| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The most abundant biomolecules on earth are carbohydrate s . From a chemical viewpoint, carbohydrates are primarily a combination of carbon and water, and many of them have the empirical formula (CH 2 O) n , where n is the number of repeated units. This view represents these molecules simply as “hydrated” carbon atom chains in which water molecules attach to each carbon atom, leading to the term “carbohydrates.” Although all carbohydrates contain carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, there are some that also contain nitrogen, phosphorus, and/or sulfur. Carbohydrates have myriad different functions. They are abundant in terrestrial ecosystems, many forms of which we use as food sources. These molecules are also vital parts of macromolecular structures that store and transmit genetic information (i.e., DNA and RNA). They are the basis of biological polymers that impart strength to various structural components of organisms (e.g., cellulose and chitin), and they are the primary source of energy storage in the form of starch and glycogen.
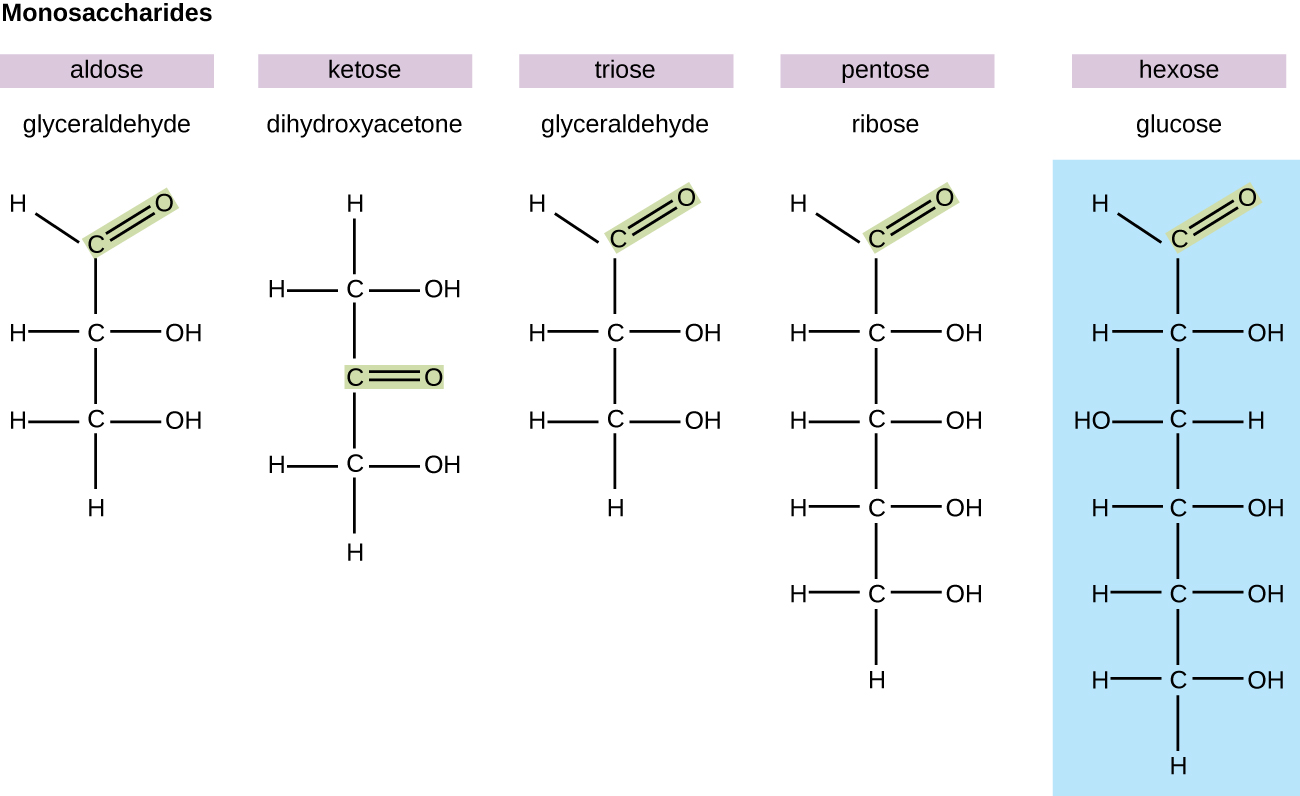
In biochemistry, carbohydrates are often called saccharide s , from the Greek sakcharon , meaning sugar, although not all the saccharides are sweet. The simplest carbohydrates are called monosaccharide s , or simple sugars. They are the building blocks (monomers) for the synthesis of polymers or complex carbohydrates, as will be discussed further in this section. Monosaccharides are classified based on the number of carbons in the molecule. General categories are identified using a prefix that indicates the number of carbons and the suffix – ose , which indicates a saccharide; for example, triose (three carbons), tetrose (four carbons), pentose (five carbons), and hexose (six carbons) ( [link] ). The hexose D-glucose is the most abundant monosaccharide in nature. Other very common and abundant hexose monosaccharides are galactose , used to make the disaccharide milk sugar lactose , and the fruit sugar fructose .
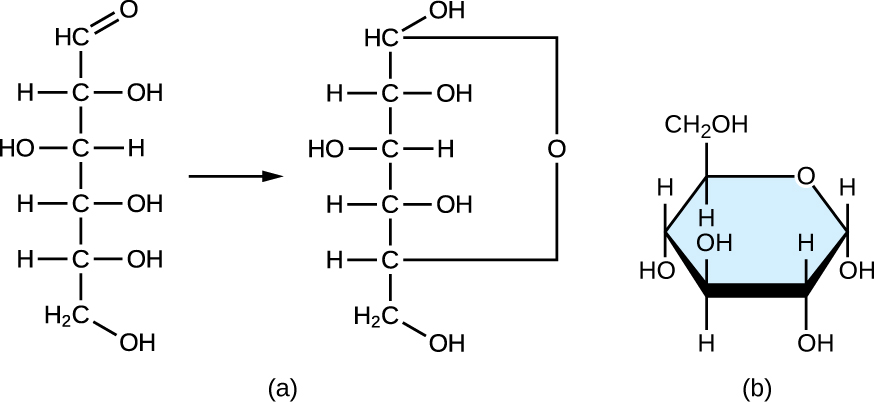
Monosaccharides of four or more carbon atoms are typically more stable when they adopt cyclic, or ring, structures. These ring structures result from a chemical reaction between functional groups on opposite ends of the sugar’s flexible carbon chain, namely the carbonyl group and a relatively distant hydroxyl group. Glucose, for example, forms a six-membered ring ( [link] ).
Two monosaccharide molecules may chemically bond to form a disaccharide . The name given to the covalent bond between the two monosaccharides is a glycosidic bond . Glycosidic bonds form between hydroxyl groups of the two saccharide molecules, an example of the dehydration synthesis described in the previous section of this chapter:

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?