| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
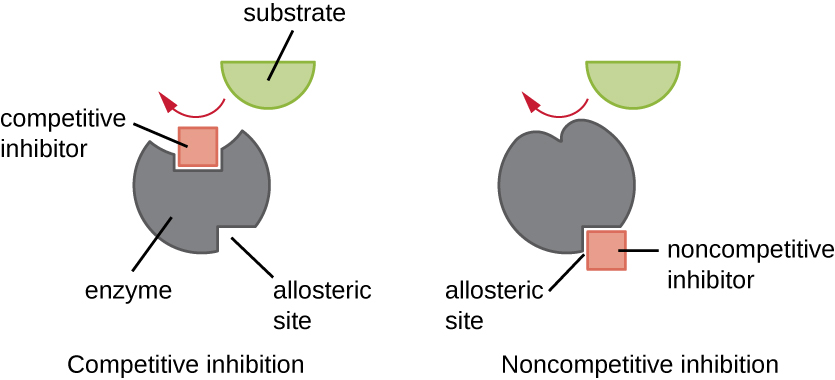
Enzymes can be regulated in ways that either promote or reduce their activity. There are many different kinds of molecules that inhibit or promote enzyme function, and various mechanisms exist for doing so ( [link] ). A competitive inhibitor is a molecule similar enough to a substrate that it can compete with the substrate for binding to the active site by simply blocking the substrate from binding. For a competitive inhibitor to be effective, the inhibitor concentration needs to be approximately equal to the substrate concentration. Sulfa drugs provide a good example of competitive competition. They are used to treat bacterial infections because they bind to the active site of an enzyme within the bacterial folic acid synthesis pathway. When present in a sufficient dose, a sulfa drug prevents folic acid synthesis, and bacteria are unable to grow because they cannot synthesize DNA, RNA, and proteins. Humans are unaffected because we obtain folic acid from our diets.
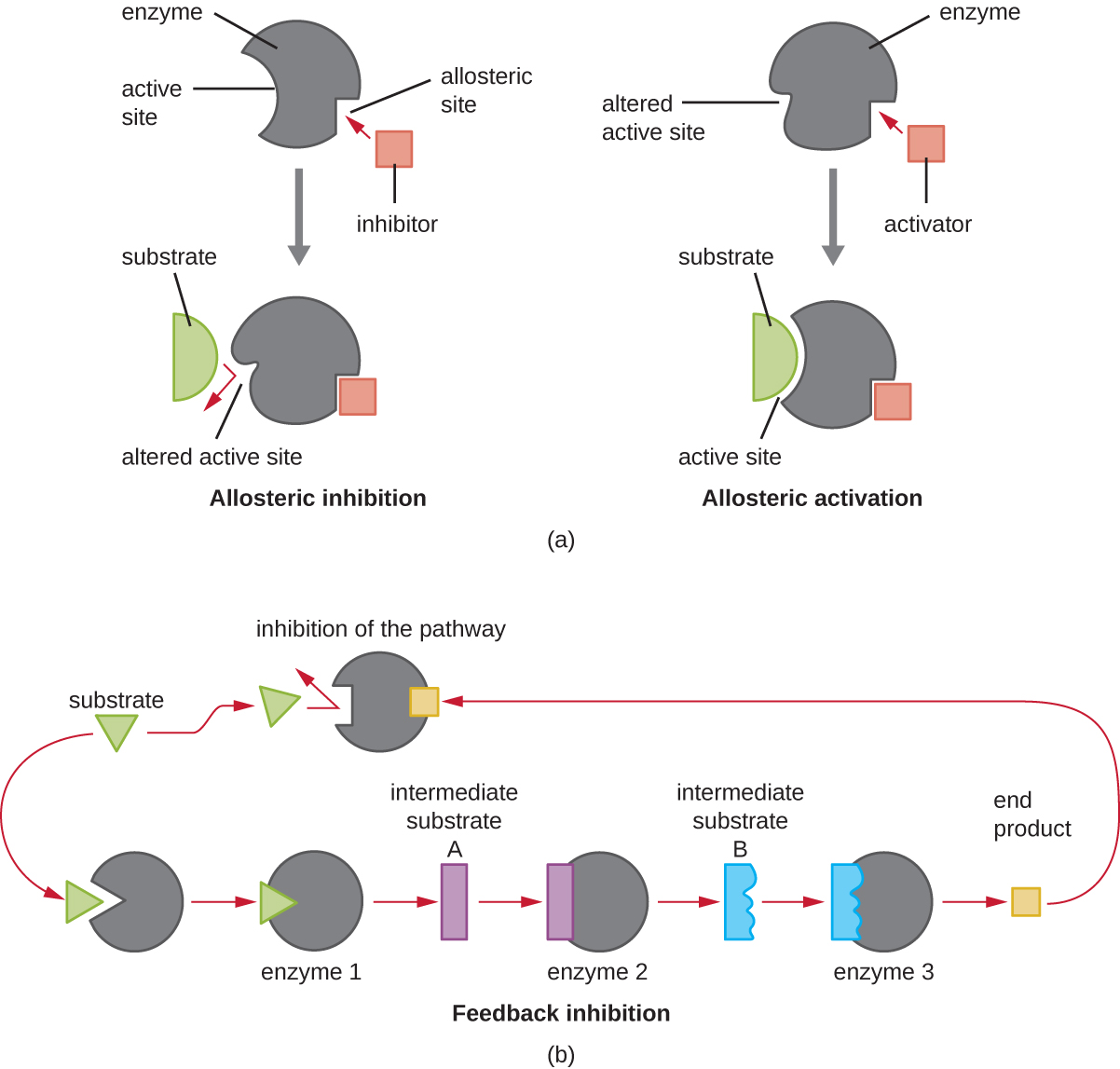
On the other hand, a noncompetitive (allosteric) inhibitor binds to the enzyme at an allosteric site , a location other than the active site, and still manages to block substrate binding to the active site by inducing a conformational change that reduces the affinity of the enzyme for its substrate ( [link] ). Because only one inhibitor molecule is needed per enzyme for effective inhibition, the concentration of inhibitors needed for noncompetitive inhibition is typically much lower than the substrate concentration.
In addition to allosteric inhibitors, there are allosteric activator s that bind to locations on an enzyme away from the active site, inducing a conformational change that increases the affinity of the enzyme’s active site(s) for its substrate(s).
Allosteric control is an important mechanism of regulation of metabolic pathways involved in both catabolism and anabolism. In a most efficient and elegant way, cells have evolved also to use the products of their own metabolic reactions for feedback inhibition of enzyme activity. Feedback inhibition involves the use of a pathway product to regulate its own further production. The cell responds to the abundance of specific products by slowing production during anabolic or catabolic reactions ( [link] ).
Processes in which cellular energy is used to make complex molecules from simpler ones are described as ________.
anabolic
The loss of an electron from a molecule is called ________.
oxidation
The part of an enzyme to which a substrate binds is called the ________.
active site
In cells, can an oxidation reaction happen in the absence of a reduction reaction? Explain.
What is the function of molecules like NAD + /NADH and FAD/FADH 2 in cells?

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?