| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
In contrast to communicable infectious diseases, a noncommunicable infectious disease is not spread from one person to another. One example is tetanus , caused by Clostridium tetani , a bacterium that produces endospores that can survive in the soil for many years. This disease is typically only transmitted through contact with a skin wound; it cannot be passed from an infected person to another person. Similarly, Legionnaires disease is caused by Legionella pneumophila , a bacterium that lives within amoebae in moist locations like water-cooling towers. An individual may contract Legionnaires disease via contact with the contaminated water, but once infected, the individual cannot pass the pathogen to other individuals.
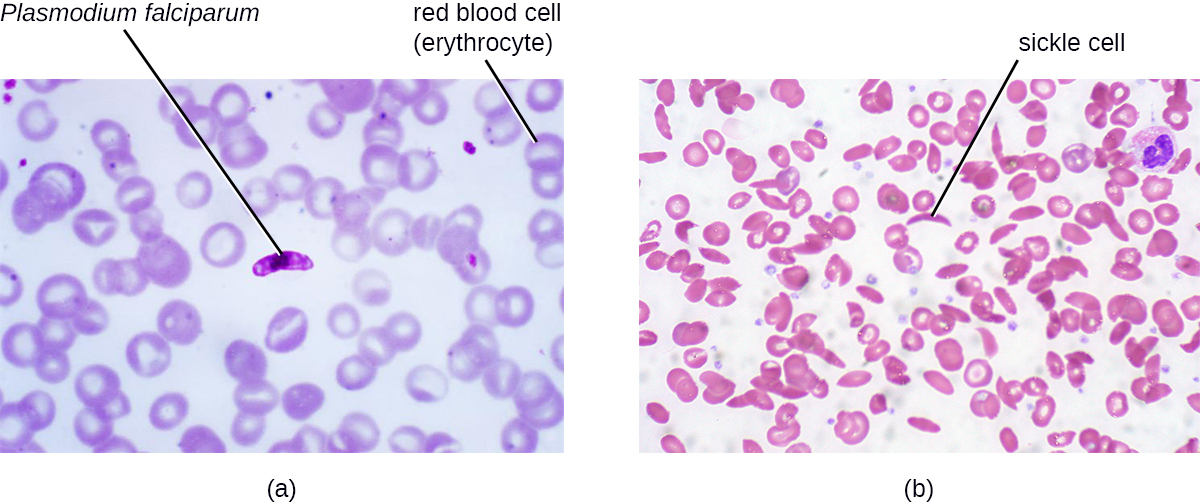
In addition to the wide variety of noncommunicable infectious diseases, noninfectious disease s (those not caused by pathogens) are an important cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Noninfectious diseases can be caused by a wide variety factors, including genetics, the environment, or immune system dysfunction, to name a few. For example, sickle cell anemia is an inherited disease caused by a genetic mutation that can be passed from parent to offspring ( [link] ). Other types of noninfectious diseases are listed in [link] .
| Types of Noninfectious Diseases | ||
|---|---|---|
| Type | Definition | Example |
| Inherited | A genetic disease | Sickle cell anemia |
| Congenital | Disease that is present at or before birth | Down syndrome |
| Degenerative | Progressive, irreversible loss of function | Parkinson disease (affecting central nervous system) |
| Nutritional deficiency | Impaired body function due to lack of nutrients | Scurvy (vitamin C deficiency) |
| Endocrine | Disease involving malfunction of glands that release hormones to regulate body functions | Hypothyroidism – thyroid does not produce enough thyroid hormone, which is important for metabolism |
| Neoplastic | Abnormal growth (benign or malignant) | Some forms of cancer |
| Idiopathic | Disease for which the cause is unknown | Idiopathic juxtafoveal retinal telangiectasia (dilated, twisted blood vessels in the retina of the eye) |

Lists of common infectious diseases can be found at the following Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), World Health Organization (WHO), and International Classification of Diseases websites.
The five periods of disease (sometimes referred to as stages or phases) include the incubation, prodromal, illness, decline, and convalescence periods ( [link] ). The incubation period occurs in an acute disease after the initial entry of the pathogen into the host (patient). It is during this time the pathogen begins multiplying in the host. However, there are insufficient numbers of pathogen particles (cells or viruses) present to cause signs and symptoms of disease. Incubation periods can vary from a day or two in acute disease to months or years in chronic disease, depending upon the pathogen. Factors involved in determining the length of the incubation period are diverse, and can include strength of the pathogen, strength of the host immune defenses, site of infection, type of infection, and the size infectious dose received. During this incubation period, the patient is unaware that a disease is beginning to develop.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?