| << Chapter < Page | Chapter >> Page > |
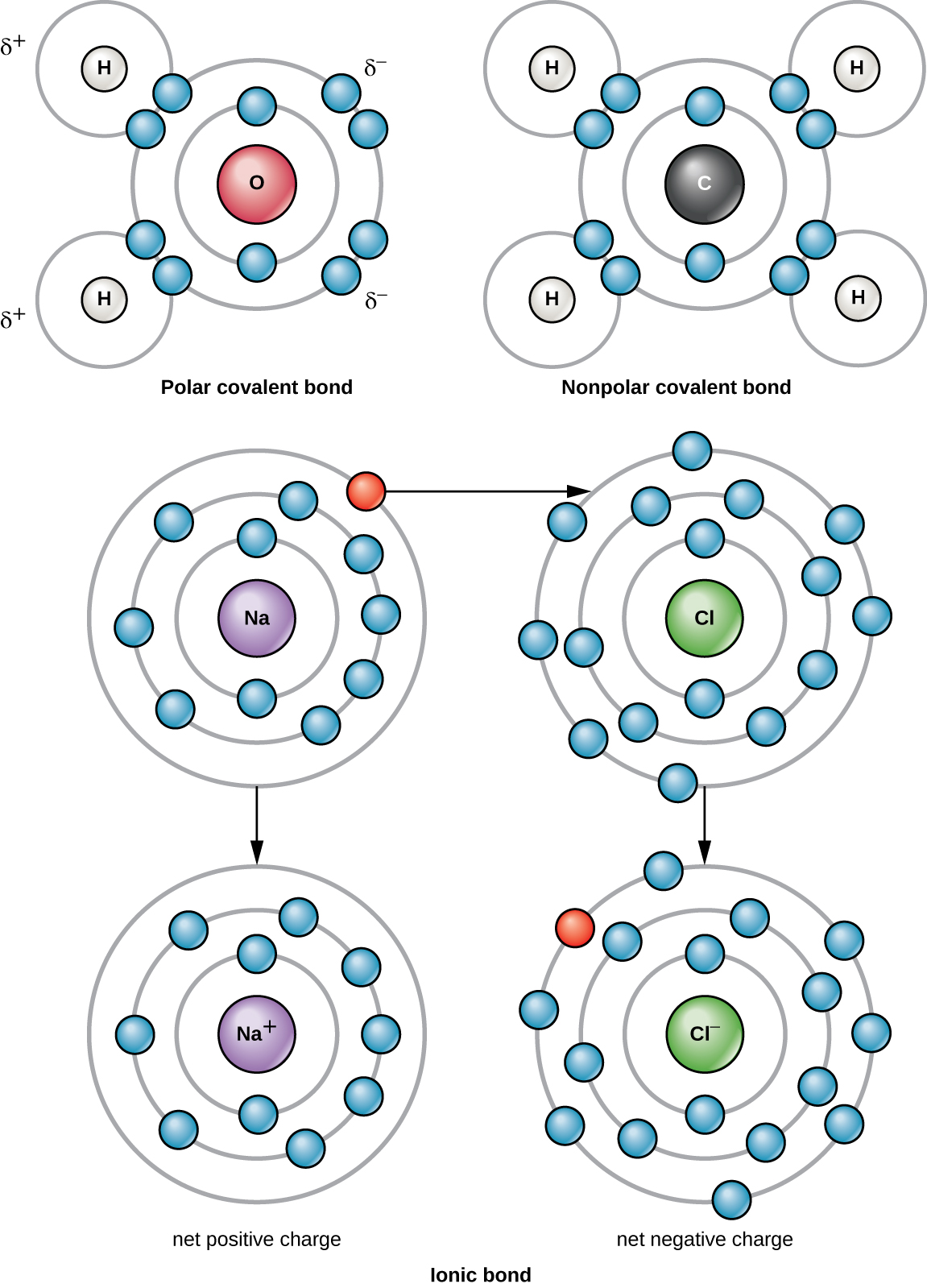
There are two types of covalent bonds: polar and nonpolar. Nonpolar covalent bonds form between two atoms of the same or different elements that share the electrons equally ( [link] ). In a polar covalent bond , the electrons shared by the atoms spend more time closer to one nucleus than to the other nucleus. Because of the unequal distribution of electrons between the different nuclei, a slightly positive (δ+) or slightly negative (δ–) charge develops. Water is an example of a molecule formed with polar covalent bonds ( [link] ).
When an atom does not contain equal numbers of protons and electrons, it is called an ion . Because the number of electrons does not equal the number of protons, each ion has a net charge. Positive ions are formed by losing electrons and are called cations . Negative ions are formed by gaining electrons and are called anions .
For example, a sodium atom has only has one electron in its outermost shell. It takes less energy for the sodium atom to donate that one electron than it does to accept seven more electrons, which it would need to fill its outer shell. If the sodium atom loses an electron, it now has 11 protons and only 10 electrons, leaving it with an overall charge of +1. It is now called a sodium ion (Na + ).
A chlorine atom has seven electrons in its outer shell. Again, it is more energy efficient for the chlorine atom to gain one electron than to lose seven. Therefore, it will more likely gain an electron to form an ion with 17 protons and 18 electrons, giving it a net negative (–1) charge. It is now called a chloride ion (Cl – ). This movement of electrons from one atom to another is referred to as electron transfer. Because positive and negative charges attract, these ions stay together and form an ionic bond , or a bond between ions. When Na + and Cl – ions combine to produce NaCl, an electron from a sodium atom stays with the other seven from the chlorine atom, and the sodium and chloride ions attract each other in a lattice of ions with a net zero charge ( [link] ).
Polyatomic ions consist of multiple atoms joined by covalent bonds; but unlike a molecule, a polyatomic ion has a positive or negative charge. It behaves as a cation or anion and can therefore form ionic bonds with other ions to form ionic compounds. The atoms in a polyatomic ion may be from the same element or different elements.
[link] lists some cations and anions that commonly occur in microbiology. Note that this table includes monoatomic as well as polyatomic ions.
| Some Common Ions in Microbiology | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cations | Anions | ||
| sodium | Na + | chloride | Cl – |
| hydrogen | H + | bicarbonate | |
| potassium | K + | carbonate | |
| ammonium | hydrogen sulfate | ||
| copper (I) | Cu + | hydrogen sulfide | HS – |
| copper (II) | Cu 2+ | hydroxide | OH – |
| iron (II) | Fe 2+ | hypochlorite | ClO – |
| iron (III) | Fe 3+ | nitrite | |
| nitrate | |||
| peroxide | |||
| phosphate | |||
| pyrophosphate | |||
| sulfite | |||
| thiosulfate |

Notification Switch
Would you like to follow the 'Microbiology' conversation and receive update notifications?