| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
Olivia, a one-year old infant, is brought to the emergency room by her parents, who report her symptoms: excessive crying, irritability, sensitivity to light, unusual lethargy, and vomiting. A physician feels swollen lymph nodes in Olivia’s throat and armpits. In addition, the area of the abdomen over the spleen is swollen and tender.
Jump to the next Clinical Focus box.
Adaptive immunity is defined by two important characteristics: specificity and memory . Specificity refers to the adaptive immune system’s ability to target specific pathogens, and memory refers to its ability to quickly respond to pathogens to which it has previously been exposed. For example, when an individual recovers from chickenpox, the body develops a memory of the infection that will specifically protect it from the causative agent, the varicella-zoster virus, if it is exposed to the virus again later.
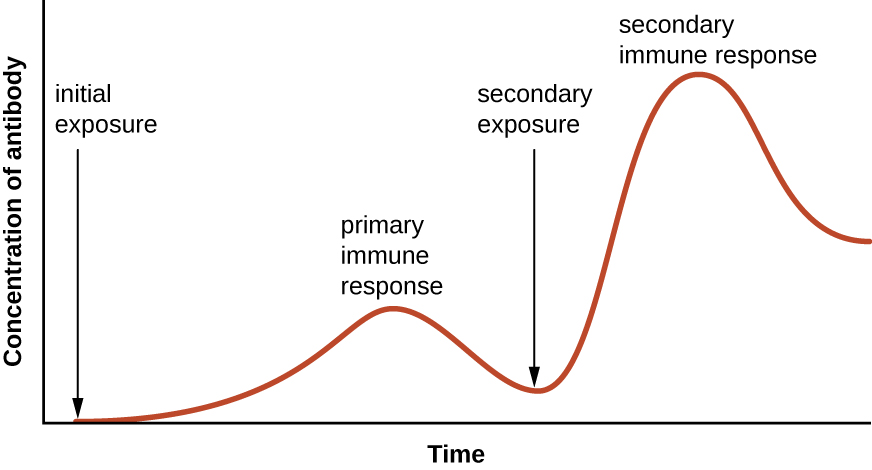
Specificity and memory are achieved by essentially programming certain cells involved in the immune response to respond rapidly to subsequent exposures of the pathogen. This programming occurs as a result of the first exposure to a pathogen or vaccine, which triggers a primary response . Subsequent exposures result in a secondary response that is faster and stronger as a result of the body’s memory of the first exposure ( [link] ). This secondary response, however, is specific to the pathogen in question. For example, exposure to one virus (e.g., varicella-zoster virus) will not provide protection against other viral diseases (e.g., measles, mumps, or polio).
Adaptive specific immunity involves the actions of two distinct cell types: B lymphocytes ( B cells ) and T lymphocytes ( T cells ). Although B cells and T cells arise from a common hematopoietic stem cell differentiation pathway (see [link] ), their sites of maturation and their roles in adaptive immunity are very different.
B cells mature in the bone marrow and are responsible for the production of glycoproteins called antibodies , or immunoglobulins . Antibodies are involved in the body’s defense against pathogens and toxins in the extracellular environment. Mechanisms of adaptive specific immunity that involve B cells and antibody production are referred to as humoral immunity . The maturation of T cells occurs in the thymus . T cells function as the central orchestrator of both innate and adaptive immune responses. They are also responsible for destruction of cells infected with intracellular pathogens. The targeting and destruction of intracellular pathogens by T cells is called cell-mediated immunity, or cellular immunity .

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?