| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
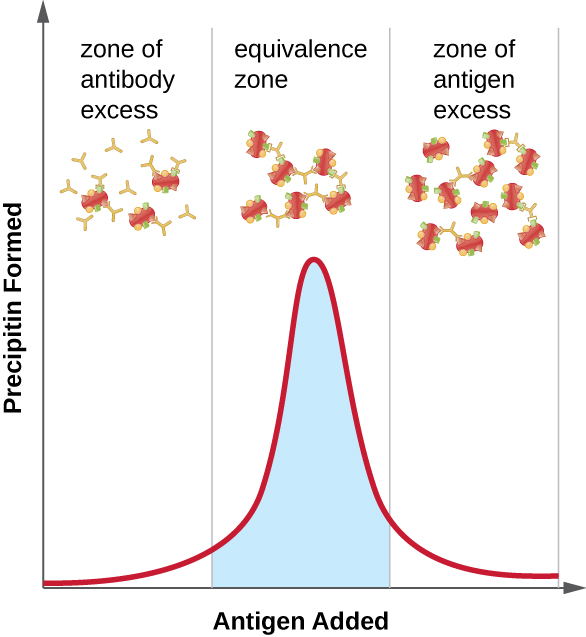
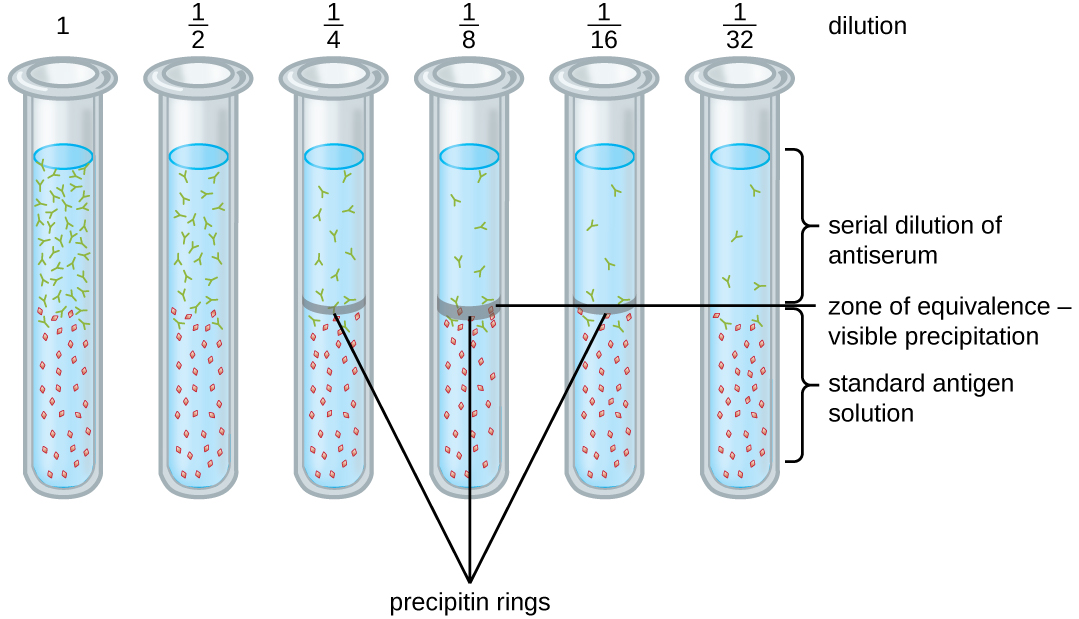
A variety of techniques allow us to use precipitin formation to quantify either antigen concentration or the amount of antibody present in an antiserum. One such technique is the precipitin ring test ( [link] ), which is used to determine the relative amount of antigen-specific antibody in a sample of serum. To perform this test, a set of test tubes is prepared by adding an antigen solution to the bottom of each tube. Each tube receives the same volume of solution, and the concentration of antigens is constant (e.g., 1 mg/mL). Next, glycerol is added to the antigen solution in each test tube, followed by a serial dilution of the antiserum. The glycerol prevents mixing of the antiserum with the antigen solution, allowing antigen-antibody binding to take place only at the interface of the two solutions. The result is a visible ring of precipitin in the tubes that have an antigen-antibody ratio within the equivalence zone. This highest dilution with a visible ring is used to determine the titer of the antibodies. The titer is the reciprocal of the highest dilution showing a positive result, expressed as a whole number. In [link] , the titer is 16.
While a measurement of titer does not tell us in absolute terms how much antibody is present, it does give a measure of biological activity, which is often more important than absolute amount. In this example, it would not be useful to know what mass of IgG were present in the antiserum, because there are many different specificities of antibody present; but it is important for us to know how much of the antibody activity in a patient’s serum is directed against the antigen of interest (e.g., a particular pathogen or allergen).
While the precipitin ring test provides insights into antibody-antigen interactions, it also has some drawbacks. It requires the use of large amounts of serum, and great care must be taken to avoid mixing the solutions and disrupting the ring. Performing a similar test in an agar gel matrix can minimize these problems. This type of assay is variously called double immunodiffusion or the Ouchterlony assay for Orjan Ouchterlony , Ouchterlony, Örjan, “In Vitro Method for Testing the Toxin-Producing Capacity of Diphtheria Bacteria,” Acta Pathologica Microbiologica Scandinavica 26, no. 4 (1949): 516-24. who first described the technique in 1948.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?