| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The epithelial cells lining the urogenital tract, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and certain other tissues are known as endothelia . These tightly packed cells provide a particularly effective frontline barrier against invaders. The endothelia of the blood-brain barrier , for example, protect the central nervous system (CNS), which consists of the brain and the spinal cord. The CNS is one of the most sensitive and important areas of the body, as microbial infection of the CNS can quickly lead to serious and often fatal inflammation. The cell junctions in the blood vessels traveling through the CNS are some of the tightest and toughest in the body, preventing any transient microbes in the bloodstream from entering the CNS. This keeps the cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds and bathes the brain and spinal cord sterile under normal conditions.
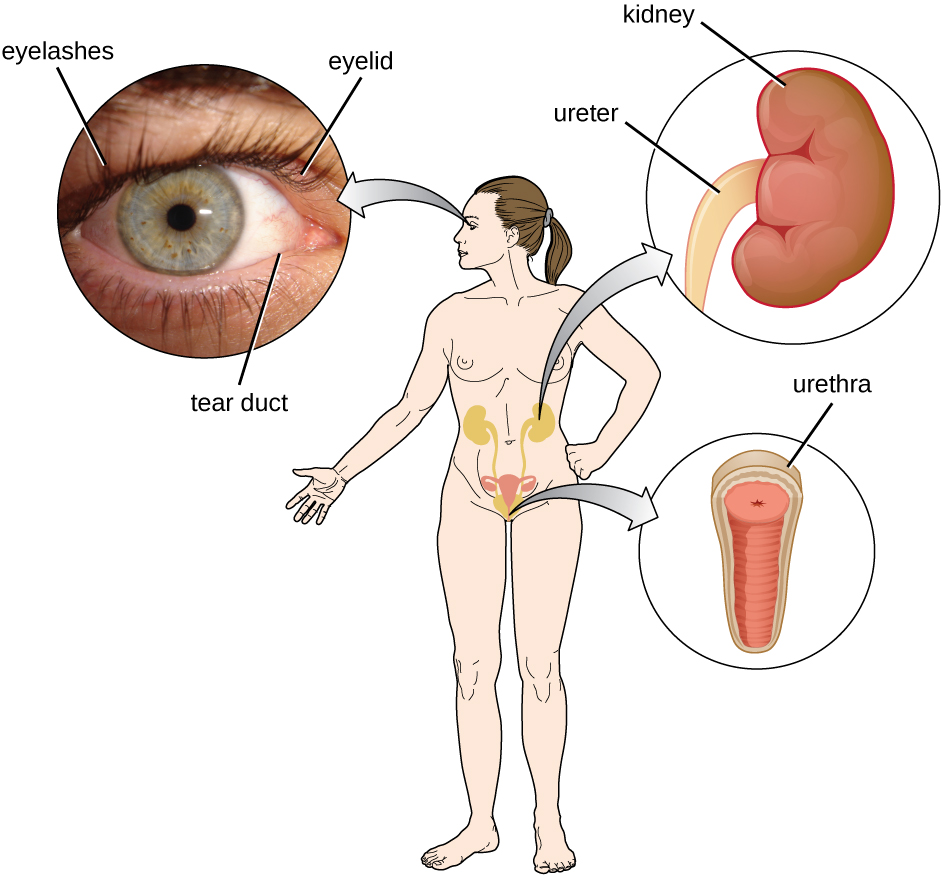
In addition to physical barriers that keep microbes out, the body has a number of mechanical defenses that physically remove pathogens from the body, preventing them from taking up residence. We have already discussed several examples of mechanical defenses, including the shedding of skin cells, the expulsion of mucus via the mucociliary escalator, and the excretion of feces through intestinal peristalsis. Other important examples of mechanical defenses include the flushing action of urine and tears, which both serve to carry microbes away from the body. The flushing action of urine is largely responsible for the normally sterile environment of the urinary tract, which includes the kidneys, ureters, and urinary bladder. Urine passing out of the body washes out transient microorganisms, preventing them from taking up residence. The eyes also have physical barriers and mechanical mechanisms for preventing infections. The eyelashes and eyelids prevent dust and airborne microorganisms from reaching the surface of the eye. Any microbes or debris that make it past these physical barriers may be flushed out by the mechanical action of blinking, which bathes the eye in tears, washing debris away ( [link] ).
In various regions of the body, resident microbiota serve as an important first-line defense against invading pathogens. Through their occupation of cellular binding sites and competition for available nutrients, the resident microbiota prevent the critical early steps of pathogen attachment and proliferation required for the establishment of an infection. For example, in the vagina , members of the resident microbiota compete with opportunistic pathogens like the yeast Candida . This competition prevents infections by limiting the availability of nutrients, thus inhibiting the growth of Candida , keeping its population in check. Similar competitions occur between the microbiota and potential pathogens on the skin, in the upper respiratory tract, and in the gastrointestinal tract. As will be discussed later in this chapter, the resident microbiota also contribute to the chemical defenses of the innate nonspecific host defenses.
The importance of the normal microbiota in host defenses is highlighted by the increased susceptibility to infectious diseases when the microbiota is disrupted or eliminated. Treatment with antibiotics can significantly deplete the normal microbiota of the gastrointestinal tract, providing an advantage for pathogenic bacteria to colonize and cause diarrheal infection. In the case of diarrhea caused by Clostridium difficile , the infection can be severe and potentially lethal. One strategy for treating C. difficile infections is fecal transplantation , which involves the transfer of fecal material from a donor (screened for potential pathogens) into the intestines of the recipient patient as a method of restoring the normal microbiota and combating C. difficile infections.
[link] provides a summary of the physical defenses discussed in this section.
| Physical Defenses of Nonspecific Innate Immunity | ||
|---|---|---|
| Defense | Examples | Function |
| Cellular barriers | Skin, mucous membranes, endothelial cells | Deny entry to pathogens |
| Mechanical defenses | Shedding of skin cells, mucociliary sweeping, peristalsis, flushing action of urine and tears | Remove pathogens from potential sites of infection |
| Microbiome | Resident bacteria of the skin, upper respiratory tract, gastrointestinal tract, and genitourinary tract | Compete with pathogens for cellular binding sites and nutrients |
The muscular contraction of the intestines that results in movement of material through the digestive tract is called ________.
peristalsis
______ are the hair-like appendages of cells lining parts of the respiratory tract that sweep debris away from the lungs.
cilia
Secretions that bathe and moisten the interior of the intestines are produced by _______ cells.
goblet
Differentiate a physical barrier from a mechanical removal mechanism and give an example of each.
Identify some ways that pathogens can breach the physical barriers of the innate immune system.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?