| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although most gene expression is regulated at the level of transcription initiation in prokaryotes, there are also mechanisms to control both the completion of transcription as well as translation concurrently. Since their discovery, these mechanisms have been shown to control the completion of transcription and translation of many prokaryotic operons. Because these mechanisms link the regulation of transcription and translation directly, they are specific to prokaryotes, because these processes are physically separated in eukaryotes.
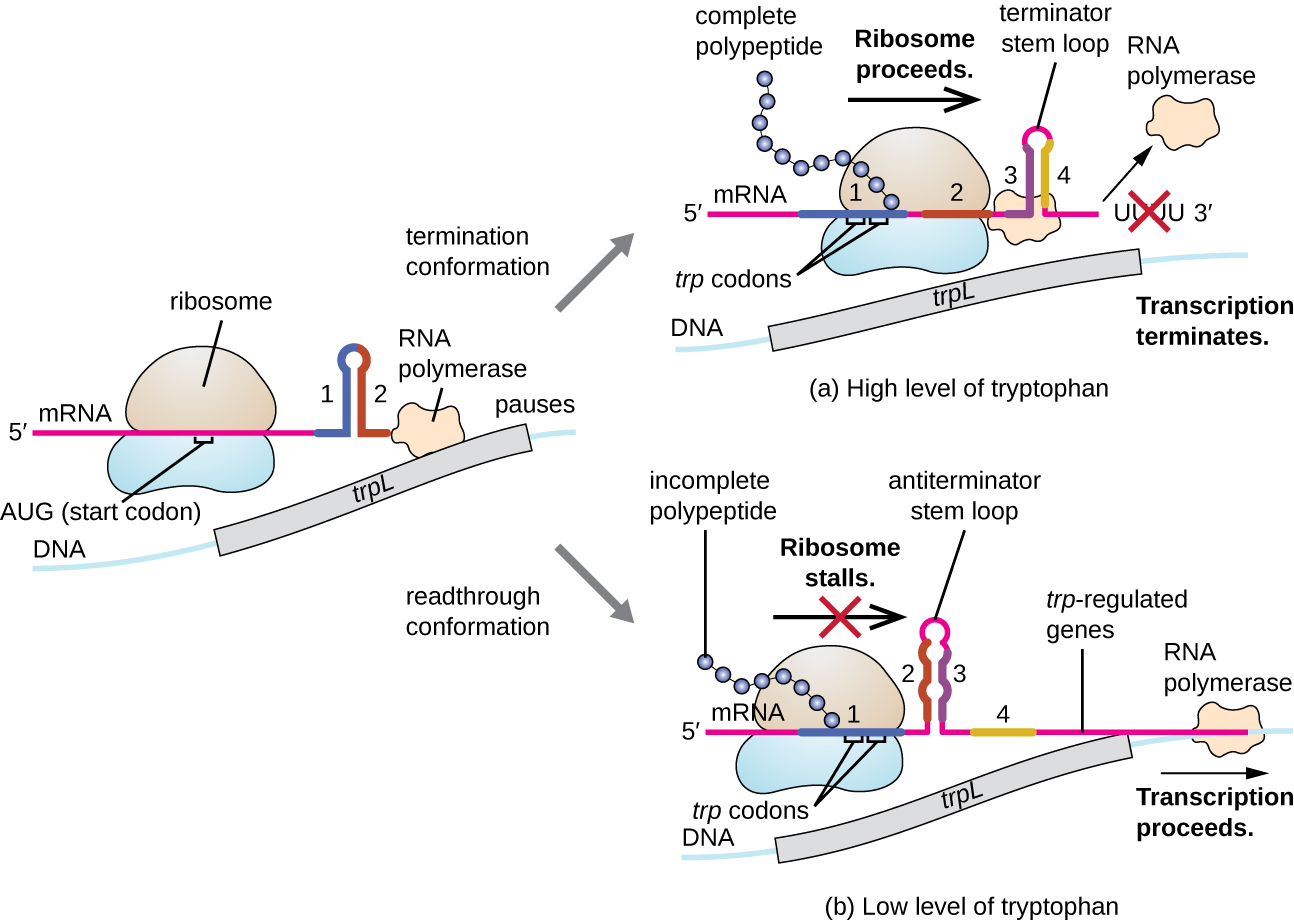
One such regulatory system is attenuation , whereby secondary stem-loop structure s formed within the 5’ end of an mRNA being transcribed determine if transcription to complete the synthesis of this mRNA will occur and if this mRNA will be used for translation. Beyond the transcriptional repression mechanism already discussed, attenuation also controls expression of the trp operon in E. coli ( [link] ). The trp operon regulatory region contains a leader sequence called trpL between the operator and the first structural gene, which has four stretches of RNA that can base pair with each other in different combinations. When a terminator stem-loop forms, transcription terminates, releasing RNA polymerase from the mRNA. However, when an antiterminator stem-loop forms, this prevents the formation of the terminator stem-loop, so RNA polymerase can transcribe the structural genes.
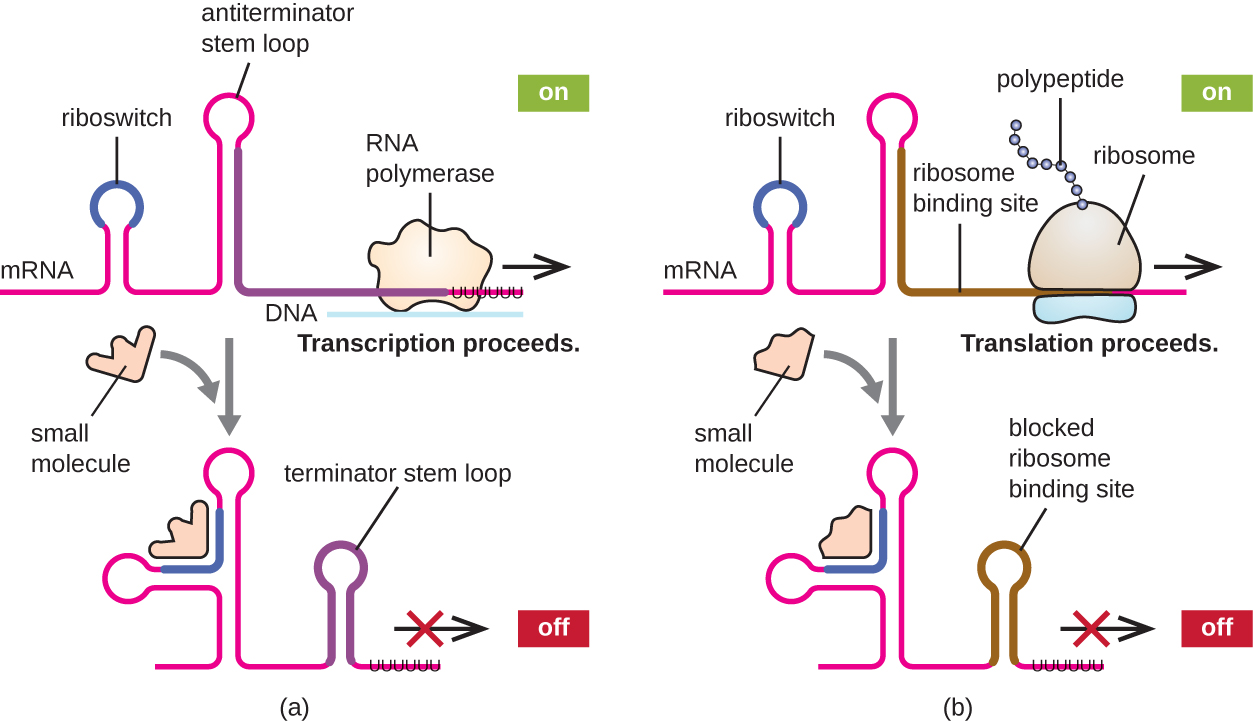
A related mechanism of concurrent regulation of transcription and translation in prokaryotes is the use of a riboswitch , a small region of noncoding RNA found within the 5’ end of some prokaryotic mRNA molecules ( [link] . A riboswitch may bind to a small intracellular molecule to stabilize certain secondary structures of the mRNA molecule. The binding of the small molecule determines which stem-loop structure forms, thus influencing the completion of mRNA synthesis and protein synthesis.
Although the focus on our discussion of transcriptional control used prokaryotic operons as examples, eukaryotic transcriptional control is similar in many ways. As in prokaryotes, eukaryotic transcription can be controlled through the binding of transcription factors including repressor s and activator s. Interestingly, eukaryotic transcription can be influenced by the binding of proteins to regions of DNA, called enhancer s, rather far away from the gene, through DNA looping facilitated between the enhancer and the promoter ( [link] ). Overall, regulating transcription is a highly effective way to control gene expression in both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. However, the control of gene expression in eukaryotes in response to environmental and cellular stresses can be accomplished in additional ways without the binding of transcription factors to regulatory regions.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?