| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
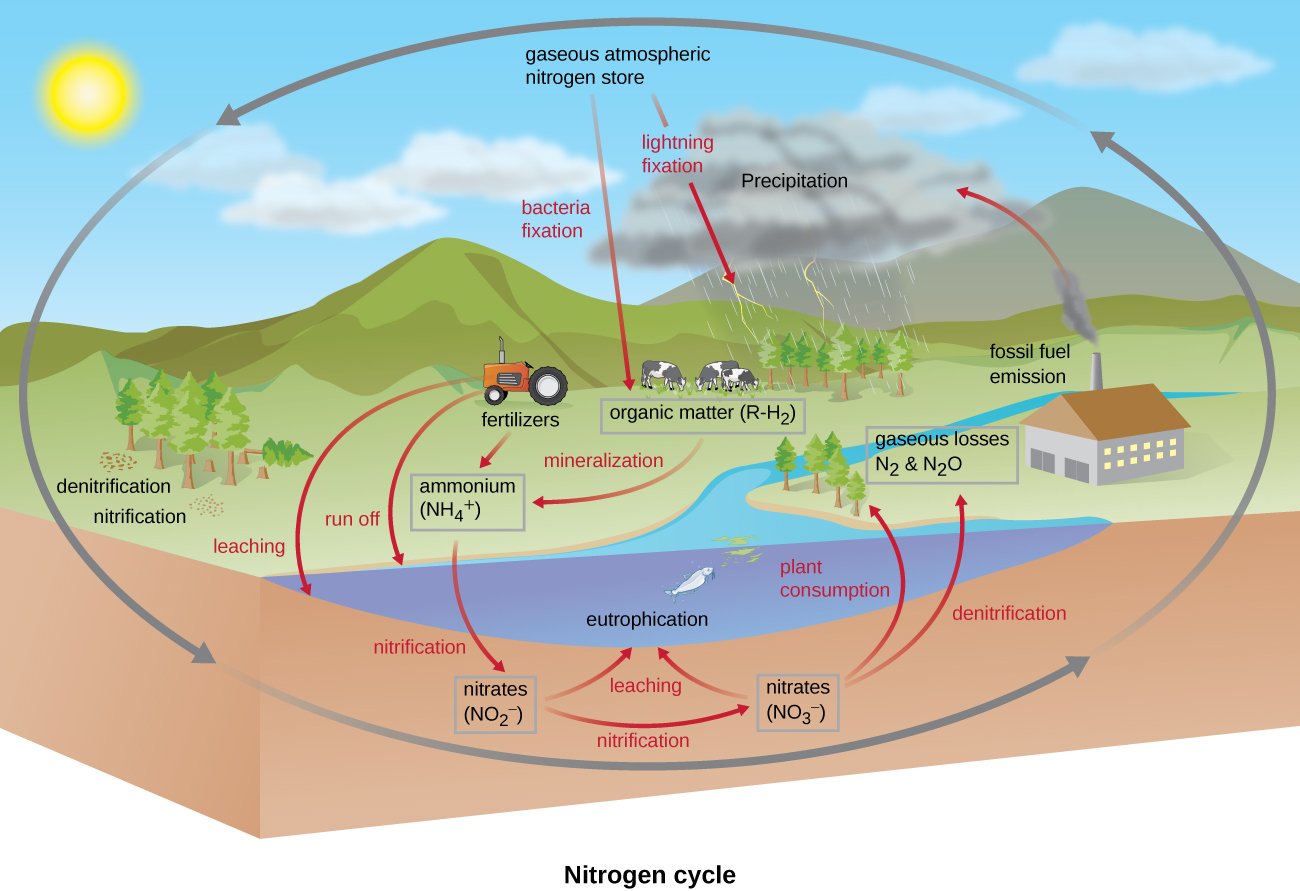
Many biological macromolecules, including proteins and nucleic acids, contain nitrogen; however, getting nitrogen into living organisms is difficult. Prokaryotes play essential roles in the nitrogen cycle ( [link] ), transforming nitrogen between various forms for their own needs, benefiting other organisms indirectly. Plants and phytoplankton cannot incorporate nitrogen from the atmosphere (where it exists as tightly bonded, triple covalent N 2 ), even though this molecule composes approximately 78% of the atmosphere. Nitrogen enters the living world through free-living and symbiotic bacteria, which incorporate nitrogen into their macromolecules through specialized biochemical pathways called nitrogen fixation . Cyanobacteria in aquatic ecosystems fix inorganic nitrogen (from nitrogen gas) into ammonia (NH 3 ) that can be easily incorporated into biological macromolecules. Rhizobium bacteria ( [link] ) also fix nitrogen and live symbiotically in the root nodules of legumes (such as beans, peanuts, and peas), providing them with needed organic nitrogen while receiving fixed carbon as sugar in exchange. Free-living bacteria, such as members of the genus Azotobacter , are also able to fix nitrogen.
The nitrogen that enters living systems by nitrogen fixation is eventually converted from organic nitrogen back into nitrogen gas by microbes through three steps: ammonification, nitrification , and denitrification . In terrestrial systems, the first step is the ammonification process, in which certain bacteria and fungi convert nitrogenous waste from living animals or from the remains of dead organisms into ammonia (NH 3 ). This ammonia is then oxidized to nitrite then to nitrate by nitrifying soil bacteria such as members of the genus Nitrosomonas , through the process of nitrification. Last, the process of denitrification occurs, whereby soil bacteria, such as members of the genera Pseudomonas and Clostridium , use nitrate as a terminal electron acceptor in anaerobic respiration , converting it into nitrogen gas that reenters the atmosphere. A similar process occurs in the marine nitrogen cycle, where these three processes are performed by marine bacteria and archaea.
Human activity releases nitrogen into the environment by the use of artificial fertilizers that contain nitrogen and phosphorus compounds, which are then washed into lakes, rivers, and streams by surface runoff. A major effect from fertilizer runoff is saltwater and freshwater eutrophication , in which nutrient runoff causes the overgrowth and subsequent death of aquatic algae, making water sources anaerobic and inhospitable for the survival of aquatic organisms.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?