| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Although the skull provides the brain with an excellent defense, it can also become problematic during infections. Any swelling of the brain or meninges that results from inflammation can cause intracranial pressure, leading to severe damage of the brain tissues, which have limited space to expand within the inflexible bones of the skull. The term meningitis is used to describe an inflammation of the meninges. Typical symptoms can include severe headache, fever, photophobia (increased sensitivity to light), stiff neck, convulsions, and confusion. An inflammation of brain tissue is called encephalitis , and patients exhibit signs and symptoms similar to those of meningitis in addition to lethargy, seizures, and personality changes. When inflammation affects both the meninges and the brain tissue, the condition is called meningoencephalitis . All three forms of inflammation are serious and can lead to blindness, deafness, coma, and death.
Meningitis and encephalitis can be caused by many different types of microbial pathogens. However, these conditions can also arise from noninfectious causes such as head trauma, some cancers, and certain drugs that trigger inflammation. To determine whether the inflammation is caused by a pathogen, a lumbar puncture is performed to obtain a sample of CSF . If the CSF contains increased levels of white blood cells and abnormal glucose and protein levels, this indicates that the inflammation is a response to an infectioninflinin.
Guillain-Barré syndrome (GBS) is a rare condition that can be preceded by a viral or bacterial infection that results in an autoimmune reaction against myelinated nerve cells. The destruction of the myelin sheath around these neurons results in a loss of sensation and function. The first symptoms of this condition are tingling and weakness in the affected tissues. The symptoms intensify over a period of several weeks and can culminate in complete paralysis. Severe cases can be life-threatening. Infections by several different microbial pathogens, including Campylobacter jejuni (the most common risk factor), cytomegalovirus, Epstein-Barr virus , varicella-zoster virus, Mycoplasma pneumoniae , Yuki, Nobuhiro and Hans-Peter Hartung, “Guillain–Barré Syndrome,” New England Journal of Medicine 366, no. 24 (2012): 2294-304. and Zika virus Cao-Lormeau, Van-Mai, Alexandre Blake, Sandrine Mons, Stéphane Lastère, Claudine Roche, Jessica Vanhomwegen, Timothée Dub et al., “Guillain-Barré Syndrome Outbreak Associated with Zika Virus Infection in French Polynesia: A Case-Control Study,” The Lancet 387, no. 10027 (2016): 1531-9. have been identified as triggers for GBS. Anti-myelin antibodies from patients with GBS have been demonstrated to also recognize C. jejuni . It is possible that cross-reactive antibodies, antibodies that react with similar antigenic sites on different proteins, might be formed during an infection and may lead to this autoimmune response.
GBS is solely identified by the appearance of clinical symptoms. There are no other diagnostic tests available. Fortunately, most cases spontaneously resolve within a few months with few permanent effects, as there is no available vaccine. GBS can be treated by plasmapheresis. In this procedure, the patient’s plasma is filtered from their blood, removing autoantibodies.
Match each strategy for microbial invasion of the CNS with its description.
| ___intercellular entry | A. pathogen gains entry by infecting peripheral white blood cells |
| ___transcellular entry | B. pathogen bypasses the blood-brain barrier by travel along the olfactory or trigeminal cranial nerves |
| ___leukocyte-facilitated entry | C. pathogen passes through the cells of the blood-brain barrier |
| ___nonhematogenous entry | D. pathogen passes between the cells of the blood-brain barrier |
D, C, A, B
A signal is transmitted down the ________ of a nerve cell.
axon
The ________ is filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
subarachnoid space
The ________ ________ prevents access of microbes in the blood from gaining access to the central nervous system.
blood-brain barrier
The ________ are a set of membranes that cover and protect the brain.
meninges
Briefly describe the defenses of the brain against trauma and infection.
Describe how the blood-brain barrier is formed.
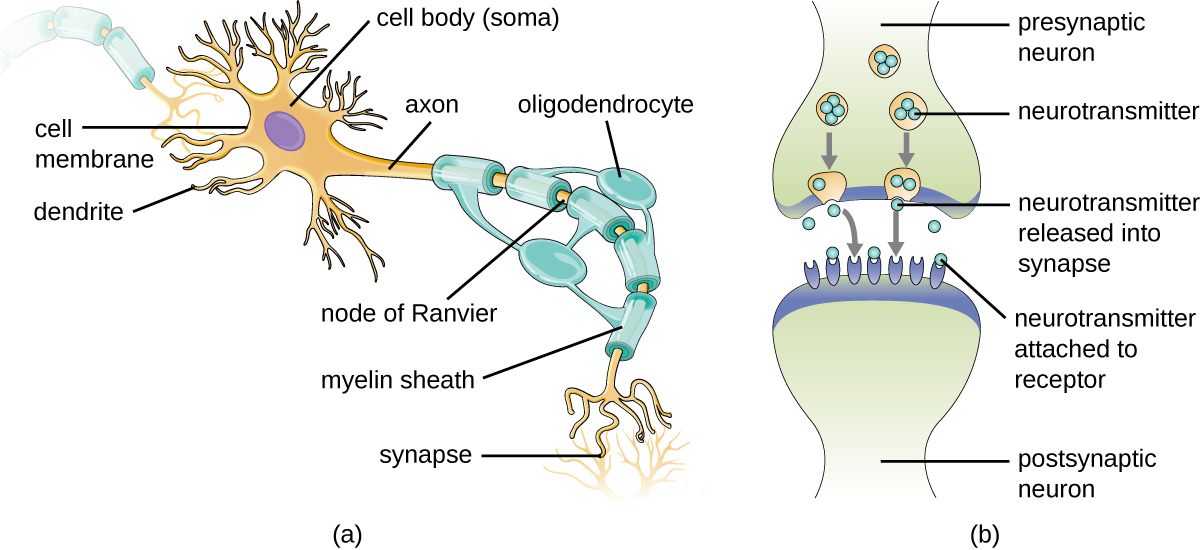
Identify the type of cell shown, as well as the following structures: axon, dendrite, myelin sheath, soma, and synapse.

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?