| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
The fungi comprise a diverse group of organisms that are heterotrophic and typically saprozoic. In addition to the well-known macroscopic fungi (such as mushrooms and molds), many unicellular yeasts and spores of macroscopic fungi are microscopic. For this reason, fungi are included within the field of microbiology.
Fungi are important to humans in a variety of ways. Both microscopic and macroscopic fungi have medical relevance, with some pathogenic species that can cause mycoses (illnesses caused by fungi). Some pathogenic fungi are opportunistic, meaning that they mainly cause infections when the host’s immune defenses are compromised and do not normally cause illness in healthy individuals. Fungi are important in other ways. They act as decomposers in the environment, and they are critical for the production of certain foods such as cheeses. Fungi are also major sources of antibiotics, such as penicillin from the fungus Penicillium .
Fungi have well-defined characteristics that set them apart from other organisms. Most multicellular fungal bodies, commonly called molds , are made up of filaments called hyphae . Hyphae can form a tangled network called a mycelium and form the thallus (body) of fleshy fungi. Hyphae that have walls between the cells are called septate hyphae ; hyphae that lack walls and cell membranes between the cells are called nonseptate or coenocytic hyphae ). ( [link] ).
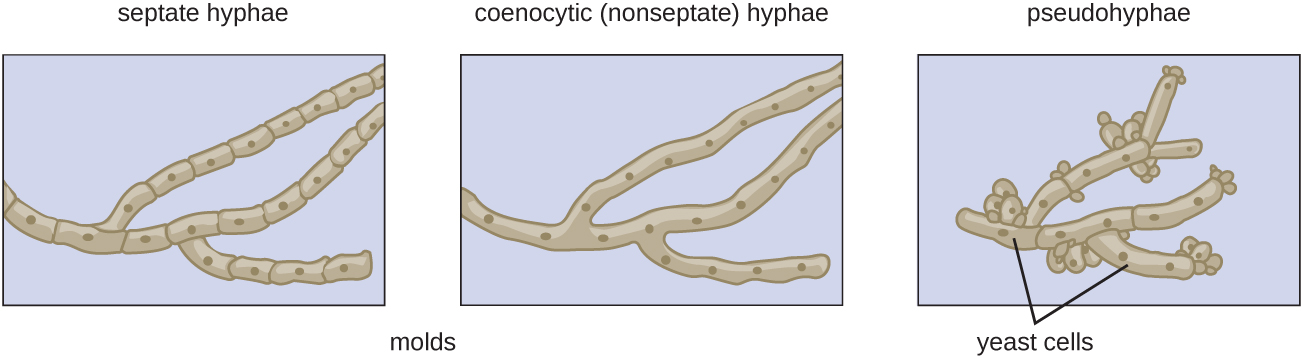
In contrast to molds, yeasts are unicellular fungi. The budding yeasts reproduce asexually by budding off a smaller daughter cell; the resulting cells may sometimes stick together as a short chain or pseudohypha ( [link] ). Candida albicans is a common yeast that forms pseudohyphae; it is associated with various infections in humans, including vaginal yeast infections, oral thrush, and candidiasis of the skin.
Some fungi are dimorphic, having more than one appearance during their life cycle. These dimorphic fungi may be able to appear as yeasts or molds, which can be important for infectivity. They are capable of changing their appearance in response to environmental changes such as nutrient availability or fluctuations in temperature, growing as a mold, for example, at 25 °C (77 °F), and as yeast cells at 37 °C (98.6 °F). This ability helps dimorphic fungi to survive in diverse environments. Histoplasma capsulatum , the pathogen that causes histoplasmosis , a lung infection, is an example of a dimorphic fungus ( [link] ).

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?