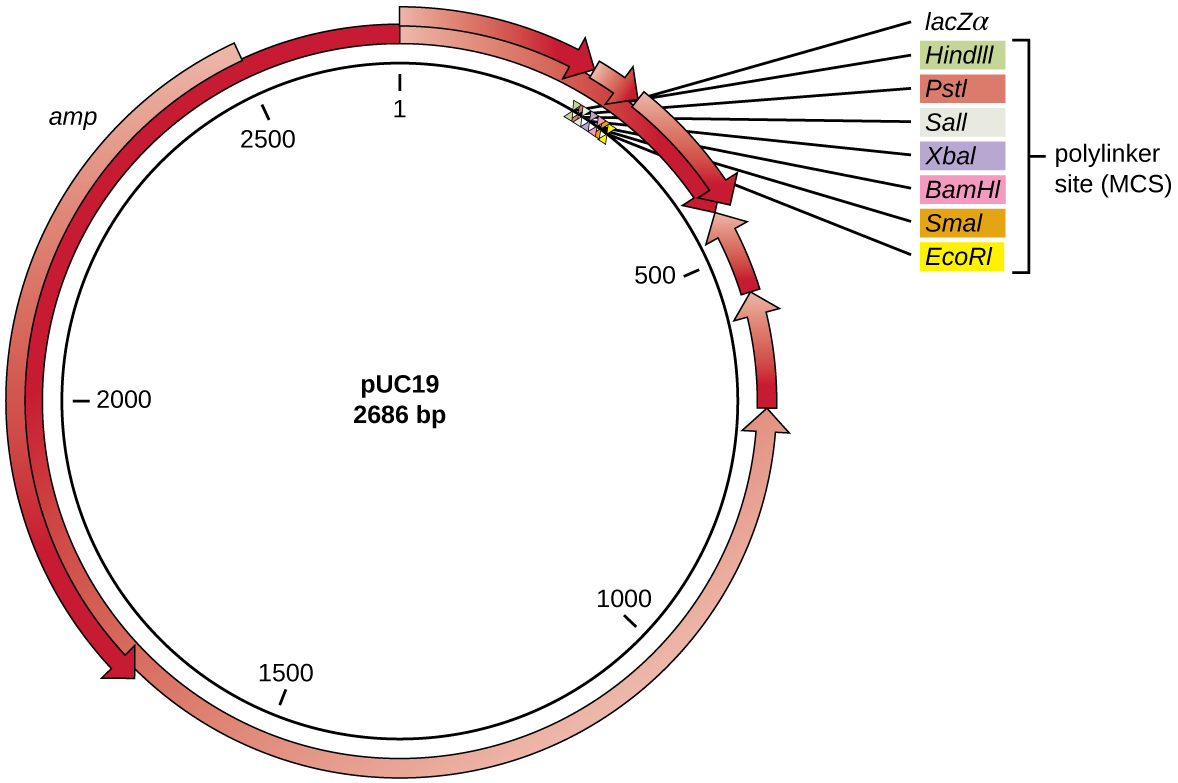
After restriction digestion, genes of interest are commonly inserted into plasmids , small pieces of typically circular, double-stranded DNA that replicate independently of the bacterial chromosome (see Unique Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells ). In recombinant DNA technology, plasmids are often used as vectors , DNA molecules that carry DNA fragments from one organism to another. Plasmids used as vectors can be genetically engineered by researchers and scientific supply companies to have specialized properties, as illustrated by the commonly used plasmid vector pUC19 ( [link] ). Some plasmid vectors contain genes that confer antibiotic resistance ; these resistance genes allow researchers to easily find plasmid-containing colonies by plating them on media containing the corresponding antibiotic. The antibiotic kills all host cells that do not harbor the desired plasmid vector, but those that contain the vector are able to survive and grow.
Plasmid vectors used for cloning typically have a polylinker site , or multiple cloning site (MCS) . A polylinker site is a short sequence containing multiple unique restriction enzyme recognition sites that are used for inserting DNA into the plasmid after restriction digestion of both the DNA and the plasmid. Having these multiple restriction enzyme recognition sites within the polylinker site makes the plasmid vector versatile, so it can be used for many different cloning experiments involving different restriction enzymes.
This polylinker site is often found within a reporter gene , another gene sequence artificially engineered into the plasmid that encodes a protein that allows for visualization of DNA insertion. The reporter gene allows a researcher to distinguish host cells that contain recombinant plasmids with cloned DNA fragments from host cells that only contain the non-recombinant plasmid vector. The most common reporter gene used in plasmid vectors is the bacterial lacZ gene encoding beta-galactosidase, an enzyme that naturally degrades lactose but can also degrade a colorless synthetic analog X-gal , thereby producing blue colonies on X-gal–containing media. The lacZ reporter gene is disabled when the recombinant DNA is spliced into the plasmid. Because the LacZ protein is not produced when the gene is disabled, X-gal is not degraded and white colonies are produced, which can then be isolated. This blue-white screening method is described later and shown in [link] . In addition to these features, some plasmids come pre-digested and with an enzyme linked to the linearized plasmid to aid in ligation after the insertion of foreign DNA fragments.
The most commonly used mechanism for introducing engineered plasmids into a bacterial cell is transformation , a process in which bacteria take up free DNA from their surroundings. In nature, free DNA typically comes from other lysed bacterial cells; in the laboratory, free DNA in the form of recombinant plasmids is introduced to the cell’s surroundings.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?