| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
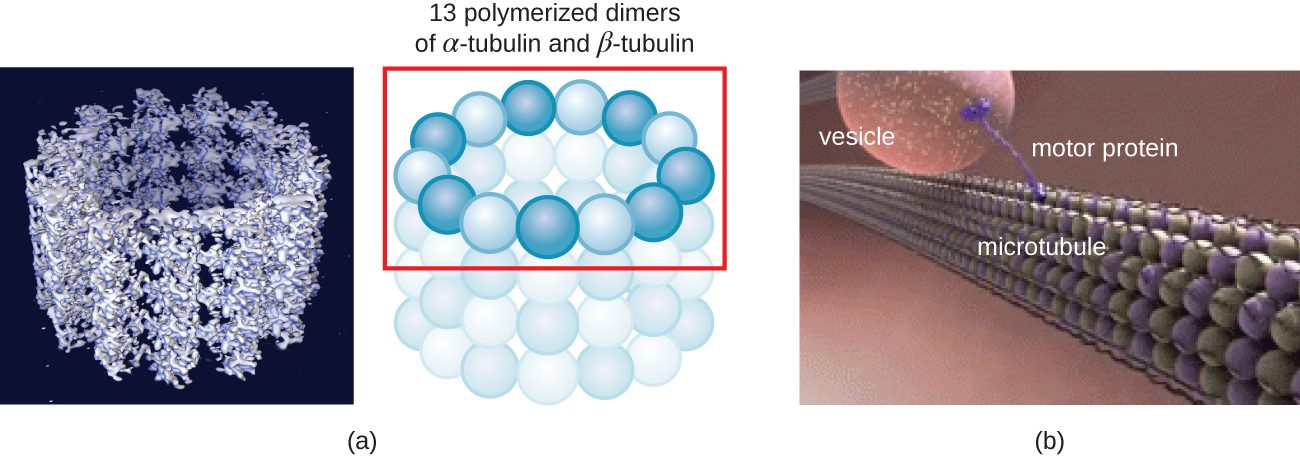
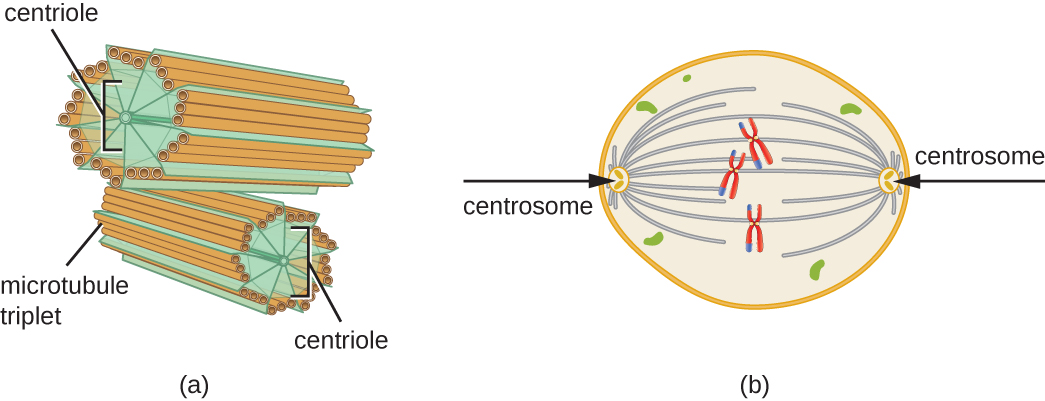
In addition, microtubules are involved in cell division, forming the mitotic spindle that serves to separate chromosomes during mitosis and meiosis. The mitotic spindle is produced by two centrosomes , which are essentially microtubule-organizing centers, at opposite ends of the cell. Each centrosome is composed of a pair of centrioles positioned at right angles to each other, and each centriole is an array of nine parallel microtubules arranged in triplets ( [link] ).
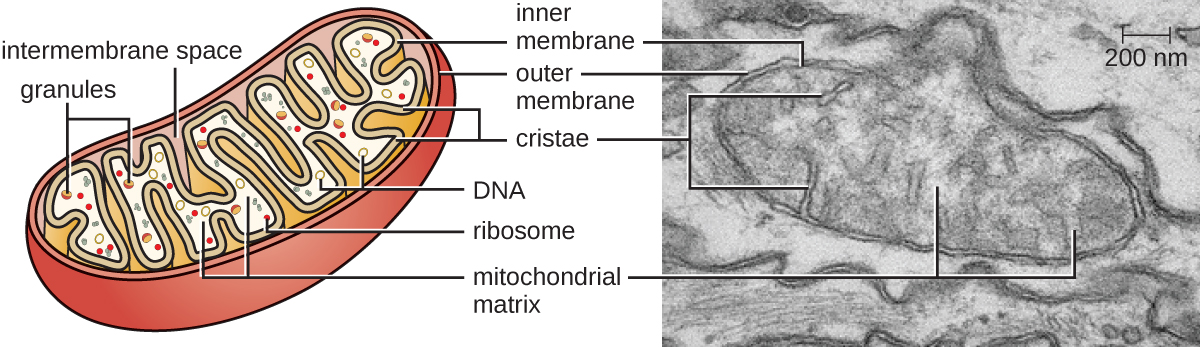
The large, complex organelles in which aerobic cellular respiration occurs in eukaryotic cells are called mitochondria ( [link] ). The term “mitochondrion” was first coined by German microbiologist Carl Benda in 1898 and was later connected with the process of respiration by Otto Warburg in 1913. Scientists during the 1960s discovered that mitochondria have their own genome and 70S ribosomes. The mitochondrial genome was found to be bacterial, when it was sequenced in 1976. These findings ultimately supported the endosymbiotic theory proposed by Lynn Margulis , which states that mitochondria originally arose through an endosymbiotic event in which a bacterium capable of aerobic cellular respiration was taken up by phagocytosis into a host cell and remained as a viable intracellular component.
Each mitochondrion has two lipid membranes. The outer membrane is a remnant of the original host cell’s membrane structures. The inner membrane was derived from the bacterial plasma membrane. The electron transport chain for aerobic respiration uses integral proteins embedded in the inner membrane. The mitochondrial matrix , corresponding to the location of the original bacterium’s cytoplasm, is the current location of many metabolic enzymes. It also contains mitochondrial DNA and 70S ribosomes . Invaginations of the inner membrane, called cristae, evolved to increase surface area for the location of biochemical reactions. The folding patterns of the cristae differ among various types of eukaryotic cells and are used to distinguish different eukaryotic organisms from each other.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?